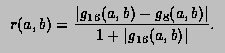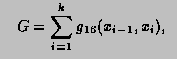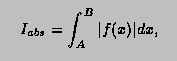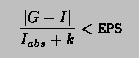 */
//
//
// Example of a function of type B
// TF1 *f1 = new TF1("f1","[0]x*sin([1]*x",-3,3);
// This creates a function of variable x with 2 parameters.
// The parameters must be initialized via:
// f1->SetParameter(0,value_first_parameter);
// f1->SetParameter(1,value_second_parameter);
// Parameters may be given a name:
// f1->SetParName(0,"Constant");
//
// Example of function of type C
// Consider the macro myfunc.C below
//-------------macro myfunc.C-----------------------------
//Double_t myfunction(Double_t *x, Double_t *par)
//{
// Float_t xx =x[0];
// Double_t f = TMath::Abs(par[0]*sin(par[1]*xx)/xx);
// return f;
//}
//void myfunc()
//{
// TF1 *f1 = new TF1("myfunc",myfunction,0,10,2);
// f1->SetParameters(2,1);
// f1->SetParNames("constant","coefficient");
// f1->Draw();
//}
//void myfit()
//{
// TH1F *h1=new TH1F("h1","test",100,0,10);
// h1->FillRandom("myfunc",20000);
// TF1 *f1=gROOT->GetFunction("myfunc");
// f1->SetParameters(800,1);
// h1.Fit("myfunc");
//}
//--------end of macro myfunc.C---------------------------------
//
// In an interactive session you can do:
// Root > .L myfunc.C
// Root > myfunc();
// Root > myfit();
//
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(): TFormula(), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 default constructor*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ======================
fType = 0;
fFunction = 0;
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fParent = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fSave = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fMethodCall = 0;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const char *name,const char *formula, Float_t xmin, Float_t xmax)
:TFormula(name,formula), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 constructor using a formula definition*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =========================================
//*-*
//*-* See TFormula constructor for explanation of the formula syntax.
//*-*
//*-* Creates a function of type A or B between xmin and xmax
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fXmin = xmin;
fXmax = xmax;
fNpx = 100;
fType = 0;
fFunction = 0;
if (fNpar) {
fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
for (int i = 0; i < fNpar; i++) {
fParErrors[i] = 0;
fParMin[i] = 0;
fParMax[i] = 0;
}
} else {
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
}
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fParent = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fSave = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fMethodCall = 0;
if (!gStyle) return;
SetLineColor(gStyle->GetFuncColor());
SetLineWidth(gStyle->GetFuncWidth());
SetLineStyle(gStyle->GetFuncStyle());
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const char *name,void *fcn, Float_t xmin, Float_t xmax, Int_t npar)
:TFormula(), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 constructor using pointer to an interpreted function*-*-*-*
//*-* =======================================================
//*-*
//*-* See TFormula constructor for explanation of the formula syntax.
//*-*
//*-* Creates a function of type C between xmin and xmax.
//*-* The function is defined with npar parameters
//*-* fcn must be a function of type:
//*-* Double_t fcn(Double_t *x, Double_t *params)
//*-*
//*-* This constructor is called for functions of type C by CINT.
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fXmin = xmin;
fXmax = xmax;
fNpx = 100;
fType = 2;
fFunction = 0;
if (npar > 0 ) fNpar = npar;
if (fNpar) {
fNames = new TString[fNpar];
fParams = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
for (int i = 0; i < fNpar; i++) {
fParams[i] = 0;
fParErrors[i] = 0;
fParMin[i] = 0;
fParMax[i] = 0;
}
} else {
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
}
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fParent = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fSave = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fMethodCall = 0;
if (!fcn) return;
TF1 *f1old = (TF1*)gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->FindObject(name);
if (f1old) delete f1old;
char *funcname = G__p2f2funcname(fcn);
if (funcname) {
fMethodCall = new TMethodCall();
fMethodCall->InitWithPrototype(funcname,"Double_t*,Double_t*");
fNumber = -1;
} else {
Printf("Function:%s cannot be compiled",name);
}
SetName(name);
SetTitle(funcname);
gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->Add(this);
if (!gStyle) return;
SetLineColor(gStyle->GetFuncColor());
SetLineWidth(gStyle->GetFuncWidth());
SetLineStyle(gStyle->GetFuncStyle());
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const char *name,Double_t (*fcn)(Double_t *, Double_t *), Float_t xmin, Float_t xmax, Int_t npar)
:TFormula(), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 constructor using a pointer to real function*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ===============================================
//*-*
//*-* npar is the number of free parameters used by the function
//*-*
//*-* This constructor creates a function of type C when invoked
//*-* with the normal C++ compiler.
