//____________________________________________________________________
//
/*
Principal Components Analysis (PCA)
The current implementation is based on the LINTRA package from CERNLIB
by R. Brun, H. Hansroul, and J. Kubler.
The class has been implemented by Christian Holm Christensen in August 2000.
Introduction
In many applications of various fields of research, the treatment of
large amounts of data requires powerful techniques capable of rapid
data reduction and analysis. Usually, the quantities most
conveniently measured by the experimentalist, are not necessarily the
most significant for classification and analysis of the data. It is
then useful to have a way of selecting an optimal set of variables
necessary for the recognition process and reducing the dimensionality
of the problem, resulting in an easier classification procedure.
This paper describes the implementation of one such method of
feature selection, namely the principal components analysis. This
multidimensional technique is well known in the field of pattern
recognition and and its use in Particle Physics has been documented
elsewhere (cf. H. Wind, Function Parameterization, CERN
72-21).
Overview
Suppose we have prototypes which are trajectories of particles,
passing through a spectrometer. If one measures the passage of the
particle at say 8 fixed planes, the trajectory is described by an
8-component vector:
in 8-dimensional pattern space.
One proceeds by generating a a representative tracks sample and
building up the covariance matrix 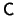 . Its eigenvectors and
eigenvalues are computed by standard methods, and thus a new basis is
obtained for the original 8-dimensional space the expansion of the
prototypes,
. Its eigenvectors and
eigenvalues are computed by standard methods, and thus a new basis is
obtained for the original 8-dimensional space the expansion of the
prototypes,
allows the study of the behavior of the coefficients  for all
the tracks of the sample. The eigenvectors which are insignificant for
the trajectory description in the expansion will have their
corresponding coefficients
for all
the tracks of the sample. The eigenvectors which are insignificant for
the trajectory description in the expansion will have their
corresponding coefficients  close to zero for all the
prototypes.
close to zero for all the
prototypes.
On one hand, a reduction of the dimensionality is then obtained by
omitting these least significant vectors in the subsequent analysis.
On the other hand, in the analysis of real data, these least
significant variables(?) can be used for the pattern
recognition problem of extracting the valid combinations of
coordinates describing a true trajectory from the set of all possible
wrong combinations.
The program described here performs this principal components analysis
on a sample of data provided by the user. It computes the covariance
matrix, its eigenvalues ands corresponding eigenvectors and exhibits
the behavior of the principal components ( ), thus providing
to the user all the means of understanding his data.
), thus providing
to the user all the means of understanding his data.
A short outline of the method of Principal Components is given in
subsection 1.3.
Principal Components Method
Let's consider a sample of 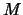 prototypes each being characterized by
prototypes each being characterized by
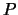 variables
variables
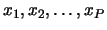 . Each prototype is a point, or a
column vector, in a
. Each prototype is a point, or a
column vector, in a 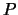 -dimensional pattern space.
-dimensional pattern space.
![\begin{displaymath}
\mathbf{x} = \left[\begin{array}{c}
x_0\\ x_1\\ \vdots\\ x_{P-1}\end{array}\right]\,,
\end{displaymath}](gif/principal_img8.gif) |
(1) |
where each 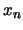 represents the particular value associated with the
represents the particular value associated with the
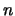 -dimension.
-dimension.
Those 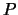 variables are the quantities accessible to the
experimentalist, but are not necessarily the most significant for the
classification purpose.
variables are the quantities accessible to the
experimentalist, but are not necessarily the most significant for the
classification purpose.
The Principal Components Method consists of applying a
linear transformation to the original variables. This
transformation is described by an orthogonal matrix and is equivalent
to a rotation of the original pattern space into a new set of
coordinate vectors, which hopefully provide easier feature
identification and dimensionality reduction.
Let's define the covariance matrix:
 |
(2) |
and the brackets indicate mean value over the sample of 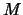 prototypes.
prototypes.
This matrix 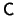 is real, positive definite, symmetric, and will
have all its eigenvalues greater then zero. It will now be show that
among the family of all the complete orthonormal bases of the pattern
space, the base formed by the eigenvectors of the covariance matrix
and belonging to the largest eigenvalues, corresponds to the most
significant features of the description of the original prototypes.
is real, positive definite, symmetric, and will
have all its eigenvalues greater then zero. It will now be show that
among the family of all the complete orthonormal bases of the pattern
space, the base formed by the eigenvectors of the covariance matrix
and belonging to the largest eigenvalues, corresponds to the most
significant features of the description of the original prototypes.
let the prototypes be expanded on into a set of 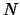 basis vectors
basis vectors
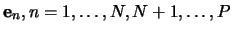 ,
,
 |
(3) |
The `best' feature coordinates 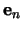 , spanning a feature
space, will be obtained by minimizing the error due to this
truncated expansion, i.e.,
, spanning a feature
space, will be obtained by minimizing the error due to this
truncated expansion, i.e.,
![\begin{displaymath}
\min\left(E_N\right) =
\min\left[\left\langle\left(\mathb...
...\sum^N_{i=0} a_{i_n} \mathbf{e}_n\right)^2\right\rangle\right]
\end{displaymath}](gif/principal_img16.gif) |
(4) |
with the conditions:
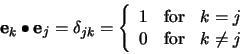 |
(5) |
Multiplying (3) by
 using (5),
we get
using (5),
we get
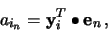 |
(6) |
so the error becomes
The minimization of the sum in (7) is obtained when each
term
 is minimum, since
is minimum, since 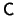 is
positive definite. By the method of Lagrange multipliers, and the
condition (5), we get
is
positive definite. By the method of Lagrange multipliers, and the
condition (5), we get
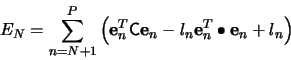 |
(8) |
The minimum condition
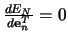 leads to the
equation
leads to the
equation
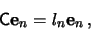 |
(9) |
which shows that 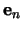 is an eigenvector of the covariance
matrix
is an eigenvector of the covariance
matrix 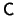 with eigenvalue
with eigenvalue  . The estimated minimum error is
then given by
. The estimated minimum error is
then given by
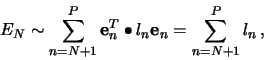 |
(10) |
where
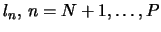 are the eigenvalues associated with the
omitted eigenvectors in the expansion (3). Thus, by choosing
the
are the eigenvalues associated with the
omitted eigenvectors in the expansion (3). Thus, by choosing
the 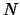 largest eigenvalues, and their associated eigenvectors, the
error
largest eigenvalues, and their associated eigenvectors, the
error 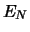 is minimized.
is minimized.
The transformation matrix to go from the pattern space to the feature
space consists of the ordered eigenvectors
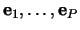 for its columns
for its columns
![\begin{displaymath}
\mathsf{T} = \left[
\begin{array}{cccc}
\mathbf{e}_0 &
\...
...bf{e}_{1_{P-1}} & \cdots & \mathbf{e}_{{P-1}_{P-1}}\\
\end{array}\right]
\end{displaymath}](gif/principal_img35.gif) |
(11) |
This is an orthogonal transformation, or rotation, of the pattern
space and feature selection results in ignoring certain coordinates
in the transformed space.
