// @(#)root/geom:$Name: $:$Id: TGeoShape.cxx,v 1.8 2003/02/07 13:46:47 brun Exp $
// Author: Andrei Gheata 31/01/02
/*************************************************************************
* Copyright (C) 1995-2000, Rene Brun and Fons Rademakers. *
* All rights reserved. *
* *
* For the licensing terms see $ROOTSYS/LICENSE. *
* For the list of contributors see $ROOTSYS/README/CREDITS. *
*************************************************************************/
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// TGeoShape - base class for all geometrical shapes. Abstract functionality
// regarding point and segment classification has to be implemented by classes
// that inherits from it.
//
//
//
/*
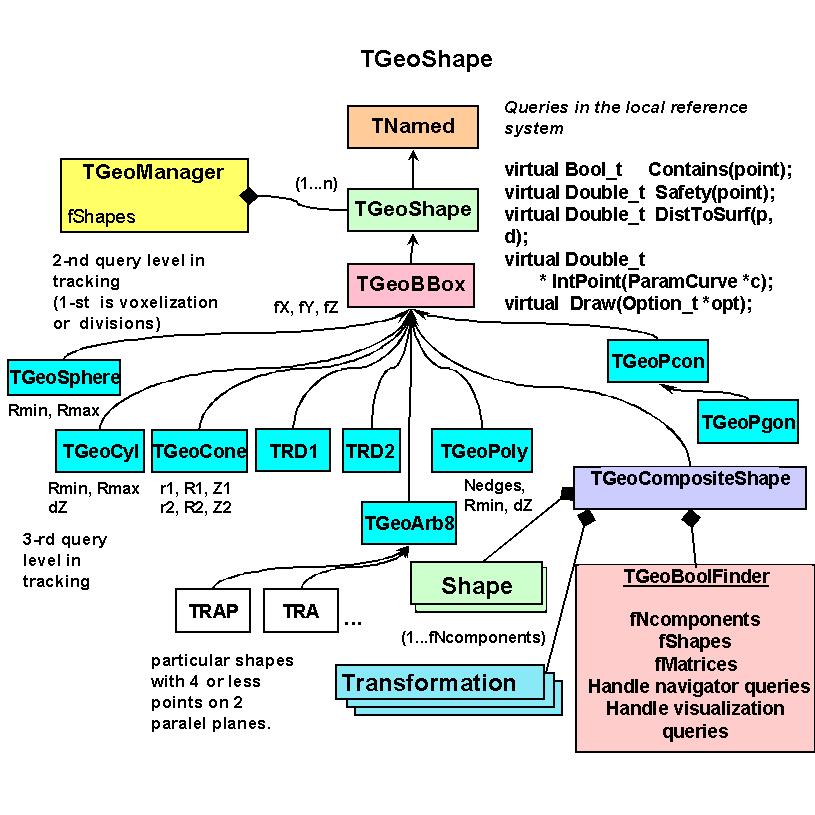 */
//
#include "TObjArray.h"
#include "TGeoMatrix.h"
#include "TGeoManager.h"
#include "TGeoVolume.h"
#include "TGeoShape.h"
#include "TVirtualGeoPainter.h"
/*************************************************************************
* TGeoShape - package description
*
* Creating shapes
*================
* Shape objects embeed only the minimum set of parameters that are fully
* describing a valid physical shape. For instance, a tube is represented by
* its half length, the minimum radius and the maximum radius. Shapes are used
* togather with media in order to create volumes, which in their turn
* are the main components of the geometrical tree. Volumes may contain other
* positioned volumes inside, which are called nodes. Each component in this
* structure : media, shapes and volumes (except nodes) are replicable (one
* instance of an object can be used in several other combinations).
* It is highly recomendable to use replicas as more as possible when volumes
* have different media but the same shape. One will never have to create
* an instance of the TGeoShape class, but only the one for specific shapes :
*
* TGeoBBox *box = new TGeoBBox(halfX, halfY, halfZ);
* TGeoTube *tub = new TGeoTube(rmin, rmax, halfZ);
* ... (see each specific shape constructors)
*
* Sometimes it is much easier to create a volume having a given shape in one
* step, since shapes are not direcly linked in the geometrical tree but volumes
* are :
*
* TGeoVolume *vol_box = gGeoManager->MakeBox("BOX_VOL", "mat1", halfX, halfY, halfZ);
* TGeoVolume *vol_tub = gGeoManager->MakeTube("TUB_VOL", "mat2", rmin, rmax, halfZ);
* ... (see MakeXXX() utilities in TGeoManager class)
*
* Volumes can be assembled also from pieces :
*
* TGeoVolume *vol = new TGeoVolume(name, ptr_shape, ptr_medium);
*
* Point and segment classification
*=================================
* The main functionalities of a shape is finding if a given point is contained
* or not or if an oriented segment crosses or not the shape. Further functionalities
* are : computing the normal to the shape surface at intersection point and finding
* the minimim distance from a point to it.
* These algorithms can be called by user only if the checked point/segment is
* converted to the local reference frame. Mainly they are used by the global
* point/segment classification algorithms of TGeoManager class.
* See also : TGeoManager::FindNode() , TGeoManager::FindNextBoundary()
*
* Classification of arbitrary curves (e.g. helixes) w.r.t shapes is not
* implemented yet.