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fXmin = xmin;
fXmax = xmax;
fNpx = 100;
fType = 1;
fFunction = fcn;
if (npar > 0 ) fNpar = npar;
if (fNpar) {
fNames = new TString[fNpar];
fParams = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
for (int i = 0; i < fNpar; i++) {
fParams[i] = 0;
fParErrors[i] = 0;
fParMin[i] = 0;
fParMax[i] = 0;
}
} else {
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
}
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fSave = 0;
fParent = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fMethodCall = 0;
//*-*- Store formula in linked list of formula in ROOT
SetName((char *)name);
if (gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->FindObject(name)) return;
gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->Add(this);
if (!gStyle) return;
SetLineColor(gStyle->GetFuncColor());
SetLineWidth(gStyle->GetFuncWidth());
SetLineStyle(gStyle->GetFuncStyle());
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::~TF1()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 default destructor*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =====================
if (fParMin) delete [] fParMin;
if (fParMax) delete [] fParMax;
if (fParErrors) delete [] fParErrors;
if (fIntegral) delete [] fIntegral;
if (fSave) delete [] fSave;
delete fHistogram;
delete fMethodCall;
if (fParent) {
if (fParent->InheritsFrom(TH1::Class())) {
((TH1*)fParent)->GetListOfFunctions()->Remove(this);
return;
}
if (fParent->InheritsFrom("TGraph")) {
((TGraph*)fParent)->GetListOfFunctions()->Remove(this);
return;
}
fParent = 0;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const TF1 &f1)
{
((TF1&)f1).Copy(*this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Browse(TBrowser *)
{
Draw();
gPad->Update();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Copy(TObject &obj)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Copy this F1 to a new F1*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ========================
TFormula::Copy(obj);
TAttLine::Copy((TF1&)obj);
TAttFill::Copy((TF1&)obj);
TAttMarker::Copy((TF1&)obj);
((TF1&)obj).fXmin = fXmin;
((TF1&)obj).fXmax = fXmax;
((TF1&)obj).fNpx = fNpx;
((TF1&)obj).fType = fType;
((TF1&)obj).fFunction = fFunction;
((TF1&)obj).fChisquare = fChisquare;
((TF1&)obj).fNpfits = fNpfits;
((TF1&)obj).fMinimum = fMinimum;
((TF1&)obj).fMaximum = fMaximum;
if (fNpar) {
((TF1&)obj).fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
((TF1&)obj).fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
((TF1&)obj).fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
}
Int_t i;
for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) ((TF1&)obj).fParErrors[i] = fParErrors[i];
for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) ((TF1&)obj).fParMin[i] = fParMin[i];
for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) ((TF1&)obj).fParMax[i] = fParMax[i];
if (fMethodCall) {
TMethodCall *m = new TMethodCall();
m->InitWithPrototype(fMethodCall->GetMethodName(),fMethodCall->GetProto());
((TF1&)obj).fMethodCall = m;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::Derivative(Double_t x, Double_t *params, Float_t epsilon)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return derivative of function at point x*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//
// The derivative is computed by computing the value of the function
// at point x-epsilon and point x+epsilon.
// if params is NULL, use the current values of parameters
Double_t xx[2];
if (epsilon <= 0) epsilon = 0.001;
epsilon *= fXmax-fXmin;
xx[0] = x - epsilon;
xx[1] = x + epsilon;
if (xx[0] < fXmin) xx[0] = fXmin;
if (xx[1] > fXmax) xx[1] = fXmax;
Double_t f1,f2,deriv;
InitArgs(&xx[0],params);
f1 = EvalPar(&xx[0],params);
InitArgs(&xx[1],params);
f2 = EvalPar(&xx[1],params);
deriv = (f2-f1)/(2*epsilon);
return deriv;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TF1::DistancetoPrimitive(Int_t px, Int_t py)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Compute distance from point px,py to a function*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ===============================================
//*-* Compute the closest distance of approach from point px,py to this function.
//*-* The distance is computed in pixels units.