Christian Holm
August 2000, CERN
*/
//
// $Id: TPrincipal.cxx,v 1.23 2002/12/02 18:50:04 rdm Exp $
// $Date: 2002/12/02 18:50:04 $
// $Author: rdm $
#include "TPrincipal.h"
#include "TVectorD.h"
#include "TMatrixD.h"
#include "TList.h"
#include "TH2.h"
#include "TDatime.h"
#include "TBrowser.h"
#include "TROOT.h"
#include "Riostream.h"
ClassImp(TPrincipal);
//____________________________________________________________________
TPrincipal::TPrincipal()
{
// Empty CTOR, Do not use.
fHistograms = 0;
}
//____________________________________________________________________
TPrincipal::TPrincipal(Int_t nVariables, Option_t *opt)
: fMeanValues(nVariables),
fSigmas(nVariables),
fCovarianceMatrix(nVariables,nVariables),
fEigenVectors(nVariables,nVariables),
fEigenValues(nVariables),
fOffDiagonal(nVariables),
fStoreData(kFALSE)
{
// Ctor. Argument is number of variables in the sample of data
// Options are:
// N Normalize the covariance matrix (default)
// D Store input data (default)
//
// The created object is named "principal" by default.
if (nVariables <= 1) {
Error("TPrincipal", "You can't be serious - nVariables == 1!!!");
return;
}
SetName("principal");
fTrace = 0;
fHistograms = 0;
fIsNormalised = kFALSE;
fNumberOfDataPoints = 0;
fNumberOfVariables = nVariables;
while (strlen(opt) > 0) {
switch(*opt++) {
case 'N':
case 'n':
fIsNormalised = kTRUE;
break;
case 'D':
case 'd':
fStoreData = kTRUE;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
if (!fMeanValues.IsValid())
Error("TPrincipal","Couldn't create vector mean values");
if (!fSigmas.IsValid())
Error("TPrincipal","Couldn't create vector sigmas");
if (!fCovarianceMatrix.IsValid())
Error("TPrincipal","Couldn't create covariance matrix");
if (!fEigenVectors.IsValid())
Error("TPrincipal","Couldn't create eigenvector matrix");
if (!fEigenValues.IsValid())
Error("TPrincipal","Couldn't create eigenvalue vector");
if (!fOffDiagonal.IsValid())
Error("TPrincipal","Couldn't create offdiagonal vector");
if (fStoreData) {
fUserData.ResizeTo(nVariables*1000);
fUserData.Zero();
if (!fUserData.IsValid())
Error("TPrincipal","Couldn't create user data vector");
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
TPrincipal::~TPrincipal()
{
// destructor
if (fHistograms) {
fHistograms->Delete();
delete fHistograms;
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::AddRow(const Double_t *p)
{
//
/*
Add a data point and update the covariance matrix. The input
array must be fNumberOfVariables long.
The Covariance matrix and mean values of the input data is caculated
on the fly by the following equations:
since this is a really fast method, with no rounding errors (please
refer to CERN 72-21 pp. 54-106).
The data is stored internally in a TVectorD, in the following
way:
With 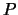 as defined in the class description.
*/
//
if (!p)
return;
// Increment the data point counter
Int_t i,j;
if (++fNumberOfDataPoints == 1) {
for (Int_t i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++)
fMeanValues(i) = p[i];
}
else {
Double_t cor = 1 - 1./Double_t(fNumberOfDataPoints);
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++) {
fMeanValues(i) *= cor;
fMeanValues(i) += p[i] / Double_t(fNumberOfDataPoints);
Double_t t1 = (p[i] - fMeanValues(i)) / (fNumberOfDataPoints - 1);
// Setting Matrix (lower triangle) elements
for (j = 0; j < i + 1; j++) {
fCovarianceMatrix(i,j) *= cor;
fCovarianceMatrix(i,j) += t1 * (p[j] - fMeanValues(j));
}
}
}
// Store data point in internal vector
// If the vector isn't big enough to hold the new data, then
// expand the vector by half it's size.
if (!fStoreData)
return;
Int_t size = fUserData.GetNrows();
if (fNumberOfDataPoints * fNumberOfVariables > size)
fUserData.ResizeTo(size + size/2);
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++) {
j = (fNumberOfDataPoints-1) * fNumberOfVariables + i;
fUserData(j) = p[i];
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::Browse(TBrowser *b)
{
// Browse the TPrincipal object in the TBrowser.
if (fHistograms) {
TIter next(fHistograms);
TH1* h = 0;
while ((h = (TH1*)next()))
b->Add(h,h->GetName());
}
if (fStoreData)
b->Add(&fUserData,"User Data");
b->Add(&fCovarianceMatrix,"Covariance Matrix");
b->Add(&fMeanValues,"Mean value vector");
b->Add(&fSigmas,"Sigma value vector");
b->Add(&fEigenValues,"Eigenvalue vector");
b->Add(&fEigenVectors,"Eigenvector Matrix");
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::Clear(Option_t *opt)
{
// Clear the data in Object. Notice, that's not possible to change
// the dimension of the original data.
if (fHistograms) {
fHistograms->Delete(opt);
}
fNumberOfDataPoints = 0;
fTrace = 0;
fCovarianceMatrix.Zero();
fEigenVectors.Zero();
fEigenValues.Zero();
fMeanValues.Zero();
fSigmas.Zero();
fOffDiagonal.Zero();
if (fStoreData) {
fUserData.ResizeTo(fNumberOfVariables * 1000);
fUserData.Zero();
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
const Double_t *TPrincipal::GetRow(Int_t row)
{
// Return a row of the user supplied data.
// If row is out of bounds, 0 is returned.
// It's up to the user to delete the returned array.
// Row 0 is the first row;
if (row >= fNumberOfDataPoints)
return 0;
if (!fStoreData)
return 0;
Int_t index = row * fNumberOfVariables;
return &fUserData(index);
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::MakeCode(const char *filename, Option_t *opt)
{
// Generates the file <filename>, with .C appended if it does
// argument doesn't end in .cxx or .C.
//
// The file contains the implementation of two functions
//
// void X2P(Double_t *x, Double *p)
// void P2X(Double_t *p, Double *x, Int_t nTest)
//
// which does the same as TPrincipal::X2P and TPrincipal::P2X
// respectively. Please refer to these methods.
//
// Further, the static variables:
//
// Int_t gNVariables
// Double_t gEigenValues[]
// Double_t gEigenVectors[]
// Double_t gMeanValues[]
// Double_t gSigmaValues[]
//
// are initialized. The only ROOT header file needed is Rtypes.h
//
// See TPrincipal::MakeRealCode for a list of options
TString outName(filename);
if (!outName.EndsWith(".C") && !outName.EndsWith(".cxx"))
outName += ".C";
MakeRealCode(outName.Data(),"",opt);
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::MakeHistograms(const char *name, Option_t *opt)
{
// Make histograms of the result of the analysis.