*
*************************************************************************/
const Double_t TGeoShape::kRadDeg = 180./TMath::Pi();
const Double_t TGeoShape::kDegRad = TMath::Pi()/180.;
const Double_t TGeoShape::kBig = 1E30;
ClassImp(TGeoParamCurve)
ClassImp(TGeoShape)
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
TGeoShape::TGeoShape()
{
// Default constructor
fShapeId = 0;
if (!gGeoManager) {
gGeoManager = new TGeoManager("Geometry", "default geometry");
// gROOT->AddGeoManager(gGeoManager);
}
// fShapeId = gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->GetSize();
// gGeoManager->AddShape(this);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
TGeoShape::TGeoShape(const char *name)
:TNamed(name, "")
{
// Default constructor
fShapeId = 0;
if (!gGeoManager) {
gGeoManager = new TGeoManager("Geometry", "default geometry");
// gROOT->AddGeoManager(gGeoManager);
}
fShapeId = gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->GetSize();
gGeoManager->AddShape(this);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
TGeoShape::~TGeoShape()
{
// Destructor
if (gGeoManager) gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->Remove(this);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
const char *TGeoShape::GetName() const
{
if (!strlen(fName)) {
return ((TObject *)this)->ClassName();
}
return TNamed::GetName();
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Int_t TGeoShape::ShapeDistancetoPrimitive(Int_t numpoints, Int_t px, Int_t py) const
{
TVirtualGeoPainter *painter = gGeoManager->GetGeomPainter();
if (!painter) return 9999;
return painter->ShapeDistancetoPrimitive(this, numpoints, px, py);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Double_t TGeoShape::ClosenessToCorner(Double_t *point, Bool_t in,
Double_t *vertex, Double_t *normals, Double_t *cldir)
{
// Static method returning distance to closest point of a corner. The corner is
// defined by vertex and normals to the 3 planes (in order X, Y, Z - norm[9]).
// also return unit vector pointing to this
Double_t safe[3]; // closest distances to the 3 planes
Double_t dvert[3]; // vector from vertex to point
Int_t snorm = -1;
Double_t close = 0;
memset(&safe[0], 0, 3*sizeof(Double_t));
memset(cldir, 0, 3*sizeof(Double_t));
Int_t i, j;
for (i=0; i<3; i++)
dvert[i]=point[i]-vertex[i];
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
for (j=0; j<3; j++)
safe[i]+=dvert[j]*normals[3*i+j];
}
// point is inside
if (in) {
snorm = TMath::LocMax(3, &safe[0]);
close = -safe[snorm];
// check if point was outside corner
if (close<0) return kBig;
memcpy(cldir, &normals[3*snorm], 3*sizeof(Double_t));
return close;
}
// point is outside
UInt_t nout=0;
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
if (safe[i]>0) {
snorm = i;
close = safe[i];
nout++;
}
}
// check if point is actually inside the corner (no visible plane)
if (!nout) return kBig;
if (nout==1) {
// only one visible plane
memcpy(cldir, &normals[3*snorm], 3*sizeof(Double_t));
return close;
}
if (nout==2) {
// two faces visible
Double_t calf = 0;
Double_t s1=0;
Double_t s2=0;
for (j=0; j<3; j++) {
if (safe[j]>0) {
if (s1==0) s1=safe[j];
else s2=safe[j];
continue;
}
for (Int_t k=0; k<3; k++)
calf += normals[3*((j+1)%3)+k]*normals[3*((j+2)%3)+k];
}
close=TMath::Sqrt((s1*s1 + s2*s2 + 2.*s1*s2*calf)/(1. - calf*calf));
return close;
}
if (nout==3) {
// an edge or even vertex more close than any of the planes
// recompute closest distance
close=0;
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
if (safe[i]>0) close+=dvert[i]*dvert[i];
}
close = TMath::Sqrt(close);
for (i=0; i<3; i++)
cldir[i] = dvert[i]/close;
return close;
}
return close; // never happens
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Double_t TGeoShape::DistToCorner(Double_t *point, Double_t *dir, Bool_t in,
Double_t *vertex, Double_t *norm, Int_t &inorm)
{
// Static method to compute distance along a direction from inside/outside point to a corner.
// The corner is defined by its normals to planes n1, n2, n3, and its vertex.
// Also compute distance to closest plane belonging to corner, normal to this plane and
// normal to shape at intersection point.
// iact=0 :
// printf("checking corner : %f %f %fn", vertex[0], vertex[1], vertex[2]);
// printf("normx : %f %f %fn", norm[0], norm[1], norm[2]);
// printf("normy : %f %f %fn", norm[3], norm[4], norm[5]);
// printf("normz : %f %f %fn", norm[6], norm[7], norm[8]);
Double_t safe[3]; // closest distances to the 3 planes
Double_t dist[3]; // distances from point to each of the 3 planes along direction
Double_t dvert[3]; // vector from vertex to point
Double_t cosa[3]; // cosines of anles between direction and each normal
Double_t snxt = kBig;
inorm = -1;
memset(&safe[0], 0, 3*sizeof(Double_t));
memset(&cosa[0], 0, 3*sizeof(Double_t));
Int_t i, j;
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
dvert[i]=point[i]-vertex[i];
dist[i] = kBig;
}
// printf("dvert : %f %f %fn", dvert[0], dvert[1], dvert[2]);
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
for (j=0; j<3; j++) {
safe[i]+=dvert[j]*norm[3*i+j];
cosa[i]+=dir[j]*norm[3*i+j];
}
}
// point is inside
if (in) {
if (safe[0]>0) return kBig;
if (safe[1]>0) return kBig;
if (safe[2]>0) return kBig;
for (i=0; i<3; i++)
if (cosa[i]>0) dist[i]=-safe[i]/cosa[i];
inorm = TMath::LocMin(3, &dist[0]);
snxt = dist[inorm];
return snxt;
}
// point is outside
UInt_t npos=0;
UInt_t nout=0;
UInt_t npp=0;
Double_t dvirt = kBig;
snxt = 0;
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
if (safe[i]>0) nout++;
if (cosa[i]!=0)
dist[i]=-safe[i]/cosa[i];
if (dist[i] < 0) continue;
npos++;
if (safe[i]>0) {
// crossing with visible plane
npp++;
if (snxt<dist[i]) {
// most distant intersection point is the real one
inorm = i;
snxt = dist[i];
}
} else {
// crossing with invisible plane
// compute distance to closest virtual intersection
dvirt=TMath::Min(dvirt, dist[i]);
}
}
// printf(" safe : %f %f %f nout=%in", safe[0], safe[1], safe[2], nout);
// printf(" dist : %f %f %fn", dist[0], dist[1], dist[2]);
// printf(" dist to next : %fn", snxt);
// printf(" closest virtual : %fn", dvirt);
// printf(" inorm=%i snorm=%in", inorm, snorm);
// printf(" nout=%i npos=%i npp=%in", nout, npos, npp);
// select distance to closest plane
if (!nout) {
// point is actually inside the corner (no visible plane)
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
if (nout==1) {
// only one face visible
if (npp!=1 || snxt>dvirt) {
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
return snxt;
}
if (!npos) {
// ray does not intersect any plane
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
if (npp!=nout) {
// ray ray does not intersect all visible faces
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
if (snxt>dvirt) {
// intersection with invisible plane closer than with real one -> no real intersection
// close=kBig;
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
return snxt;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Int_t TGeoShape::GetVertexNumber(Bool_t vx, Bool_t vy, Bool_t vz)
{
// get visible vertex number for : box, trd1, trd2, trap, gtra, para shapes
Int_t imin, imax;
if (!vz) {
imin = 0;
imax = 3;
} else {
imin = 4;
imax = 7;
}
if (!vx)
imax=imin+1;
else
imin = imax-1;
if(!vy) {
if (!vx) return imin;
return imax;
}
if (!vx) return imax;
return imin;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Double_t TGeoShape::SafetyPhi(Double_t *point, Bool_t in, Double_t c1, Double_t s1, Double_t c2, Double_t s2)
{
// Static method to compute safety w.r.t a phi corner defined by cosines/sines
// of the angles phi1, phi2.