//*-*
//*-* Algorithm:
//*-*
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
if (!fHistogram) return 9999;
Int_t distance = fHistogram->DistancetoPrimitive(px,py);
if (distance <= 0) return distance;
Double_t xx[1];
Float_t x = gPad->AbsPixeltoX(px);
xx[0] = gPad->PadtoX(x);
Double_t fval = Eval(xx[0]);
Float_t y = gPad->YtoPad(fval);
Int_t pybin = gPad->YtoAbsPixel(y);
return TMath::Abs(py - pybin);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Draw(Option_t *option)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Draw this function with its current attributes*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==============================================
//*-*
//*-* Possible option values are:
//*-* "SAME" superimpose on top of existing picture
//*-* "L" connect all computed points with a straight line
//*-* "C" connect all computed points with a smooth curve.
//*-*
//*-* Note that the default value is "L". Therefore to draw on top
//*-* of an existing picture, specify option "LSAME"
//*-*
//*-* NB. You must use DrawCopy if you want to draw several times the same
//*-* function in the current canvas.
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
TString opt = option;
opt.ToLower();
if (gPad && !opt.Contains("same")) gPad->Clear();
AppendPad(option);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::DrawCopy(Option_t *option)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Draw a copy of this function with its current attributes*-*-*
//*-* ========================================================
//*-*
//*-* This function MUST be used instead of Draw when you want to draw
//*-* the same function with different parameters settings in the same canvas.
//*-*
//*-* Possible option values are:
//*-* "SAME" superimpose on top of existing picture
//*-* "L" connect all computed points with a straight line
//*-* "C" connect all computed points with a smooth curve.
//*-*
//*-* Note that the default value is "L". Therefore to draw on top
//*-* of an existing picture, specify option "LSAME"
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
TF1 *newf1 = new TF1();
Copy(*newf1);
newf1->AppendPad(option);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::DrawF1(const char *formula, Float_t xmin, Float_t xmax, Option_t *option)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Draw formula between xmin and xmax*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==================================
//*-*
if (Compile((char*)formula)) return;
SetRange(xmin, xmax);
Draw(option);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::DrawPanel()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*Display a panel with all function drawing options*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =================================================
//*-*
//*-* See class TDrawPanelHist for example
if (gPad) {
//gROOT->SetSelectedPrimitive(gPad->GetSelected());
//gROOT->SetSelectedPad(gPad->GetSelectedPad());
gROOT->SetSelectedPrimitive(this);
gROOT->SetSelectedPad(gPad);
}
TList *lc = (TList*)gROOT->GetListOfCanvases();
if (!lc->FindObject("drawpanelhist")) {
char cmd[] = "drawpanelhist = new TDrawPanelHist("drawpanelhist","Hist Draw Panel",330,450)";
gInterpreter->ProcessLine(cmd);
return;
}
char cmdupd[] = "drawpanelhist->SetDefaults()";
gInterpreter->ProcessLine(cmdupd);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::Eval(Double_t x, Double_t y, Double_t z)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Evaluate this formula*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =====================
//*-*
//*-* Computes the value of this function (general case for a 3-d function)
//*-* at point x,y,z.
//*-* For a 1-d function give y=0 and z=0
//*-* The current value of variables x,y,z is passed through x, y and z.
//*-* The parameters used will be the ones in the array params if params is given
//*-* otherwise parameters will be taken from the stored data members fParams
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
Double_t xx[3];
xx[0] = x;
xx[1] = y;
xx[2] = z;
InitArgs(xx,fParams);
return TF1::EvalPar(xx,fParams);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::EvalPar(Double_t *x, Double_t *params)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*Evaluate function with given coordinates and parameters*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =======================================================
//*-*
// Compute the value of this function at point defined by array x
// and current values of parameters in array params.
// If argument params is omitted or equal 0, the internal values
// of parameters (array fParams) will be used instead.
// For a 1-D function only x[0] must be given.
// In case of a multi-dimemsional function, the arrays x must be
// filled with the corresponding number of dimensions.
//
// WARNING. In case of an interpreted function (fType=2), it is the
// user's responsability to initialize the parameters via InitArgs
// before calling this function.
// InitArgs should be called at least once to specify the addresses
// of the arguments x and params.
// InitArgs should be called everytime these addresses change.