// The option string say which histograms to create
// X Histogram original data
// P Histogram principal components corresponding to
// original data
// D Histogram the difference between the original data
// and the projection of principal unto a lower
// dimensional subspace (2D histograms)
// E Histogram the eigenvalues
// S Histogram the square of the residues
// (see TPrincipal::SumOfSquareResidues)
// The histograms will be named <name>_<type><number>, where <name>
// is the first argument, <type> is one of X,P,D,E,S, and <number>
// is the variable.
Bool_t makeX = kFALSE;
Bool_t makeD = kFALSE;
Bool_t makeP = kFALSE;
Bool_t makeE = kFALSE;
Bool_t makeS = kFALSE;
Int_t len = strlen(opt);
Int_t i,j,k;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
switch (opt[i]) {
case 'X':
case 'x':
if (fStoreData)
makeX = kTRUE;
break;
case 'd':
case 'D':
if (fStoreData)
makeD = kTRUE;
break;
case 'P':
case 'p':
if (fStoreData)
makeP = kTRUE;
break;
case 'E':
case 'e':
makeE = kTRUE;
break;
case 's':
case 'S':
if (fStoreData)
makeS = kTRUE;
break;
default:
Warning("MakeHistograms","Unknown option: %c",opt[i]);
}
}
// If no option was given, then exit gracefully
if (!makeX && !makeD && !makeP && !makeE && !makeS)
return;
// If the list of histograms doesn't exist, create it.
if (!fHistograms)
fHistograms = new TList;
// Don't create the histograms if they are already in the TList.
if (makeX && fHistograms->FindObject(Form("%s_x000",name)))
makeX = kFALSE;
if (makeD && fHistograms->FindObject(Form("%s_d000",name)))
makeD = kFALSE;
if (makeP && fHistograms->FindObject(Form("%s_p000",name)))
makeP = kFALSE;
if (makeE && fHistograms->FindObject(Form("%s_e",name)))
makeE = kFALSE;
if (makeS && fHistograms->FindObject(Form("%s_s",name)))
makeS = kFALSE;
TH1F **hX = 0;
TH2F **hD = 0;
TH1F **hP = 0;
TH1F *hE = 0;
TH1F *hS = 0;
// Initialize the arrays of histograms needed
if (makeX)
hX = new TH1F * [fNumberOfVariables];
if (makeD)
hD = new TH2F * [fNumberOfVariables];
if (makeP)
hP = new TH1F * [fNumberOfVariables];
if (makeE){
hE = new TH1F(Form("%s_e",name), "Eigenvalues of Covariance matrix",
fNumberOfVariables,0,fNumberOfVariables);
hE->SetXTitle("Eigenvalue");
fHistograms->Add(hE);
}
if (makeS) {
hS = new TH1F(Form("%s_s",name),"E_{N}",
fNumberOfVariables-1,1,fNumberOfVariables);
hS->SetXTitle("N");
hS->SetYTitle("#sum_{i=1}^{M} (x_{i} - x'_{N,i})^{2}");
fHistograms->Add(hS);
}
// Initialize sub elements of the histogram arrays
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++) {
if (makeX) {
// We allow 4 sigma spread in the original data in our
// histogram.
Double_t xlowb = fMeanValues(i) - 4 * fSigmas(i);
Double_t xhighb = fMeanValues(i) + 4 * fSigmas(i);
Int_t xbins = fNumberOfDataPoints/100;
hX[i] = new TH1F(Form("%s_x%03d", name, i),
Form("Pattern space, variable %d", i),
xbins,xlowb,xhighb);
hX[i]->SetXTitle(Form("x_{%d}",i));
fHistograms->Add(hX[i]);
}
if(makeD) {
// The upper limit below is arbitrary!!!
Double_t dlowb = 0;
Double_t dhighb = 20;
Int_t dbins = fNumberOfDataPoints/100;
hD[i] = new TH2F(Form("%s_d%03d", name, i),
Form("Distance from pattern to "
"feature space, variable %d", i),
dbins,dlowb,dhighb,
fNumberOfVariables-1,
1,
fNumberOfVariables);
hD[i]->SetXTitle(Form("|x_{%d} - x'_{%d,N}|/#sigma_{%d}",i,i,i));
hD[i]->SetYTitle("N");
fHistograms->Add(hD[i]);
}
if(makeP) {
// For some reason, the trace of the none-scaled matrix
// (see TPrincipal::MakeNormalised) should enter here. Taken
// from LINTRA code.
Double_t plowb = -10 * TMath::Sqrt(fEigenValues(i) * fTrace);
Double_t phighb = -plowb;
Int_t pbins = 100;
hP[i] = new TH1F(Form("%s_p%03d", name, i),
Form("Feature space, variable %d", i),
pbins,plowb,phighb);
hX[i]->SetXTitle(Form("p_{%d}",i));
fHistograms->Add(hP[i]);
}
if (makeE)
// The Eigenvector histogram is easy
hE->Fill(i,fEigenValues(i));
}
if (!makeX && !makeP && !makeD && !makeS)
return;
Double_t *x = 0;
Double_t *p = new Double_t[fNumberOfVariables];
Double_t *d = new Double_t[fNumberOfVariables];
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfDataPoints; i++) {
// Zero arrays
for (j = 0; j < fNumberOfVariables; j++)
p[j] = d[j] = 0;
// update the original data histogram
x = (Double_t*)(GetRow(i));
if (makeP||makeD||makeS)
// calculate the corresponding principal component
X2P(x,p);
if (makeD || makeS) {
// Calculate the difference between the original data, and the
// same project onto principal components, and then to a lower
// dimensional sub-space
for (j = fNumberOfVariables; j > 0; j--) {
P2X(p,d,j);
for (k = 0; k < fNumberOfVariables; k++) {
// We use the absolute value of the difference!
d[k] = x[k] - d[k];
if (makeS)
hS->Fill(j,d[k]*d[k]);
if (makeD) {
d[k] = TMath::Abs(d[k]) / (fIsNormalised ? fSigmas(k) : 1);
(hD[k])->Fill(d[k],j);
}
}
}
}
if (makeX||makeP) {
// If we are asked to make any of these histograms, we have to
// go here
for (j = 0; j < fNumberOfVariables; j++) {
if (makeX)
(hX[j])->Fill(x[j]);
if (makeP)
(hP[j])->Fill(p[j]);
}
}
}
// Clean up
if (d)
delete [] d;
if (p)
delete [] p;
// Normalize the residues
if (makeS)
hS->Scale(Double_t(1.)/fNumberOfDataPoints);
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::MakeNormalised()
{
// PRIVATE METHOD: Normalize the covariance matrix
Int_t i,j;
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++) {
fSigmas(i) = TMath::Sqrt(fCovarianceMatrix(i,i));
if (fIsNormalised)
for (j = 0; j <= i; j++)
fCovarianceMatrix(i,j) /= (fSigmas(i) * fSigmas(j));
fTrace += fCovarianceMatrix(i,i);
}
// Fill remaining parts of matrix, and scale.