Double_t saf1 = kBig;
Double_t saf2 = kBig;
if (point[0]*c1+point[1]*s1 >= 0) saf1 = -point[0]*s1 + point[1]*c1;
if (point[0]*c2+point[1]*s2 >= 0) saf2 = point[0]*s2 - point[1]*c2;
if (in) {
if (saf1<0) saf1=kBig;
if (saf2<0) saf2=kBig;
return TMath::Min(saf1,saf2);
}
if (saf1<0 && saf2<0) return TMath::Max(saf1,saf2);
return TMath::Min(saf1,saf2);
}
*/
//
#include "TObjArray.h"
#include "TGeoMatrix.h"
#include "TGeoManager.h"
#include "TGeoVolume.h"
#include "TGeoShape.h"
#include "TVirtualGeoPainter.h"
/*************************************************************************
* TGeoShape - package description
*
* Creating shapes
*================
* Shape objects embeed only the minimum set of parameters that are fully
* describing a valid physical shape. For instance, a tube is represented by
* its half length, the minimum radius and the maximum radius. Shapes are used
* togather with media in order to create volumes, which in their turn
* are the main components of the geometrical tree. Volumes may contain other
* positioned volumes inside, which are called nodes. Each component in this
* structure : media, shapes and volumes (except nodes) are replicable (one
* instance of an object can be used in several other combinations).
* It is highly recomendable to use replicas as more as possible when volumes
* have different media but the same shape. One will never have to create
* an instance of the TGeoShape class, but only the one for specific shapes :
*
* TGeoBBox *box = new TGeoBBox(halfX, halfY, halfZ);
* TGeoTube *tub = new TGeoTube(rmin, rmax, halfZ);
* ... (see each specific shape constructors)
*
* Sometimes it is much easier to create a volume having a given shape in one
* step, since shapes are not direcly linked in the geometrical tree but volumes
* are :
*
* TGeoVolume *vol_box = gGeoManager->MakeBox("BOX_VOL", "mat1", halfX, halfY, halfZ);
* TGeoVolume *vol_tub = gGeoManager->MakeTube("TUB_VOL", "mat2", rmin, rmax, halfZ);
* ... (see MakeXXX() utilities in TGeoManager class)
*
* Volumes can be assembled also from pieces :
*
* TGeoVolume *vol = new TGeoVolume(name, ptr_shape, ptr_medium);
*
* Point and segment classification
*=================================
* The main functionalities of a shape is finding if a given point is contained
* or not or if an oriented segment crosses or not the shape. Further functionalities
* are : computing the normal to the shape surface at intersection point and finding
* the minimim distance from a point to it.
* These algorithms can be called by user only if the checked point/segment is
* converted to the local reference frame. Mainly they are used by the global
* point/segment classification algorithms of TGeoManager class.
* See also : TGeoManager::FindNode() , TGeoManager::FindNextBoundary()
*
* Classification of arbitrary curves (e.g. helixes) w.r.t shapes is not
* implemented yet.
*
*************************************************************************/
const Double_t TGeoShape::kRadDeg = 180./TMath::Pi();
const Double_t TGeoShape::kDegRad = TMath::Pi()/180.;
const Double_t TGeoShape::kBig = 1E30;
ClassImp(TGeoParamCurve)
ClassImp(TGeoShape)
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
TGeoShape::TGeoShape()
{
// Default constructor
fShapeId = 0;
if (!gGeoManager) {
gGeoManager = new TGeoManager("Geometry", "default geometry");
// gROOT->AddGeoManager(gGeoManager);
}
// fShapeId = gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->GetSize();
// gGeoManager->AddShape(this);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
TGeoShape::TGeoShape(const char *name)
:TNamed(name, "")
{
// Default constructor
fShapeId = 0;
if (!gGeoManager) {
gGeoManager = new TGeoManager("Geometry", "default geometry");
// gROOT->AddGeoManager(gGeoManager);
}
fShapeId = gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->GetSize();
gGeoManager->AddShape(this);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
TGeoShape::~TGeoShape()
{
// Destructor
if (gGeoManager) gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->Remove(this);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
const char *TGeoShape::GetName() const
{
if (!strlen(fName)) {
return ((TObject *)this)->ClassName();
}
return TNamed::GetName();
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Int_t TGeoShape::ShapeDistancetoPrimitive(Int_t numpoints, Int_t px, Int_t py) const
{
TVirtualGeoPainter *painter = gGeoManager->GetGeomPainter();
if (!painter) return 9999;
return painter->ShapeDistancetoPrimitive(this, numpoints, px, py);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Double_t TGeoShape::ClosenessToCorner(Double_t *point, Bool_t in,
Double_t *vertex, Double_t *normals, Double_t *cldir)
{
// Static method returning distance to closest point of a corner. The corner is
// defined by vertex and normals to the 3 planes (in order X, Y, Z - norm[9]).