//
if (fType == 0) return TFormula::EvalPar(x,params);
Double_t result = 0;
if (fType == 1) {
if (fFunction) result = (*fFunction)(x,params);
else result = GetSave(x);
}
if (fType == 2) {
if (fMethodCall) fMethodCall->Execute(result);
else result = GetSave(x);
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::ExecuteEvent(Int_t event, Int_t px, Int_t py)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Execute action corresponding to one event*-*-*-*
//*-* =========================================
//*-* This member function is called when a F1 is clicked with the locator
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fHistogram->ExecuteEvent(event,px,py);
if (!gPad->GetView()) {
if (event == kMouseMotion) gPad->SetCursor(kHand);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::GetParLimits(Int_t ipar, Double_t &parmin, Double_t &parmax)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*Return limits for parameter ipar*-*-*-*
//*-* ================================
parmin = 0;
parmax = 0;
if (ipar < 0 || ipar > fNpar-1) return;
if (fParMin) parmin = fParMin[ipar];
if (fParMax) parmax = fParMax[ipar];
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetRandom()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*Return a random number following this function shape*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ====================================================
//*-*
//*-* The distribution contained in the function fname (TF1) is integrated
//*-* over the channel contents.
//*-* It is normalized to 1.
//*-* Getting one random number implies:
//*-* - Generating a random number between 0 and 1 (say r1)
//*-* - Look in which bin in the normalized integral r1 corresponds to
//*-* - make a linear interpolation in the returned bin
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-**-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
// Check if integral array must be build
Int_t i;
Float_t dx = (fXmax-fXmin)/fNpx;
if (fIntegral == 0) {
fIntegral = new Double_t[fNpx+1];
fIntegral[0] = 0;
Double_t integ;
Int_t intNegative = 0;
for (i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
integ = Integral(fXmin+i*dx, fXmin+i*dx+dx);
if (integ < 0) {intNegative++; integ = -integ;}
fIntegral[i+1] = fIntegral[i] + integ;
}
if (intNegative > 0) {
Warning("GetRandom","function:%s has %d negative values: abs assumed",GetName(),intNegative);
}
if (fIntegral[fNpx] == 0) {
Error("GetRandom","Integral of function is zero");
return 0;
}
for (i=1;i<=fNpx;i++) { // normalize integral to 1
fIntegral[i] /= fIntegral[fNpx];
}
}
// return random number
Float_t r = gRandom->Rndm();
Int_t bin = LocateBinary(r,fIntegral,fNpx);
Float_t dy = fIntegral[bin+1] - fIntegral[bin];
if (dy > 0) return fXmin + (r-fIntegral[bin])*dx/dy +dx*bin;
else return fXmin + dx*bin;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::GetRange(Float_t &xmin, Float_t &xmax)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return range of a 1-D function*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==============================
xmin = fXmin;
xmax = fXmax;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::GetRange(Float_t &xmin, Float_t &ymin, Float_t &xmax, Float_t &ymax)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return range of a 2-D function*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==============================
xmin = fXmin;
xmax = fXmax;
ymin = 0;
ymax = 0;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::GetRange(Float_t &xmin, Float_t &ymin, Float_t &zmin, Float_t &xmax, Float_t &ymax, Float_t &zmax)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return range of function*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ========================
xmin = fXmin;
xmax = fXmax;
ymin = 0;
ymax = 0;
zmin = 0;
zmax = 0;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetSave(Double_t *xx)
{
// Get value corresponding to X in array of fSave values
if (fNsave <= 0) return 0;
if (fSave == 0) return 0;
Float_t xmin = Float_t(fSave[fNsave+2]);
Float_t xmax = Float_t(fSave[fNsave+3]);
Float_t x = Float_t(xx[0]);
Float_t dx = (xmax-xmin)/fNsave;
if (x < xmin || x > xmax) return 0;
if (dx <= 0) return 0;
Int_t bin = Int_t((x-xmin)/dx);
Float_t xlow = xmin + bin*dx;
Float_t xup = xlow + dx;
Double_t ylow = fSave[bin];
Double_t yup = fSave[bin+1];
Double_t y = ((xup*ylow-xlow*yup) + x*(yup-ylow))/dx;
return y;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::InitArgs(Double_t *x, Double_t *params)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Initialize parameters addresses*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ===============================
if (fMethodCall) {
Long_t args[2];
args[0] = (Long_t)x;
if (params) args[1] = (Long_t)params;
else args[1] = (Long_t)fParams;
fMethodCall->SetParamPtrs(args);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::Integral(Float_t a, Float_t b, Double_t *params, Float_t epsilon)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return Integral of function between a and b*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//
// based on original CERNLIB routine DGAUSS by Sigfried Kolbig
// converted to C++ by Rene Brun
//
//
/*
*/
//
//
// Example of a function of type B
// TF1 *f1 = new TF1("f1","[0]x*sin([1]*x",-3,3);
// This creates a function of variable x with 2 parameters.
