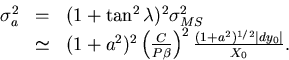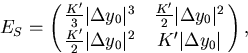

Next: Track Fitting with Multiple
Up: Track Fitting in r-z
Previous: Track Fitting in r-z
The parameter vector for a r-z track
has only two components (see Eq.3.1.1):
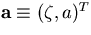 which transforms
as
which transforms
as
where
| 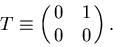 |
(82) |
As we did in the r-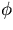 case, we set dz0=0.
Then, we have, in vacuum,
case, we set dz0=0.
Then, we have, in vacuum,
| 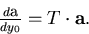 |
(83) |
The equation to transform the error matrix is then
| 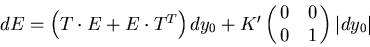 |
(84) |
with
| 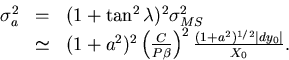 |
(85) |
The solution to this equation can be written in the form:
| 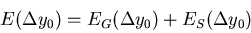 |
(86) |
where EG is the general solution for K'=0 and ES is a
special solution:
| 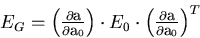 |
(87) |
with
| 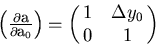 |
(88) |
and
| 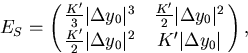 |
(89) |
where E0 is the error matrix at 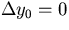 .Notice that the second term, which is due to multiple scattering,
must be dropped when one moves the pivot in the sensitive volume of
the tracker which gave E0, since the effect of multiple scattering
is presumably taken into account in E0.
For instance, if one wants to extrapolate the track in the increasing
y direction, one should first move the pivot to the outermost hit
with K'=0 and then use to above formulae.
.Notice that the second term, which is due to multiple scattering,
must be dropped when one moves the pivot in the sensitive volume of
the tracker which gave E0, since the effect of multiple scattering
is presumably taken into account in E0.
For instance, if one wants to extrapolate the track in the increasing
y direction, one should first move the pivot to the outermost hit
with K'=0 and then use to above formulae.


Next: Track Fitting with Multiple
Up: Track Fitting in r-z
Previous: Track Fitting in r-z
Keisuke Fujii
12/4/1998
![]() which transforms
as
which transforms
as