// also return unit vector pointing to this
Double_t safe[3]; // closest distances to the 3 planes
Double_t dvert[3]; // vector from vertex to point
Int_t snorm = -1;
Double_t close = 0;
memset(&safe[0], 0, 3*sizeof(Double_t));
memset(cldir, 0, 3*sizeof(Double_t));
Int_t i, j;
for (i=0; i<3; i++)
dvert[i]=point[i]-vertex[i];
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
for (j=0; j<3; j++)
safe[i]+=dvert[j]*normals[3*i+j];
}
// point is inside
if (in) {
snorm = TMath::LocMax(3, &safe[0]);
close = -safe[snorm];
// check if point was outside corner
if (close<0) return kBig;
memcpy(cldir, &normals[3*snorm], 3*sizeof(Double_t));
return close;
}
// point is outside
UInt_t nout=0;
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
if (safe[i]>0) {
snorm = i;
close = safe[i];
nout++;
}
}
// check if point is actually inside the corner (no visible plane)
if (!nout) return kBig;
if (nout==1) {
// only one visible plane
memcpy(cldir, &normals[3*snorm], 3*sizeof(Double_t));
return close;
}
if (nout==2) {
// two faces visible
Double_t calf = 0;
Double_t s1=0;
Double_t s2=0;
for (j=0; j<3; j++) {
if (safe[j]>0) {
if (s1==0) s1=safe[j];
else s2=safe[j];
continue;
}
for (Int_t k=0; k<3; k++)
calf += normals[3*((j+1)%3)+k]*normals[3*((j+2)%3)+k];
}
close=TMath::Sqrt((s1*s1 + s2*s2 + 2.*s1*s2*calf)/(1. - calf*calf));
return close;
}
if (nout==3) {
// an edge or even vertex more close than any of the planes
// recompute closest distance
close=0;
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
if (safe[i]>0) close+=dvert[i]*dvert[i];
}
close = TMath::Sqrt(close);
for (i=0; i<3; i++)
cldir[i] = dvert[i]/close;
return close;
}
return close; // never happens
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Double_t TGeoShape::DistToCorner(Double_t *point, Double_t *dir, Bool_t in,
Double_t *vertex, Double_t *norm, Int_t &inorm)
{
// Static method to compute distance along a direction from inside/outside point to a corner.
// The corner is defined by its normals to planes n1, n2, n3, and its vertex.
// Also compute distance to closest plane belonging to corner, normal to this plane and
// normal to shape at intersection point.
// iact=0 :
// printf("checking corner : %f %f %fn", vertex[0], vertex[1], vertex[2]);
// printf("normx : %f %f %fn", norm[0], norm[1], norm[2]);
// printf("normy : %f %f %fn", norm[3], norm[4], norm[5]);
// printf("normz : %f %f %fn", norm[6], norm[7], norm[8]);
Double_t safe[3]; // closest distances to the 3 planes
Double_t dist[3]; // distances from point to each of the 3 planes along direction
Double_t dvert[3]; // vector from vertex to point
Double_t cosa[3]; // cosines of anles between direction and each normal
Double_t snxt = kBig;
inorm = -1;
memset(&safe[0], 0, 3*sizeof(Double_t));
memset(&cosa[0], 0, 3*sizeof(Double_t));
Int_t i, j;
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
dvert[i]=point[i]-vertex[i];
dist[i] = kBig;
}
// printf("dvert : %f %f %fn", dvert[0], dvert[1], dvert[2]);
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
for (j=0; j<3; j++) {
safe[i]+=dvert[j]*norm[3*i+j];
cosa[i]+=dir[j]*norm[3*i+j];
}
}
// point is inside
if (in) {
if (safe[0]>0) return kBig;
if (safe[1]>0) return kBig;
if (safe[2]>0) return kBig;
for (i=0; i<3; i++)
if (cosa[i]>0) dist[i]=-safe[i]/cosa[i];
inorm = TMath::LocMin(3, &dist[0]);
snxt = dist[inorm];
return snxt;
}
// point is outside
UInt_t npos=0;
UInt_t nout=0;
UInt_t npp=0;
Double_t dvirt = kBig;
snxt = 0;
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
if (safe[i]>0) nout++;
if (cosa[i]!=0)
dist[i]=-safe[i]/cosa[i];
if (dist[i] < 0) continue;
npos++;
if (safe[i]>0) {
// crossing with visible plane
npp++;
if (snxt<dist[i]) {
// most distant intersection point is the real one
inorm = i;
snxt = dist[i];
}
} else {
// crossing with invisible plane
// compute distance to closest virtual intersection
dvirt=TMath::Min(dvirt, dist[i]);
}
}
// printf(" safe : %f %f %f nout=%in", safe[0], safe[1], safe[2], nout);
// printf(" dist : %f %f %fn", dist[0], dist[1], dist[2]);
// printf(" dist to next : %fn", snxt);
// printf(" closest virtual : %fn", dvirt);
// printf(" inorm=%i snorm=%in", inorm, snorm);
// printf(" nout=%i npos=%i npp=%in", nout, npos, npp);
// select distance to closest plane
if (!nout) {
// point is actually inside the corner (no visible plane)
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
if (nout==1) {
// only one face visible
if (npp!=1 || snxt>dvirt) {
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
return snxt;
}
if (!npos) {
// ray does not intersect any plane
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
if (npp!=nout) {
// ray ray does not intersect all visible faces
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
if (snxt>dvirt) {
// intersection with invisible plane closer than with real one -> no real intersection
// close=kBig;
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
return snxt;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Int_t TGeoShape::GetVertexNumber(Bool_t vx, Bool_t vy, Bool_t vz)
{
// get visible vertex number for : box, trd1, trd2, trap, gtra, para shapes
Int_t imin, imax;
if (!vz) {
imin = 0;
imax = 3;
} else {
imin = 4;
imax = 7;
}
if (!vx)
imax=imin+1;
else
imin = imax-1;
if(!vy) {
if (!vx) return imin;
return imax;
}
if (!vx) return imax;
return imin;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Double_t TGeoShape::SafetyPhi(Double_t *point, Bool_t in, Double_t c1, Double_t s1, Double_t c2, Double_t s2)
{
// Static method to compute safety w.r.t a phi corner defined by cosines/sines
// of the angles phi1, phi2.