// The parameters must be initialized via:
// f1->SetParameter(0,value_first_parameter);
// f1->SetParameter(1,value_second_parameter);
// Parameters may be given a name:
// f1->SetParName(0,"Constant");
//
// Example of function of type C
// Consider the macro myfunc.C below
//-------------macro myfunc.C-----------------------------
//Double_t myfunction(Double_t *x, Double_t *par)
//{
// Float_t xx =x[0];
// Double_t f = TMath::Abs(par[0]*sin(par[1]*xx)/xx);
// return f;
//}
//void myfunc()
//{
// TF1 *f1 = new TF1("myfunc",myfunction,0,10,2);
// f1->SetParameters(2,1);
// f1->SetParNames("constant","coefficient");
// f1->Draw();
//}
//void myfit()
//{
// TH1F *h1=new TH1F("h1","test",100,0,10);
// h1->FillRandom("myfunc",20000);
// TF1 *f1=gROOT->GetFunction("myfunc");
// f1->SetParameters(800,1);
// h1.Fit("myfunc");
//}
//--------end of macro myfunc.C---------------------------------
//
// In an interactive session you can do:
// Root > .L myfunc.C
// Root > myfunc();
// Root > myfit();
//
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(): TFormula(), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 default constructor*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ======================
fType = 0;
fFunction = 0;
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fParent = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fSave = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fMethodCall = 0;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const char *name,const char *formula, Float_t xmin, Float_t xmax)
:TFormula(name,formula), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 constructor using a formula definition*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =========================================
//*-*
//*-* See TFormula constructor for explanation of the formula syntax.
//*-*
//*-* Creates a function of type A or B between xmin and xmax
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fXmin = xmin;
fXmax = xmax;
fNpx = 100;
fType = 0;
fFunction = 0;
if (fNpar) {
fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
for (int i = 0; i < fNpar; i++) {
fParErrors[i] = 0;
fParMin[i] = 0;
fParMax[i] = 0;
}
} else {
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
}
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fParent = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fSave = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fMethodCall = 0;
if (!gStyle) return;
SetLineColor(gStyle->GetFuncColor());
SetLineWidth(gStyle->GetFuncWidth());
SetLineStyle(gStyle->GetFuncStyle());
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const char *name,void *fcn, Float_t xmin, Float_t xmax, Int_t npar)
:TFormula(), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 constructor using pointer to an interpreted function*-*-*-*
//*-* =======================================================
//*-*
//*-* See TFormula constructor for explanation of the formula syntax.
//*-*
//*-* Creates a function of type C between xmin and xmax.
//*-* The function is defined with npar parameters
//*-* fcn must be a function of type:
//*-* Double_t fcn(Double_t *x, Double_t *params)
//*-*
//*-* This constructor is called for functions of type C by CINT.
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fXmin = xmin;
fXmax = xmax;
fNpx = 100;
fType = 2;
fFunction = 0;
if (npar > 0 ) fNpar = npar;
if (fNpar) {
fNames = new TString[fNpar];
fParams = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
for (int i = 0; i < fNpar; i++) {
fParams[i] = 0;
fParErrors[i] = 0;
fParMin[i] = 0;
fParMax[i] = 0;
}
} else {
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
}
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fParent = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fSave = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fMethodCall = 0;
if (!fcn) return;
TF1 *f1old = (TF1*)gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->FindObject(name);
if (f1old) delete f1old;
char *funcname = G__p2f2funcname(fcn);
if (funcname) {
fMethodCall = new TMethodCall();
fMethodCall->InitWithPrototype(funcname,"Double_t*,Double_t*");
fNumber = -1;
} else {
Printf("Function:%s cannot be compiled",name);
}
SetName(name);
SetTitle(funcname);
gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->Add(this);
if (!gStyle) return;
SetLineColor(gStyle->GetFuncColor());
SetLineWidth(gStyle->GetFuncWidth());
SetLineStyle(gStyle->GetFuncStyle());
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const char *name,Double_t (*fcn)(Double_t *, Double_t *), Float_t xmin, Float_t xmax, Int_t npar)
:TFormula(), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 constructor using a pointer to real function*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ===============================================
//*-*
//*-* npar is the number of free parameters used by the function
//*-*
//*-* This constructor creates a function of type C when invoked
//*-* with the normal C++ compiler.