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++)
for (j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
fCovarianceMatrix(i,j) /= fTrace;
fCovarianceMatrix(j,i) = fCovarianceMatrix(i,j);
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::MakeMethods(const char *classname, Option_t *opt)
{
// Generate the file <classname>PCA.cxx which contains the
// implementation of two methods:
//
// void <classname>::X2P(Double_t *x, Double *p)
// void <classname>::P2X(Double_t *p, Double *x, Int_t nTest)
//
// which does the same as TPrincipal::X2P and TPrincipal::P2X
// respectivly. Please refer to these methods.
//
// Further, the public static members:
//
// Int_t <classname>::fgNVariables
// Double_t <classname>::fgEigenValues[]
// Double_t <classname>::fgEigenVectors[]
// Double_t <classname>::fgMeanValues[]
// Double_t <classname>::fgSigmaValues[]
//
// are initialized, and assumed to exist. The class declaration is
// assumed to be in <classname>.h and assumed to be provided by the
// user.
//
// See TPrincipal::MakeRealCode for a list of options
//
// The minimal class definition is:
//
// class <classname> {
// public:
// static Int_t fgNVariables;
// static Double_t fgEigenVectors[];
// static Double_t fgEigenValues[];
// static Double_t fgMeanValues[];
// static Double_t fgSigmaValues[];
//
// void X2P(Double_t *x, Double_t *p);
// void P2X(Double_t *p, Double_t *x, Int_t nTest);
// };
//
// Whether the methods <classname>::X2P and <classname>::P2X should
// be static or not, is up to the user.
MakeRealCode(Form("%sPCA.cxx", classname), classname, opt);
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::MakePrincipals()
{
// Perform the principal components analysis.
// This is done in several stages in the TMatrix::EigenVectors method:
// * Transform the covariance matrix into a tridiagonal matrix.
// * Find the eigenvalues and vectors of the tridiagonal matrix.
// Normalize matrix covariance matrix
MakeNormalised();
fEigenVectors= fCovarianceMatrix.EigenVectors(fEigenValues);
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::MakeRealCode(const char *filename, const char *classname,
Option_t *)
{
// PRIVATE METHOD:
// This is the method that actually generates the code for the
// transformations to and from feature space and pattern space
// It's called by TPrincipal::MakeCode and TPrincipal::MakeMethods.
//
// The options are: NONE so far
Bool_t isMethod = (classname[0] == '0' ? kFALSE : kTRUE);
const char *prefix = (isMethod ? Form("%s::", classname) : "");
const char *cv_qual = (isMethod ? "" : "static ");
ofstream outFile(filename,ios::out
if (!outFile) {
Error("MakeRealCode","couldn't open output file '%s'",filename);
return;
}
cout << "Writing on file "" << filename << "" ... " << flush;
//
// Write header of file
//
// Emacs mode line ;-)
outFile << "// -*- mode: c++ -*-" << endl;
// Info about creator
outFile << "// " << endl
<< "// File " << filename
<< " generated by TPrincipal::MakeCode" << endl;
// Time stamp
TDatime date;
outFile << "// on " << date.AsString() << endl;
// ROOT version info
outFile << "// ROOT version " << gROOT->GetVersion()
<< endl << "//" << endl;
// General information on the code
outFile << "// This file contains the functions " << endl
<< "//" << endl
<< "// void " << prefix
<< "X2P(Double_t *x, Double_t *p); " << endl
<< "// void " << prefix
<< "P2X(Double_t *p, Double_t *x, Int_t nTest);"
<< endl << "//" << endl
<< "// The first for transforming original data x in " << endl
<< "// pattern space, to principal components p in " << endl
<< "// feature space. The second function is for the" << endl
<< "// inverse transformation, but using only nTest" << endl
<< "// of the principal components in the expansion" << endl
<< "// " << endl
<< "// See TPrincipal class documentation for more "
<< "information " << endl << "// " << endl;
// Header files
outFile << "#ifndef __CINT__" << endl;
if (isMethod)
// If these are methods, we need the class header
outFile << "#include "" << classname << ".h"" << endl;
else
// otherwise, we need the typedefs of Int_t and Double_t
outFile << "#include <Rtypes.h> // needed for Double_t etc" << endl;
// Finish the preprocessor block
outFile << "#endif" << endl << endl;
//
// Now for the data
//
// We make the Eigenvector matrix, Eigenvalue vector, Sigma vector,
// and Mean value vector static, since all are needed in both
// functions. Also ,the number of variables are stored in a static
// variable.
outFile << "//" << endl
<< "// Static data variables" << endl
<< "//" << endl;
outFile << cv_qual << "Int_t " << prefix << "gNVariables = "
<< fNumberOfVariables << ";" << endl;
// Assign the values to the Eigenvector matrix. The elements are
// stored row-wise, that is element
// M[i][j] = e[i * nVariables + j]
// where i and j are zero-based.
outFile << endl << "// Assignment of eigenvector matrix." << endl
<< "// Elements are stored row-wise, that is" << endl
<< "// M[i][j] = e[i * nVariables + j] " << endl
<< "// where i and j are zero-based" << endl;
outFile << cv_qual << "Double_t " << prefix
<< "gEigenVectors[] = {" << flush;
Int_t i,j;
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < fNumberOfVariables; j++) {
Int_t index = i * fNumberOfVariables + j;
outFile << (index != 0 ? "," : "" ) << endl
<< " " << fEigenVectors(i,j) << flush;
}
}
outFile << "};" << endl << endl;
// Assignment to eigenvalue vector. Zero-based.
outFile << "// Assignment to eigen value vector. Zero-based." << endl;
outFile << cv_qual << "Double_t " << prefix
<< "gEigenValues[] = {" << flush;
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++)
outFile << (i != 0 ? "," : "") << endl
<< " " << fEigenValues(i) << flush;
outFile << endl << "};" << endl << endl;
// Assignment to mean Values vector. Zero-based.
outFile << "// Assignment to mean value vector. Zero-based." << endl;
outFile << cv_qual << "Double_t " << prefix
<< "gMeanValues[] = {" << flush;
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++)
outFile << (i != 0 ? "," : "") << endl
<< " " << fMeanValues(i) << flush;
outFile << endl << "};" << endl << endl;
// Assignment to mean Values vector. Zero-based.