Double_t saf1 = kBig;
Double_t saf2 = kBig;
if (point[0]*c1+point[1]*s1 >= 0) saf1 = -point[0]*s1 + point[1]*c1;
if (point[0]*c2+point[1]*s2 >= 0) saf2 = point[0]*s2 - point[1]*c2;
if (in) {
if (saf1<0) saf1=kBig;
if (saf2<0) saf2=kBig;
return TMath::Min(saf1,saf2);
}
if (saf1<0 && saf2<0) return TMath::Max(saf1,saf2);
return TMath::Min(saf1,saf2);
}
ROOT page - Class index - Top of the page
This page has been automatically generated. If you have any comments or suggestions about the page layout send a mail to ROOT support, or contact the developers with any questions or problems regarding ROOT.
 */
//
#include "TObjArray.h"
#include "TGeoMatrix.h"
#include "TGeoManager.h"
#include "TGeoVolume.h"
#include "TGeoShape.h"
#include "TVirtualGeoPainter.h"
/*************************************************************************
* TGeoShape - package description
*
* Creating shapes
*================
* Shape objects embeed only the minimum set of parameters that are fully
* describing a valid physical shape. For instance, a tube is represented by
* its half length, the minimum radius and the maximum radius. Shapes are used
* togather with media in order to create volumes, which in their turn
* are the main components of the geometrical tree. Volumes may contain other
* positioned volumes inside, which are called nodes. Each component in this
* structure : media, shapes and volumes (except nodes) are replicable (one
* instance of an object can be used in several other combinations).
* It is highly recomendable to use replicas as more as possible when volumes
* have different media but the same shape. One will never have to create
* an instance of the TGeoShape class, but only the one for specific shapes :
*
* TGeoBBox *box = new TGeoBBox(halfX, halfY, halfZ);
* TGeoTube *tub = new TGeoTube(rmin, rmax, halfZ);
* ... (see each specific shape constructors)
*
* Sometimes it is much easier to create a volume having a given shape in one
* step, since shapes are not direcly linked in the geometrical tree but volumes
* are :
*
* TGeoVolume *vol_box = gGeoManager->MakeBox("BOX_VOL", "mat1", halfX, halfY, halfZ);
* TGeoVolume *vol_tub = gGeoManager->MakeTube("TUB_VOL", "mat2", rmin, rmax, halfZ);
* ... (see MakeXXX() utilities in TGeoManager class)
*
* Volumes can be assembled also from pieces :
*
* TGeoVolume *vol = new TGeoVolume(name, ptr_shape, ptr_medium);
*
* Point and segment classification
*=================================
* The main functionalities of a shape is finding if a given point is contained
* or not or if an oriented segment crosses or not the shape. Further functionalities
* are : computing the normal to the shape surface at intersection point and finding
* the minimim distance from a point to it.
* These algorithms can be called by user only if the checked point/segment is
* converted to the local reference frame. Mainly they are used by the global
* point/segment classification algorithms of TGeoManager class.
* See also : TGeoManager::FindNode() , TGeoManager::FindNextBoundary()
*
* Classification of arbitrary curves (e.g. helixes) w.r.t shapes is not
* implemented yet.
*
*************************************************************************/
const Double_t TGeoShape::kRadDeg = 180./TMath::Pi();
const Double_t TGeoShape::kDegRad = TMath::Pi()/180.;
const Double_t TGeoShape::kBig = 1E30;
ClassImp(TGeoParamCurve)
ClassImp(TGeoShape)
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
TGeoShape::TGeoShape()
{
// Default constructor
fShapeId = 0;
if (!gGeoManager) {
gGeoManager = new TGeoManager("Geometry", "default geometry");
// gROOT->AddGeoManager(gGeoManager);
}
// fShapeId = gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->GetSize();
// gGeoManager->AddShape(this);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
TGeoShape::TGeoShape(const char *name)
:TNamed(name, "")
{
// Default constructor
fShapeId = 0;
if (!gGeoManager) {
gGeoManager = new TGeoManager("Geometry", "default geometry");
// gROOT->AddGeoManager(gGeoManager);
}
fShapeId = gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->GetSize();
gGeoManager->AddShape(this);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
TGeoShape::~TGeoShape()
{
// Destructor
if (gGeoManager) gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->Remove(this);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
const char *TGeoShape::GetName() const
{
if (!strlen(fName)) {
return ((TObject *)this)->ClassName();
}
return TNamed::GetName();
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Int_t TGeoShape::ShapeDistancetoPrimitive(Int_t numpoints, Int_t px, Int_t py) const
{
TVirtualGeoPainter *painter = gGeoManager->GetGeomPainter();
if (!painter) return 9999;
return painter->ShapeDistancetoPrimitive(this, numpoints, px, py);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Double_t TGeoShape::ClosenessToCorner(Double_t *point, Bool_t in,
Double_t *vertex, Double_t *normals, Double_t *cldir)
{
// Static method returning distance to closest point of a corner. The corner is
// defined by vertex and normals to the 3 planes (in order X, Y, Z - norm[9]).