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fXmin = xmin;
fXmax = xmax;
fNpx = 100;
fType = 1;
fFunction = fcn;
if (npar > 0 ) fNpar = npar;
if (fNpar) {
fNames = new TString[fNpar];
fParams = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
for (int i = 0; i < fNpar; i++) {
fParams[i] = 0;
fParErrors[i] = 0;
fParMin[i] = 0;
fParMax[i] = 0;
}
} else {
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
}
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fSave = 0;
fParent = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fMethodCall = 0;
//*-*- Store formula in linked list of formula in ROOT
SetName((char *)name);
if (gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->FindObject(name)) return;
gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->Add(this);
if (!gStyle) return;
SetLineColor(gStyle->GetFuncColor());
SetLineWidth(gStyle->GetFuncWidth());
SetLineStyle(gStyle->GetFuncStyle());
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::~TF1()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 default destructor*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =====================
if (fParMin) delete [] fParMin;
if (fParMax) delete [] fParMax;
if (fParErrors) delete [] fParErrors;
if (fIntegral) delete [] fIntegral;
if (fSave) delete [] fSave;
delete fHistogram;
delete fMethodCall;
if (fParent) {
if (fParent->InheritsFrom(TH1::Class())) {
((TH1*)fParent)->GetListOfFunctions()->Remove(this);
return;
}
if (fParent->InheritsFrom("TGraph")) {
((TGraph*)fParent)->GetListOfFunctions()->Remove(this);
return;
}
fParent = 0;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const TF1 &f1)
{
((TF1&)f1).Copy(*this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Browse(TBrowser *)
{
Draw();
gPad->Update();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Copy(TObject &obj)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Copy this F1 to a new F1*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ========================
TFormula::Copy(obj);
TAttLine::Copy((TF1&)obj);
TAttFill::Copy((TF1&)obj);
TAttMarker::Copy((TF1&)obj);
((TF1&)obj).fXmin = fXmin;
((TF1&)obj).fXmax = fXmax;
((TF1&)obj).fNpx = fNpx;
((TF1&)obj).fType = fType;
((TF1&)obj).fFunction = fFunction;
((TF1&)obj).fChisquare = fChisquare;
((TF1&)obj).fNpfits = fNpfits;
((TF1&)obj).fMinimum = fMinimum;
((TF1&)obj).fMaximum = fMaximum;
if (fNpar) {
((TF1&)obj).fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
((TF1&)obj).fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
((TF1&)obj).fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
}
Int_t i;
for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) ((TF1&)obj).fParErrors[i] = fParErrors[i];
for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) ((TF1&)obj).fParMin[i] = fParMin[i];
for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) ((TF1&)obj).fParMax[i] = fParMax[i];
if (fMethodCall) {
TMethodCall *m = new TMethodCall();
m->InitWithPrototype(fMethodCall->GetMethodName(),fMethodCall->GetProto());
((TF1&)obj).fMethodCall = m;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::Derivative(Double_t x, Double_t *params, Float_t epsilon)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return derivative of function at point x*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//
// The derivative is computed by computing the value of the function
// at point x-epsilon and point x+epsilon.
// if params is NULL, use the current values of parameters
Double_t xx[2];
if (epsilon <= 0) epsilon = 0.001;
epsilon *= fXmax-fXmin;
xx[0] = x - epsilon;
xx[1] = x + epsilon;
if (xx[0] < fXmin) xx[0] = fXmin;
if (xx[1] > fXmax) xx[1] = fXmax;
Double_t f1,f2,deriv;
InitArgs(&xx[0],params);
f1 = EvalPar(&xx[0],params);
InitArgs(&xx[1],params);
f2 = EvalPar(&xx[1],params);
deriv = (f2-f1)/(2*epsilon);
return deriv;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TF1::DistancetoPrimitive(Int_t px, Int_t py)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Compute distance from point px,py to a function*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ===============================================
//*-* Compute the closest distance of approach from point px,py to this function.
//*-* The distance is computed in pixels units.