outFile << "// Assignment to sigma value vector. Zero-based." << endl;
outFile << cv_qual << "Double_t " << prefix
<< "gSigmaValues[] = {" << flush;
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++)
outFile << (i != 0 ? "," : "") << endl
<< " " << (fIsNormalised ? fSigmas(i) : 1) << flush;
// << " " << fSigmas(i) << flush;
outFile << endl << "};" << endl << endl;
//
// Finally we reach the functions themselves
//
// First: void x2p(Double_t *x, Double_t *p);
//
outFile << "// " << endl
<< "// The "
<< (isMethod ? "method " : "function ")
<< " void " << prefix
<< "X2P(Double_t *x, Double_t *p)"
<< endl << "// " << endl;
outFile << "void " << prefix
<< "X2P(Double_t *x, Double_t *p) {" << endl
<< " for (Int_t i = 0; i < gNVariables; i++) {" << endl
<< " p[i] = 0;" << endl
<< " for (Int_t j = 0; j < gNVariables; j++)" << endl
<< " p[i] += (x[j] - gMeanValues[j]) " << endl
<< " * gEigenVectors[j * gNVariables + i] "
<< "/ gSigmaValues[j];" << endl << endl << " }"
<< endl << "}" << endl << endl;
//
// Now: void p2x(Double_t *p, Double_t *x, Int_t nTest);
//
outFile << "// " << endl << "// The "
<< (isMethod ? "method " : "function ")
<< " void " << prefix
<< "P2X(Double_t *p, Double_t *x, Int_t nTest)"
<< endl << "// " << endl;
outFile << "void " << prefix
<< "P2X(Double_t *p, Double_t *x, Int_t nTest) {" << endl
<< " for (Int_t i = 0; i < gNVariables; i++) {" << endl
<< " x[i] = gMeanValues[i];" << endl
<< " for (Int_t j = 0; j < nTest; j++)" << endl
<< " x[i] += p[j] * gSigmaValues[i] " << endl
<< " * gEigenVectors[i * gNVariables + j];" << endl
<< " }" << endl << "}" << endl << endl;
// EOF
outFile << "// EOF for " << filename << endl;
// Close the file
outFile.close();
cout << "done" << endl;
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::P2X(const Double_t *p, Double_t *x, Int_t nTest)
{
// Calculate x as a function of nTest of the most significant
// principal components p, and return it in x.
// It's the users responsibility to make sure that both x and p are
// of the right size (i.e., memory must be allocated for x).
for (Int_t i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++){
x[i] = fMeanValues(i);
for (Int_t j = 0; j < nTest; j++)
x[i] += p[j] * (fIsNormalised ? fSigmas(i) : 1)
* fEigenVectors(i,j);
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::Print(Option_t *opt) const
{
// Print the statistics
// Options are
// M Print mean values of original data
// S Print sigma values of original data
// E Print eigenvalues of covarinace matrix
// V Print eigenvectors of covarinace matrix
// Default is MSE
Bool_t printV = kFALSE;
Bool_t printM = kFALSE;
Bool_t printS = kFALSE;
Bool_t printE = kFALSE;
Int_t len = strlen(opt);
for (Int_t i = 0; i < len; i++) {
switch (opt[i]) {
case 'V':
case 'v':
printV = kTRUE;
break;
case 'M':
case 'm':
printM = kTRUE;
break;
case 'S':
case 's':
printS = kTRUE;
break;
case 'E':
case 'e':
printE = kTRUE;
break;
default:
Warning("Print", "Unknown option '%c'",opt[i]);
break;
}
}
if (printM||printS||printE) {
cout << " Variable # " << flush;
if (printM)
cout << "| Mean Value " << flush;
if (printS)
cout << "| Sigma " << flush;
if (printE)
cout << "| Eigenvalue" << flush;
cout << endl;
cout << "-------------" << flush;
if (printM)
cout << "+------------" << flush;
if (printS)
cout << "+------------" << flush;
if (printE)
cout << "+------------" << flush;
cout << endl;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++) {
#ifndef R__MACOSX
cout << setw(12) << i << " " << flush;
if (printM)
cout << "| " << setw(10) << setprecision(4)
<< fMeanValues(i) << " " << flush;
if (printS)
cout << "| " << setw(10) << setprecision(4)
<< fSigmas(i) << " " << flush;
if (printE)
cout << "| " << setw(10) << setprecision(4)
<< fEigenValues(i) << " " << flush;
#else
fprintf(stdout,"%d12 ",i);
fflush(stdout);
if (printM) {
fprintf(stdout,"| %g10.4 ",fMeanValues(i));
fflush(stdout);
}
if (printS) {
fprintf(stdout,"| %g10.4 ",fSigmas(i));
fflush(stdout);
}
if (printE) {
fprintf(stdout,"| %g10.4 ",fEigenValues(i));
fflush(stdout);
}
#endif
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
if(printV) {
for (Int_t i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++) {
cout << "Eigenvector # " << i << flush;
TVectorD v(fNumberOfVariables);
v = TMatrixDColumn(fEigenVectors,i);
v.Print();
}
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::SumOfSquareResiduals(const Double_t *x, Double_t *s)
{
// PRIVATE METHOD:
//
/*
Calculates the sum of the square residuals, that is
as defined in the class description.
*/
//
if (!p)
return;
// Increment the data point counter
Int_t i,j;
if (++fNumberOfDataPoints == 1) {
for (Int_t i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++)
fMeanValues(i) = p[i];
}
else {
Double_t cor = 1 - 1./Double_t(fNumberOfDataPoints);
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++) {
fMeanValues(i) *= cor;
fMeanValues(i) += p[i] / Double_t(fNumberOfDataPoints);
Double_t t1 = (p[i] - fMeanValues(i)) / (fNumberOfDataPoints - 1);
// Setting Matrix (lower triangle) elements
for (j = 0; j < i + 1; j++) {
fCovarianceMatrix(i,j) *= cor;
fCovarianceMatrix(i,j) += t1 * (p[j] - fMeanValues(j));
}
}
}
// Store data point in internal vector
// If the vector isn't big enough to hold the new data, then
// expand the vector by half it's size.
if (!fStoreData)
return;
Int_t size = fUserData.GetNrows();
if (fNumberOfDataPoints * fNumberOfVariables > size)
fUserData.ResizeTo(size + size/2);
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++) {
j = (fNumberOfDataPoints-1) * fNumberOfVariables + i;
fUserData(j) = p[i];
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::Browse(TBrowser *b)
{
// Browse the TPrincipal object in the TBrowser.
if (fHistograms) {
TIter next(fHistograms);
TH1* h = 0;
while ((h = (TH1*)next()))
b->Add(h,h->GetName());
}
if (fStoreData)
b->Add(&fUserData,"User Data");
b->Add(&fCovarianceMatrix,"Covariance Matrix");
b->Add(&fMeanValues,"Mean value vector");
b->Add(&fSigmas,"Sigma value vector");
b->Add(&fEigenValues,"Eigenvalue vector");
b->Add(&fEigenVectors,"Eigenvector Matrix");
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::Clear(Option_t *opt)
{
// Clear the data in Object. Notice, that's not possible to change
// the dimension of the original data.
if (fHistograms) {
fHistograms->Delete(opt);
}
fNumberOfDataPoints = 0;
fTrace = 0;
fCovarianceMatrix.Zero();
fEigenVectors.Zero();
fEigenValues.Zero();
fMeanValues.Zero();
fSigmas.Zero();
fOffDiagonal.Zero();
if (fStoreData) {
fUserData.ResizeTo(fNumberOfVariables * 1000);
fUserData.Zero();
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
const Double_t *TPrincipal::GetRow(Int_t row)
{
// Return a row of the user supplied data.
// If row is out of bounds, 0 is returned.
// It's up to the user to delete the returned array.
// Row 0 is the first row;
if (row >= fNumberOfDataPoints)
return 0;
if (!fStoreData)
return 0;
Int_t index = row * fNumberOfVariables;
return &fUserData(index);
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::MakeCode(const char *filename, Option_t *opt)
{
// Generates the file <filename>, with .C appended if it does
// argument doesn't end in .cxx or .C.