// also return unit vector pointing to this
Double_t safe[3]; // closest distances to the 3 planes
Double_t dvert[3]; // vector from vertex to point
Int_t snorm = -1;
Double_t close = 0;
memset(&safe[0], 0, 3*sizeof(Double_t));
memset(cldir, 0, 3*sizeof(Double_t));
Int_t i, j;
for (i=0; i<3; i++)
dvert[i]=point[i]-vertex[i];
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
for (j=0; j<3; j++)
safe[i]+=dvert[j]*normals[3*i+j];
}
// point is inside
if (in) {
snorm = TMath::LocMax(3, &safe[0]);
close = -safe[snorm];
// check if point was outside corner
if (close<0) return kBig;
memcpy(cldir, &normals[3*snorm], 3*sizeof(Double_t));
return close;
}
// point is outside
UInt_t nout=0;
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
if (safe[i]>0) {
snorm = i;
close = safe[i];
nout++;
}
}
// check if point is actually inside the corner (no visible plane)
if (!nout) return kBig;
if (nout==1) {
// only one visible plane
memcpy(cldir, &normals[3*snorm], 3*sizeof(Double_t));
return close;
}
if (nout==2) {
// two faces visible
Double_t calf = 0;
Double_t s1=0;
Double_t s2=0;
for (j=0; j<3; j++) {
if (safe[j]>0) {
if (s1==0) s1=safe[j];
else s2=safe[j];
continue;
}
for (Int_t k=0; k<3; k++)
calf += normals[3*((j+1)%3)+k]*normals[3*((j+2)%3)+k];
}
close=TMath::Sqrt((s1*s1 + s2*s2 + 2.*s1*s2*calf)/(1. - calf*calf));
return close;
}
if (nout==3) {
// an edge or even vertex more close than any of the planes
// recompute closest distance
close=0;
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
if (safe[i]>0) close+=dvert[i]*dvert[i];
}
close = TMath::Sqrt(close);
for (i=0; i<3; i++)
cldir[i] = dvert[i]/close;
return close;
}
return close; // never happens
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Double_t TGeoShape::DistToCorner(Double_t *point, Double_t *dir, Bool_t in,
Double_t *vertex, Double_t *norm, Int_t &inorm)
{
// Static method to compute distance along a direction from inside/outside point to a corner.
// The corner is defined by its normals to planes n1, n2, n3, and its vertex.
// Also compute distance to closest plane belonging to corner, normal to this plane and
// normal to shape at intersection point.
// iact=0 :
// printf("checking corner : %f %f %fn", vertex[0], vertex[1], vertex[2]);
// printf("normx : %f %f %fn", norm[0], norm[1], norm[2]);
// printf("normy : %f %f %fn", norm[3], norm[4], norm[5]);
// printf("normz : %f %f %fn", norm[6], norm[7], norm[8]);
Double_t safe[3]; // closest distances to the 3 planes
Double_t dist[3]; // distances from point to each of the 3 planes along direction
Double_t dvert[3]; // vector from vertex to point
Double_t cosa[3]; // cosines of anles between direction and each normal
Double_t snxt = kBig;
inorm = -1;
memset(&safe[0], 0, 3*sizeof(Double_t));
memset(&cosa[0], 0, 3*sizeof(Double_t));
Int_t i, j;
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
dvert[i]=point[i]-vertex[i];
dist[i] = kBig;
}
// printf("dvert : %f %f %fn", dvert[0], dvert[1], dvert[2]);
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
for (j=0; j<3; j++) {
safe[i]+=dvert[j]*norm[3*i+j];
cosa[i]+=dir[j]*norm[3*i+j];
}
}
// point is inside
if (in) {
if (safe[0]>0) return kBig;
if (safe[1]>0) return kBig;
if (safe[2]>0) return kBig;
for (i=0; i<3; i++)
if (cosa[i]>0) dist[i]=-safe[i]/cosa[i];
inorm = TMath::LocMin(3, &dist[0]);
snxt = dist[inorm];
return snxt;
}
// point is outside
UInt_t npos=0;
UInt_t nout=0;
UInt_t npp=0;
Double_t dvirt = kBig;
snxt = 0;
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
if (safe[i]>0) nout++;
if (cosa[i]!=0)
dist[i]=-safe[i]/cosa[i];
if (dist[i] < 0) continue;
npos++;
if (safe[i]>0) {
// crossing with visible plane
npp++;
if (snxt<dist[i]) {
// most distant intersection point is the real one
inorm = i;
snxt = dist[i];
}
} else {
// crossing with invisible plane
// compute distance to closest virtual intersection
dvirt=TMath::Min(dvirt, dist[i]);
}
}
// printf(" safe : %f %f %f nout=%in", safe[0], safe[1], safe[2], nout);
// printf(" dist : %f %f %fn", dist[0], dist[1], dist[2]);
// printf(" dist to next : %fn", snxt);
// printf(" closest virtual : %fn", dvirt);
// printf(" inorm=%i snorm=%in", inorm, snorm);
// printf(" nout=%i npos=%i npp=%in", nout, npos, npp);
// select distance to closest plane
if (!nout) {
// point is actually inside the corner (no visible plane)
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
if (nout==1) {
// only one face visible
if (npp!=1 || snxt>dvirt) {
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
return snxt;
}
if (!npos) {
// ray does not intersect any plane
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
if (npp!=nout) {
// ray ray does not intersect all visible faces
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
if (snxt>dvirt) {
// intersection with invisible plane closer than with real one -> no real intersection
// close=kBig;
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
return snxt;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Int_t TGeoShape::GetVertexNumber(Bool_t vx, Bool_t vy, Bool_t vz)
{
// get visible vertex number for : box, trd1, trd2, trap, gtra, para shapes
Int_t imin, imax;
if (!vz) {
imin = 0;
imax = 3;
} else {
imin = 4;
imax = 7;
}
if (!vx)
imax=imin+1;
else
imin = imax-1;
if(!vy) {
if (!vx) return imin;
return imax;
}
if (!vx) return imax;
return imin;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Double_t TGeoShape::SafetyPhi(Double_t *point, Bool_t in, Double_t c1, Double_t s1, Double_t c2, Double_t s2)
{
// Static method to compute safety w.r.t a phi corner defined by cosines/sines
// of the angles phi1, phi2.