//*-*
//*-* Algorithm:
//*-*
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
if (!fHistogram) return 9999;
Int_t distance = fHistogram->DistancetoPrimitive(px,py);
if (distance <= 0) return distance;
Double_t xx[1];
Float_t x = gPad->AbsPixeltoX(px);
xx[0] = gPad->PadtoX(x);
Double_t fval = Eval(xx[0]);
Float_t y = gPad->YtoPad(fval);
Int_t pybin = gPad->YtoAbsPixel(y);
return TMath::Abs(py - pybin);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Draw(Option_t *option)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Draw this function with its current attributes*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==============================================
//*-*
//*-* Possible option values are:
//*-* "SAME" superimpose on top of existing picture
//*-* "L" connect all computed points with a straight line
//*-* "C" connect all computed points with a smooth curve.
//*-*
//*-* Note that the default value is "L". Therefore to draw on top
//*-* of an existing picture, specify option "LSAME"
//*-*
//*-* NB. You must use DrawCopy if you want to draw several times the same
//*-* function in the current canvas.
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
TString opt = option;
opt.ToLower();
if (gPad && !opt.Contains("same")) gPad->Clear();
AppendPad(option);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::DrawCopy(Option_t *option)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Draw a copy of this function with its current attributes*-*-*
//*-* ========================================================
//*-*
//*-* This function MUST be used instead of Draw when you want to draw
//*-* the same function with different parameters settings in the same canvas.
//*-*
//*-* Possible option values are:
//*-* "SAME" superimpose on top of existing picture
//*-* "L" connect all computed points with a straight line
//*-* "C" connect all computed points with a smooth curve.
//*-*
//*-* Note that the default value is "L". Therefore to draw on top
//*-* of an existing picture, specify option "LSAME"
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
TF1 *newf1 = new TF1();
Copy(*newf1);
newf1->AppendPad(option);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::DrawF1(const char *formula, Float_t xmin, Float_t xmax, Option_t *option)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Draw formula between xmin and xmax*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==================================
//*-*
if (Compile((char*)formula)) return;
SetRange(xmin, xmax);
Draw(option);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::DrawPanel()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*Display a panel with all function drawing options*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =================================================
//*-*
//*-* See class TDrawPanelHist for example
if (gPad) {
//gROOT->SetSelectedPrimitive(gPad->GetSelected());
//gROOT->SetSelectedPad(gPad->GetSelectedPad());
gROOT->SetSelectedPrimitive(this);
gROOT->SetSelectedPad(gPad);
}
TList *lc = (TList*)gROOT->GetListOfCanvases();
if (!lc->FindObject("drawpanelhist")) {
char cmd[] = "drawpanelhist = new TDrawPanelHist("drawpanelhist","Hist Draw Panel",330,450)";
gInterpreter->ProcessLine(cmd);
return;
}
char cmdupd[] = "drawpanelhist->SetDefaults()";
gInterpreter->ProcessLine(cmdupd);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::Eval(Double_t x, Double_t y, Double_t z)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Evaluate this formula*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =====================
//*-*
//*-* Computes the value of this function (general case for a 3-d function)
//*-* at point x,y,z.
//*-* For a 1-d function give y=0 and z=0
//*-* The current value of variables x,y,z is passed through x, y and z.
//*-* The parameters used will be the ones in the array params if params is given
//*-* otherwise parameters will be taken from the stored data members fParams
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
Double_t xx[3];
xx[0] = x;
xx[1] = y;
xx[2] = z;
InitArgs(xx,fParams);
return TF1::EvalPar(xx,fParams);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::EvalPar(Double_t *x, Double_t *params)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*Evaluate function with given coordinates and parameters*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =======================================================
//*-*
// Compute the value of this function at point defined by array x
// and current values of parameters in array params.
// If argument params is omitted or equal 0, the internal values
// of parameters (array fParams) will be used instead.
// For a 1-D function only x[0] must be given.
// In case of a multi-dimemsional function, the arrays x must be
// filled with the corresponding number of dimensions.
//
// WARNING. In case of an interpreted function (fType=2), it is the
// user's responsability to initialize the parameters via InitArgs
// before calling this function.
// InitArgs should be called at least once to specify the addresses
// of the arguments x and params.
// InitArgs should be called everytime these addresses change.