//
// The file contains the implementation of two functions
//
// void X2P(Double_t *x, Double *p)
// void P2X(Double_t *p, Double *x, Int_t nTest)
//
// which does the same as TPrincipal::X2P and TPrincipal::P2X
// respectively. Please refer to these methods.
//
// Further, the static variables:
//
// Int_t gNVariables
// Double_t gEigenValues[]
// Double_t gEigenVectors[]
// Double_t gMeanValues[]
// Double_t gSigmaValues[]
//
// are initialized. The only ROOT header file needed is Rtypes.h
//
// See TPrincipal::MakeRealCode for a list of options
TString outName(filename);
if (!outName.EndsWith(".C") && !outName.EndsWith(".cxx"))
outName += ".C";
MakeRealCode(outName.Data(),"",opt);
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::MakeHistograms(const char *name, Option_t *opt)
{
// Make histograms of the result of the analysis.
// The option string say which histograms to create
// X Histogram original data
// P Histogram principal components corresponding to
// original data
// D Histogram the difference between the original data
// and the projection of principal unto a lower
// dimensional subspace (2D histograms)
// E Histogram the eigenvalues
// S Histogram the square of the residues
// (see TPrincipal::SumOfSquareResidues)
// The histograms will be named <name>_<type><number>, where <name>
// is the first argument, <type> is one of X,P,D,E,S, and <number>
// is the variable.
Bool_t makeX = kFALSE;
Bool_t makeD = kFALSE;
Bool_t makeP = kFALSE;
Bool_t makeE = kFALSE;
Bool_t makeS = kFALSE;
Int_t len = strlen(opt);
Int_t i,j,k;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
switch (opt[i]) {
case 'X':
case 'x':
if (fStoreData)
makeX = kTRUE;
break;
case 'd':
case 'D':
if (fStoreData)
makeD = kTRUE;
break;
case 'P':
case 'p':
if (fStoreData)
makeP = kTRUE;
break;
case 'E':
case 'e':
makeE = kTRUE;
break;
case 's':
case 'S':
if (fStoreData)
makeS = kTRUE;
break;
default:
Warning("MakeHistograms","Unknown option: %c",opt[i]);
}
}
// If no option was given, then exit gracefully
if (!makeX && !makeD && !makeP && !makeE && !makeS)
return;
// If the list of histograms doesn't exist, create it.
if (!fHistograms)
fHistograms = new TList;
// Don't create the histograms if they are already in the TList.
if (makeX && fHistograms->FindObject(Form("%s_x000",name)))
makeX = kFALSE;
if (makeD && fHistograms->FindObject(Form("%s_d000",name)))
makeD = kFALSE;
if (makeP && fHistograms->FindObject(Form("%s_p000",name)))
makeP = kFALSE;
if (makeE && fHistograms->FindObject(Form("%s_e",name)))
makeE = kFALSE;
if (makeS && fHistograms->FindObject(Form("%s_s",name)))
makeS = kFALSE;
TH1F **hX = 0;
TH2F **hD = 0;
TH1F **hP = 0;
TH1F *hE = 0;
TH1F *hS = 0;
// Initialize the arrays of histograms needed
if (makeX)
hX = new TH1F * [fNumberOfVariables];
if (makeD)
hD = new TH2F * [fNumberOfVariables];
if (makeP)
hP = new TH1F * [fNumberOfVariables];
if (makeE){
hE = new TH1F(Form("%s_e",name), "Eigenvalues of Covariance matrix",
fNumberOfVariables,0,fNumberOfVariables);
hE->SetXTitle("Eigenvalue");
fHistograms->Add(hE);
}
if (makeS) {
hS = new TH1F(Form("%s_s",name),"E_{N}",
fNumberOfVariables-1,1,fNumberOfVariables);
hS->SetXTitle("N");
hS->SetYTitle("#sum_{i=1}^{M} (x_{i} - x'_{N,i})^{2}");
fHistograms->Add(hS);
}
// Initialize sub elements of the histogram arrays
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++) {
if (makeX) {
// We allow 4 sigma spread in the original data in our
// histogram.
Double_t xlowb = fMeanValues(i) - 4 * fSigmas(i);
Double_t xhighb = fMeanValues(i) + 4 * fSigmas(i);
Int_t xbins = fNumberOfDataPoints/100;
hX[i] = new TH1F(Form("%s_x%03d", name, i),
Form("Pattern space, variable %d", i),
xbins,xlowb,xhighb);
hX[i]->SetXTitle(Form("x_{%d}",i));
fHistograms->Add(hX[i]);
}
if(makeD) {
// The upper limit below is arbitrary!!!
Double_t dlowb = 0;
Double_t dhighb = 20;
Int_t dbins = fNumberOfDataPoints/100;
hD[i] = new TH2F(Form("%s_d%03d", name, i),
Form("Distance from pattern to "
"feature space, variable %d", i),
dbins,dlowb,dhighb,
fNumberOfVariables-1,
1,
fNumberOfVariables);
hD[i]->SetXTitle(Form("|x_{%d} - x'_{%d,N}|/#sigma_{%d}",i,i,i));
hD[i]->SetYTitle("N");
fHistograms->Add(hD[i]);
}
if(makeP) {
// For some reason, the trace of the none-scaled matrix
// (see TPrincipal::MakeNormalised) should enter here. Taken
// from LINTRA code.
Double_t plowb = -10 * TMath::Sqrt(fEigenValues(i) * fTrace);
Double_t phighb = -plowb;
Int_t pbins = 100;
hP[i] = new TH1F(Form("%s_p%03d", name, i),
Form("Feature space, variable %d", i),
pbins,plowb,phighb);
hX[i]->SetXTitle(Form("p_{%d}",i));
fHistograms->Add(hP[i]);
}
if (makeE)
// The Eigenvector histogram is easy
hE->Fill(i,fEigenValues(i));
}
if (!makeX && !makeP && !makeD && !makeS)
return;
Double_t *x = 0;
Double_t *p = new Double_t[fNumberOfVariables];
Double_t *d = new Double_t[fNumberOfVariables];
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfDataPoints; i++) {
// Zero arrays
for (j = 0; j < fNumberOfVariables; j++)
p[j] = d[j] = 0;
// update the original data histogram
x = (Double_t*)(GetRow(i));
if (makeP||makeD||makeS)
// calculate the corresponding principal component
X2P(x,p);
if (makeD || makeS) {
// Calculate the difference between the original data, and the
// same project onto principal components, and then to a lower
// dimensional sub-space
for (j = fNumberOfVariables; j > 0; j--) {
P2X(p,d,j);
for (k = 0; k < fNumberOfVariables; k++) {
// We use the absolute value of the difference!
d[k] = x[k] - d[k];
if (makeS)
hS->Fill(j,d[k]*d[k]);
if (makeD) {
d[k] = TMath::Abs(d[k]) / (fIsNormalised ? fSigmas(k) : 1);
(hD[k])->Fill(d[k],j);
}
}
}
}
if (makeX||makeP) {
// If we are asked to make any of these histograms, we have to
// go here
for (j = 0; j < fNumberOfVariables; j++) {
if (makeX)
(hX[j])->Fill(x[j]);
if (makeP)
(hP[j])->Fill(p[j]);
}
}
}
// Clean up
if (d)
delete [] d;
if (p)
delete [] p;
// Normalize the residues
if (makeS)
hS->Scale(Double_t(1.)/fNumberOfDataPoints);
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::MakeNormalised()
{
// PRIVATE METHOD: Normalize the covariance matrix
Int_t i,j;
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++) {
fSigmas(i) = TMath::Sqrt(fCovarianceMatrix(i,i));
if (fIsNormalised)
for (j = 0; j <= i; j++)
fCovarianceMatrix(i,j) /= (fSigmas(i) * fSigmas(j));
fTrace += fCovarianceMatrix(i,i);
}
// Fill remaining parts of matrix, and scale.