Double_t saf1 = kBig;
Double_t saf2 = kBig;
if (point[0]*c1+point[1]*s1 >= 0) saf1 = -point[0]*s1 + point[1]*c1;
if (point[0]*c2+point[1]*s2 >= 0) saf2 = point[0]*s2 - point[1]*c2;
if (in) {
if (saf1<0) saf1=kBig;
if (saf2<0) saf2=kBig;
return TMath::Min(saf1,saf2);
}
if (saf1<0 && saf2<0) return TMath::Max(saf1,saf2);
return TMath::Min(saf1,saf2);
}
*/
//
#include "TObjArray.h"
#include "TGeoMatrix.h"
#include "TGeoManager.h"
#include "TGeoVolume.h"
#include "TGeoShape.h"
#include "TVirtualGeoPainter.h"
/*************************************************************************
* TGeoShape - package description
*
* Creating shapes
*================
* Shape objects embeed only the minimum set of parameters that are fully
* describing a valid physical shape. For instance, a tube is represented by
* its half length, the minimum radius and the maximum radius. Shapes are used
* togather with media in order to create volumes, which in their turn
* are the main components of the geometrical tree. Volumes may contain other
* positioned volumes inside, which are called nodes. Each component in this
* structure : media, shapes and volumes (except nodes) are replicable (one
* instance of an object can be used in several other combinations).
* It is highly recomendable to use replicas as more as possible when volumes
* have different media but the same shape. One will never have to create
* an instance of the TGeoShape class, but only the one for specific shapes :
*
* TGeoBBox *box = new TGeoBBox(halfX, halfY, halfZ);
* TGeoTube *tub = new TGeoTube(rmin, rmax, halfZ);
* ... (see each specific shape constructors)
*
* Sometimes it is much easier to create a volume having a given shape in one
* step, since shapes are not direcly linked in the geometrical tree but volumes
* are :
*
* TGeoVolume *vol_box = gGeoManager->MakeBox("BOX_VOL", "mat1", halfX, halfY, halfZ);
* TGeoVolume *vol_tub = gGeoManager->MakeTube("TUB_VOL", "mat2", rmin, rmax, halfZ);
* ... (see MakeXXX() utilities in TGeoManager class)
*
* Volumes can be assembled also from pieces :
*
* TGeoVolume *vol = new TGeoVolume(name, ptr_shape, ptr_medium);
*
* Point and segment classification
*=================================
* The main functionalities of a shape is finding if a given point is contained
* or not or if an oriented segment crosses or not the shape. Further functionalities
* are : computing the normal to the shape surface at intersection point and finding
* the minimim distance from a point to it.
* These algorithms can be called by user only if the checked point/segment is
* converted to the local reference frame. Mainly they are used by the global
* point/segment classification algorithms of TGeoManager class.
* See also : TGeoManager::FindNode() , TGeoManager::FindNextBoundary()
*
* Classification of arbitrary curves (e.g. helixes) w.r.t shapes is not
* implemented yet.
*
*************************************************************************/
const Double_t TGeoShape::kRadDeg = 180./TMath::Pi();
const Double_t TGeoShape::kDegRad = TMath::Pi()/180.;
const Double_t TGeoShape::kBig = 1E30;
ClassImp(TGeoParamCurve)
ClassImp(TGeoShape)
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
TGeoShape::TGeoShape()
{
// Default constructor
fShapeId = 0;
if (!gGeoManager) {
gGeoManager = new TGeoManager("Geometry", "default geometry");
// gROOT->AddGeoManager(gGeoManager);
}
// fShapeId = gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->GetSize();
// gGeoManager->AddShape(this);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
TGeoShape::TGeoShape(const char *name)
:TNamed(name, "")
{
// Default constructor
fShapeId = 0;
if (!gGeoManager) {
gGeoManager = new TGeoManager("Geometry", "default geometry");
// gROOT->AddGeoManager(gGeoManager);
}
fShapeId = gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->GetSize();
gGeoManager->AddShape(this);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
TGeoShape::~TGeoShape()
{
// Destructor
if (gGeoManager) gGeoManager->GetListOfShapes()->Remove(this);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
const char *TGeoShape::GetName() const
{
if (!strlen(fName)) {
return ((TObject *)this)->ClassName();
}
return TNamed::GetName();
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Int_t TGeoShape::ShapeDistancetoPrimitive(Int_t numpoints, Int_t px, Int_t py) const
{
TVirtualGeoPainter *painter = gGeoManager->GetGeomPainter();
if (!painter) return 9999;
return painter->ShapeDistancetoPrimitive(this, numpoints, px, py);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Double_t TGeoShape::ClosenessToCorner(Double_t *point, Bool_t in,
Double_t *vertex, Double_t *normals, Double_t *cldir)
{
// Static method returning distance to closest point of a corner. The corner is
// defined by vertex and normals to the 3 planes (in order X, Y, Z - norm[9]).