//
if (fType == 0) return TFormula::EvalPar(x,params);
Double_t result = 0;
if (fType == 1) {
if (fFunction) result = (*fFunction)(x,params);
else result = GetSave(x);
}
if (fType == 2) {
if (fMethodCall) fMethodCall->Execute(result);
else result = GetSave(x);
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::ExecuteEvent(Int_t event, Int_t px, Int_t py)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Execute action corresponding to one event*-*-*-*
//*-* =========================================
//*-* This member function is called when a F1 is clicked with the locator
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fHistogram->ExecuteEvent(event,px,py);
if (!gPad->GetView()) {
if (event == kMouseMotion) gPad->SetCursor(kHand);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::GetParLimits(Int_t ipar, Double_t &parmin, Double_t &parmax)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*Return limits for parameter ipar*-*-*-*
//*-* ================================
parmin = 0;
parmax = 0;
if (ipar < 0 || ipar > fNpar-1) return;
if (fParMin) parmin = fParMin[ipar];
if (fParMax) parmax = fParMax[ipar];
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetRandom()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*Return a random number following this function shape*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ====================================================
//*-*
//*-* The distribution contained in the function fname (TF1) is integrated
//*-* over the channel contents.
//*-* It is normalized to 1.
//*-* Getting one random number implies:
//*-* - Generating a random number between 0 and 1 (say r1)
//*-* - Look in which bin in the normalized integral r1 corresponds to
//*-* - make a linear interpolation in the returned bin
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-**-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
// Check if integral array must be build
Int_t i;
Float_t dx = (fXmax-fXmin)/fNpx;
if (fIntegral == 0) {
fIntegral = new Double_t[fNpx+1];
fIntegral[0] = 0;
Double_t integ;
Int_t intNegative = 0;
for (i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
integ = Integral(fXmin+i*dx, fXmin+i*dx+dx);
if (integ < 0) {intNegative++; integ = -integ;}
fIntegral[i+1] = fIntegral[i] + integ;
}
if (intNegative > 0) {
Warning("GetRandom","function:%s has %d negative values: abs assumed",GetName(),intNegative);
}
if (fIntegral[fNpx] == 0) {
Error("GetRandom","Integral of function is zero");
return 0;
}
for (i=1;i<=fNpx;i++) { // normalize integral to 1
fIntegral[i] /= fIntegral[fNpx];
}
}
// return random number
Float_t r = gRandom->Rndm();
Int_t bin = LocateBinary(r,fIntegral,fNpx);
Float_t dy = fIntegral[bin+1] - fIntegral[bin];
if (dy > 0) return fXmin + (r-fIntegral[bin])*dx/dy +dx*bin;
else return fXmin + dx*bin;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::GetRange(Float_t &xmin, Float_t &xmax)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return range of a 1-D function*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==============================
xmin = fXmin;
xmax = fXmax;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::GetRange(Float_t &xmin, Float_t &ymin, Float_t &xmax, Float_t &ymax)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return range of a 2-D function*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==============================
xmin = fXmin;
xmax = fXmax;
ymin = 0;
ymax = 0;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::GetRange(Float_t &xmin, Float_t &ymin, Float_t &zmin, Float_t &xmax, Float_t &ymax, Float_t &zmax)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return range of function*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ========================
xmin = fXmin;
xmax = fXmax;
ymin = 0;
ymax = 0;
zmin = 0;
zmax = 0;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetSave(Double_t *xx)
{
// Get value corresponding to X in array of fSave values
if (fNsave <= 0) return 0;
if (fSave == 0) return 0;
Float_t xmin = Float_t(fSave[fNsave+2]);
Float_t xmax = Float_t(fSave[fNsave+3]);
Float_t x = Float_t(xx[0]);
Float_t dx = (xmax-xmin)/fNsave;
if (x < xmin || x > xmax) return 0;
if (dx <= 0) return 0;
Int_t bin = Int_t((x-xmin)/dx);
Float_t xlow = xmin + bin*dx;
Float_t xup = xlow + dx;
Double_t ylow = fSave[bin];
Double_t yup = fSave[bin+1];
Double_t y = ((xup*ylow-xlow*yup) + x*(yup-ylow))/dx;
return y;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::InitArgs(Double_t *x, Double_t *params)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Initialize parameters addresses*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ===============================
if (fMethodCall) {
Long_t args[2];
args[0] = (Long_t)x;
if (params) args[1] = (Long_t)params;
else args[1] = (Long_t)fParams;
fMethodCall->SetParamPtrs(args);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::Integral(Float_t a, Float_t b, Double_t *params, Float_t epsilon)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return Integral of function between a and b*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//
// based on original CERNLIB routine DGAUSS by Sigfried Kolbig
// converted to C++ by Rene Brun
//
//
/*
This function computes, to an attempted specified accuracy, the value of the integral
![]()
Usage:
In any arithmetic expression, this function has the approximate value of the integral I.