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++)
for (j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
fCovarianceMatrix(i,j) /= fTrace;
fCovarianceMatrix(j,i) = fCovarianceMatrix(i,j);
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::MakeMethods(const char *classname, Option_t *opt)
{
// Generate the file <classname>PCA.cxx which contains the
// implementation of two methods:
//
// void <classname>::X2P(Double_t *x, Double *p)
// void <classname>::P2X(Double_t *p, Double *x, Int_t nTest)
//
// which does the same as TPrincipal::X2P and TPrincipal::P2X
// respectivly. Please refer to these methods.
//
// Further, the public static members:
//
// Int_t <classname>::fgNVariables
// Double_t <classname>::fgEigenValues[]
// Double_t <classname>::fgEigenVectors[]
// Double_t <classname>::fgMeanValues[]
// Double_t <classname>::fgSigmaValues[]
//
// are initialized, and assumed to exist. The class declaration is
// assumed to be in <classname>.h and assumed to be provided by the
// user.
//
// See TPrincipal::MakeRealCode for a list of options
//
// The minimal class definition is:
//
// class <classname> {
// public:
// static Int_t fgNVariables;
// static Double_t fgEigenVectors[];
// static Double_t fgEigenValues[];
// static Double_t fgMeanValues[];
// static Double_t fgSigmaValues[];
//
// void X2P(Double_t *x, Double_t *p);
// void P2X(Double_t *p, Double_t *x, Int_t nTest);
// };
//
// Whether the methods <classname>::X2P and <classname>::P2X should
// be static or not, is up to the user.
MakeRealCode(Form("%sPCA.cxx", classname), classname, opt);
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::MakePrincipals()
{
// Perform the principal components analysis.
// This is done in several stages in the TMatrix::EigenVectors method:
// * Transform the covariance matrix into a tridiagonal matrix.
// * Find the eigenvalues and vectors of the tridiagonal matrix.
// Normalize matrix covariance matrix
MakeNormalised();
fEigenVectors= fCovarianceMatrix.EigenVectors(fEigenValues);
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::MakeRealCode(const char *filename, const char *classname,
Option_t *)
{
// PRIVATE METHOD:
// This is the method that actually generates the code for the
// transformations to and from feature space and pattern space
// It's called by TPrincipal::MakeCode and TPrincipal::MakeMethods.
//
// The options are: NONE so far
Bool_t isMethod = (classname[0] == '0' ? kFALSE : kTRUE);
const char *prefix = (isMethod ? Form("%s::", classname) : "");
const char *cv_qual = (isMethod ? "" : "static ");
ofstream outFile(filename,ios::out
if (!outFile) {
Error("MakeRealCode","couldn't open output file '%s'",filename);
return;
}
cout << "Writing on file "" << filename << "" ... " << flush;
//
// Write header of file
//
// Emacs mode line ;-)
outFile << "// -*- mode: c++ -*-" << endl;
// Info about creator
outFile << "// " << endl
<< "// File " << filename
<< " generated by TPrincipal::MakeCode" << endl;
// Time stamp
TDatime date;
outFile << "// on " << date.AsString() << endl;
// ROOT version info
outFile << "// ROOT version " << gROOT->GetVersion()
<< endl << "//" << endl;
// General information on the code
outFile << "// This file contains the functions " << endl
<< "//" << endl
<< "// void " << prefix
<< "X2P(Double_t *x, Double_t *p); " << endl
<< "// void " << prefix
<< "P2X(Double_t *p, Double_t *x, Int_t nTest);"
<< endl << "//" << endl
<< "// The first for transforming original data x in " << endl
<< "// pattern space, to principal components p in " << endl
<< "// feature space. The second function is for the" << endl
<< "// inverse transformation, but using only nTest" << endl
<< "// of the principal components in the expansion" << endl
<< "// " << endl
<< "// See TPrincipal class documentation for more "
<< "information " << endl << "// " << endl;
// Header files
outFile << "#ifndef __CINT__" << endl;
if (isMethod)
// If these are methods, we need the class header
outFile << "#include "" << classname << ".h"" << endl;
else
// otherwise, we need the typedefs of Int_t and Double_t
outFile << "#include <Rtypes.h> // needed for Double_t etc" << endl;
// Finish the preprocessor block
outFile << "#endif" << endl << endl;
//
// Now for the data
//
// We make the Eigenvector matrix, Eigenvalue vector, Sigma vector,
// and Mean value vector static, since all are needed in both
// functions. Also ,the number of variables are stored in a static
// variable.
outFile << "//" << endl
<< "// Static data variables" << endl
<< "//" << endl;
outFile << cv_qual << "Int_t " << prefix << "gNVariables = "
<< fNumberOfVariables << ";" << endl;
// Assign the values to the Eigenvector matrix. The elements are
// stored row-wise, that is element
// M[i][j] = e[i * nVariables + j]
// where i and j are zero-based.
outFile << endl << "// Assignment of eigenvector matrix." << endl
<< "// Elements are stored row-wise, that is" << endl
<< "// M[i][j] = e[i * nVariables + j] " << endl
<< "// where i and j are zero-based" << endl;
outFile << cv_qual << "Double_t " << prefix
<< "gEigenVectors[] = {" << flush;
Int_t i,j;
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < fNumberOfVariables; j++) {
Int_t index = i * fNumberOfVariables + j;
outFile << (index != 0 ? "," : "" ) << endl
<< " " << fEigenVectors(i,j) << flush;
}
}
outFile << "};" << endl << endl;
// Assignment to eigenvalue vector. Zero-based.
outFile << "// Assignment to eigen value vector. Zero-based." << endl;
outFile << cv_qual << "Double_t " << prefix
<< "gEigenValues[] = {" << flush;
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++)
outFile << (i != 0 ? "," : "") << endl
<< " " << fEigenValues(i) << flush;
outFile << endl << "};" << endl << endl;
// Assignment to mean Values vector. Zero-based.
outFile << "// Assignment to mean value vector. Zero-based." << endl;
outFile << cv_qual << "Double_t " << prefix
<< "gMeanValues[] = {" << flush;
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++)
outFile << (i != 0 ? "," : "") << endl
<< " " << fMeanValues(i) << flush;
outFile << endl << "};" << endl << endl;
// Assignment to mean Values vector. Zero-based.