// also return unit vector pointing to this
Double_t safe[3]; // closest distances to the 3 planes
Double_t dvert[3]; // vector from vertex to point
Int_t snorm = -1;
Double_t close = 0;
memset(&safe[0], 0, 3*sizeof(Double_t));
memset(cldir, 0, 3*sizeof(Double_t));
Int_t i, j;
for (i=0; i<3; i++)
dvert[i]=point[i]-vertex[i];
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
for (j=0; j<3; j++)
safe[i]+=dvert[j]*normals[3*i+j];
}
// point is inside
if (in) {
snorm = TMath::LocMax(3, &safe[0]);
close = -safe[snorm];
// check if point was outside corner
if (close<0) return kBig;
memcpy(cldir, &normals[3*snorm], 3*sizeof(Double_t));
return close;
}
// point is outside
UInt_t nout=0;
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
if (safe[i]>0) {
snorm = i;
close = safe[i];
nout++;
}
}
// check if point is actually inside the corner (no visible plane)
if (!nout) return kBig;
if (nout==1) {
// only one visible plane
memcpy(cldir, &normals[3*snorm], 3*sizeof(Double_t));
return close;
}
if (nout==2) {
// two faces visible
Double_t calf = 0;
Double_t s1=0;
Double_t s2=0;
for (j=0; j<3; j++) {
if (safe[j]>0) {
if (s1==0) s1=safe[j];
else s2=safe[j];
continue;
}
for (Int_t k=0; k<3; k++)
calf += normals[3*((j+1)%3)+k]*normals[3*((j+2)%3)+k];
}
close=TMath::Sqrt((s1*s1 + s2*s2 + 2.*s1*s2*calf)/(1. - calf*calf));
return close;
}
if (nout==3) {
// an edge or even vertex more close than any of the planes
// recompute closest distance
close=0;
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
if (safe[i]>0) close+=dvert[i]*dvert[i];
}
close = TMath::Sqrt(close);
for (i=0; i<3; i++)
cldir[i] = dvert[i]/close;
return close;
}
return close; // never happens
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Double_t TGeoShape::DistToCorner(Double_t *point, Double_t *dir, Bool_t in,
Double_t *vertex, Double_t *norm, Int_t &inorm)
{
// Static method to compute distance along a direction from inside/outside point to a corner.
// The corner is defined by its normals to planes n1, n2, n3, and its vertex.
// Also compute distance to closest plane belonging to corner, normal to this plane and
// normal to shape at intersection point.
// iact=0 :
// printf("checking corner : %f %f %fn", vertex[0], vertex[1], vertex[2]);
// printf("normx : %f %f %fn", norm[0], norm[1], norm[2]);
// printf("normy : %f %f %fn", norm[3], norm[4], norm[5]);
// printf("normz : %f %f %fn", norm[6], norm[7], norm[8]);
Double_t safe[3]; // closest distances to the 3 planes
Double_t dist[3]; // distances from point to each of the 3 planes along direction
Double_t dvert[3]; // vector from vertex to point
Double_t cosa[3]; // cosines of anles between direction and each normal
Double_t snxt = kBig;
inorm = -1;
memset(&safe[0], 0, 3*sizeof(Double_t));
memset(&cosa[0], 0, 3*sizeof(Double_t));
Int_t i, j;
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
dvert[i]=point[i]-vertex[i];
dist[i] = kBig;
}
// printf("dvert : %f %f %fn", dvert[0], dvert[1], dvert[2]);
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
for (j=0; j<3; j++) {
safe[i]+=dvert[j]*norm[3*i+j];
cosa[i]+=dir[j]*norm[3*i+j];
}
}
// point is inside
if (in) {
if (safe[0]>0) return kBig;
if (safe[1]>0) return kBig;
if (safe[2]>0) return kBig;
for (i=0; i<3; i++)
if (cosa[i]>0) dist[i]=-safe[i]/cosa[i];
inorm = TMath::LocMin(3, &dist[0]);
snxt = dist[inorm];
return snxt;
}
// point is outside
UInt_t npos=0;
UInt_t nout=0;
UInt_t npp=0;
Double_t dvirt = kBig;
snxt = 0;
for (i=0; i<3; i++) {
if (safe[i]>0) nout++;
if (cosa[i]!=0)
dist[i]=-safe[i]/cosa[i];
if (dist[i] < 0) continue;
npos++;
if (safe[i]>0) {
// crossing with visible plane
npp++;
if (snxt<dist[i]) {
// most distant intersection point is the real one
inorm = i;
snxt = dist[i];
}
} else {
// crossing with invisible plane
// compute distance to closest virtual intersection
dvirt=TMath::Min(dvirt, dist[i]);
}
}
// printf(" safe : %f %f %f nout=%in", safe[0], safe[1], safe[2], nout);
// printf(" dist : %f %f %fn", dist[0], dist[1], dist[2]);
// printf(" dist to next : %fn", snxt);
// printf(" closest virtual : %fn", dvirt);
// printf(" inorm=%i snorm=%in", inorm, snorm);
// printf(" nout=%i npos=%i npp=%in", nout, npos, npp);
// select distance to closest plane
if (!nout) {
// point is actually inside the corner (no visible plane)
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
if (nout==1) {
// only one face visible
if (npp!=1 || snxt>dvirt) {
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
return snxt;
}
if (!npos) {
// ray does not intersect any plane
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
if (npp!=nout) {
// ray ray does not intersect all visible faces
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
if (snxt>dvirt) {
// intersection with invisible plane closer than with real one -> no real intersection
// close=kBig;
inorm = -1;
return kBig;
}
return snxt;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Int_t TGeoShape::GetVertexNumber(Bool_t vx, Bool_t vy, Bool_t vz)
{
// get visible vertex number for : box, trd1, trd2, trap, gtra, para shapes
Int_t imin, imax;
if (!vz) {
imin = 0;
imax = 3;
} else {
imin = 4;
imax = 7;
}
if (!vx)
imax=imin+1;
else
imin = imax-1;
if(!vy) {
if (!vx) return imin;
return imax;
}
if (!vx) return imax;
return imin;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Double_t TGeoShape::SafetyPhi(Double_t *point, Bool_t in, Double_t c1, Double_t s1, Double_t c2, Double_t s2)
{
// Static method to compute safety w.r.t a phi corner defined by cosines/sines
// of the angles phi1, phi2.
Double_t saf1 = kBig;
Double_t saf2 = kBig;
if (point[0]*c1+point[1]*s1 >= 0) saf1 = -point[0]*s1 + point[1]*c1;
if (point[0]*c2+point[1]*s2 >= 0) saf2 = point[0]*s2 - point[1]*c2;
if (in) {
if (saf1<0) saf1=kBig;
if (saf2<0) saf2=kBig;
return TMath::Min(saf1,saf2);
}
if (saf1<0 && saf2<0) return TMath::Max(saf1,saf2);
return TMath::Min(saf1,saf2);
}