outFile << "// Assignment to sigma value vector. Zero-based." << endl;
outFile << cv_qual << "Double_t " << prefix
<< "gSigmaValues[] = {" << flush;
for (i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++)
outFile << (i != 0 ? "," : "") << endl
<< " " << (fIsNormalised ? fSigmas(i) : 1) << flush;
// << " " << fSigmas(i) << flush;
outFile << endl << "};" << endl << endl;
//
// Finally we reach the functions themselves
//
// First: void x2p(Double_t *x, Double_t *p);
//
outFile << "// " << endl
<< "// The "
<< (isMethod ? "method " : "function ")
<< " void " << prefix
<< "X2P(Double_t *x, Double_t *p)"
<< endl << "// " << endl;
outFile << "void " << prefix
<< "X2P(Double_t *x, Double_t *p) {" << endl
<< " for (Int_t i = 0; i < gNVariables; i++) {" << endl
<< " p[i] = 0;" << endl
<< " for (Int_t j = 0; j < gNVariables; j++)" << endl
<< " p[i] += (x[j] - gMeanValues[j]) " << endl
<< " * gEigenVectors[j * gNVariables + i] "
<< "/ gSigmaValues[j];" << endl << endl << " }"
<< endl << "}" << endl << endl;
//
// Now: void p2x(Double_t *p, Double_t *x, Int_t nTest);
//
outFile << "// " << endl << "// The "
<< (isMethod ? "method " : "function ")
<< " void " << prefix
<< "P2X(Double_t *p, Double_t *x, Int_t nTest)"
<< endl << "// " << endl;
outFile << "void " << prefix
<< "P2X(Double_t *p, Double_t *x, Int_t nTest) {" << endl
<< " for (Int_t i = 0; i < gNVariables; i++) {" << endl
<< " x[i] = gMeanValues[i];" << endl
<< " for (Int_t j = 0; j < nTest; j++)" << endl
<< " x[i] += p[j] * gSigmaValues[i] " << endl
<< " * gEigenVectors[i * gNVariables + j];" << endl
<< " }" << endl << "}" << endl << endl;
// EOF
outFile << "// EOF for " << filename << endl;
// Close the file
outFile.close();
cout << "done" << endl;
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::P2X(const Double_t *p, Double_t *x, Int_t nTest)
{
// Calculate x as a function of nTest of the most significant
// principal components p, and return it in x.
// It's the users responsibility to make sure that both x and p are
// of the right size (i.e., memory must be allocated for x).
for (Int_t i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++){
x[i] = fMeanValues(i);
for (Int_t j = 0; j < nTest; j++)
x[i] += p[j] * (fIsNormalised ? fSigmas(i) : 1)
* fEigenVectors(i,j);
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::Print(Option_t *opt) const
{
// Print the statistics
// Options are
// M Print mean values of original data
// S Print sigma values of original data
// E Print eigenvalues of covarinace matrix
// V Print eigenvectors of covarinace matrix
// Default is MSE
Bool_t printV = kFALSE;
Bool_t printM = kFALSE;
Bool_t printS = kFALSE;
Bool_t printE = kFALSE;
Int_t len = strlen(opt);
for (Int_t i = 0; i < len; i++) {
switch (opt[i]) {
case 'V':
case 'v':
printV = kTRUE;
break;
case 'M':
case 'm':
printM = kTRUE;
break;
case 'S':
case 's':
printS = kTRUE;
break;
case 'E':
case 'e':
printE = kTRUE;
break;
default:
Warning("Print", "Unknown option '%c'",opt[i]);
break;
}
}
if (printM||printS||printE) {
cout << " Variable # " << flush;
if (printM)
cout << "| Mean Value " << flush;
if (printS)
cout << "| Sigma " << flush;
if (printE)
cout << "| Eigenvalue" << flush;
cout << endl;
cout << "-------------" << flush;
if (printM)
cout << "+------------" << flush;
if (printS)
cout << "+------------" << flush;
if (printE)
cout << "+------------" << flush;
cout << endl;
for (Int_t i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++) {
#ifndef R__MACOSX
cout << setw(12) << i << " " << flush;
if (printM)
cout << "| " << setw(10) << setprecision(4)
<< fMeanValues(i) << " " << flush;
if (printS)
cout << "| " << setw(10) << setprecision(4)
<< fSigmas(i) << " " << flush;
if (printE)
cout << "| " << setw(10) << setprecision(4)
<< fEigenValues(i) << " " << flush;
#else
fprintf(stdout,"%d12 ",i);
fflush(stdout);
if (printM) {
fprintf(stdout,"| %g10.4 ",fMeanValues(i));
fflush(stdout);
}
if (printS) {
fprintf(stdout,"| %g10.4 ",fSigmas(i));
fflush(stdout);
}
if (printE) {
fprintf(stdout,"| %g10.4 ",fEigenValues(i));
fflush(stdout);
}
#endif
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
if(printV) {
for (Int_t i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++) {
cout << "Eigenvector # " << i << flush;
TVectorD v(fNumberOfVariables);
v = TMatrixDColumn(fEigenVectors,i);
v.Print();
}
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::SumOfSquareResiduals(const Double_t *x, Double_t *s)
{
// PRIVATE METHOD:
//
/*
Calculates the sum of the square residuals, that is
where
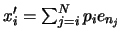 ,
, 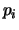 is the
is the
 component of the principal vector, corresponding to
component of the principal vector, corresponding to
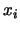 , the original data; I.e., the square distance to the space
spanned by
, the original data; I.e., the square distance to the space
spanned by 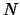 eigenvectors.
eigenvectors.
*/
//
if (!x)
return;
Double_t p[100];
Double_t xp[100];
X2P(x,p);
for (Int_t i = fNumberOfVariables-1; i >= 0; i--) {
P2X(p,xp,i);
for (Int_t j = 0; j < fNumberOfVariables; j++) {
s[i] += (x[j] - xp[j])*(x[j] - xp[j]);
}
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::Test(Option_t *)
{
// Test the PCA, bye calculating the sum square of residuals
// (see method SumOfSquareResiduals), and display the histogram
MakeHistograms("pca","S");
if (!fStoreData)
return;
TH1 *pca_s = 0;
if (fHistograms) pca_s = (TH1*)fHistograms->FindObject("pca_s");
if (!pca_s) {
Warning("Test", "Couldn't get histogram of square residuals");
return;
}
pca_s->Draw();
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TPrincipal::X2P(const Double_t *x, Double_t *p)
{
// Calculate the principal components from the original data vector
// x, and return it in p.
// It's the users responsibility to make sure that both x and p are
// of the right size (i.e., memory must be allocated for p).
for (Int_t i = 0; i < fNumberOfVariables; i++){
p[i] = 0;
for (Int_t j = 0; j < fNumberOfVariables; j++)
p[i] += (x[j] - fMeanValues(j)) * fEigenVectors(j,i) /
(fIsNormalised ? fSigmas(j) : 1);
}
}
ROOT page - Class index - Top of the page
This page has been automatically generated. If you have any comments or suggestions about the page layout send a mail to ROOT support, or contact the developers with any questions or problems regarding ROOT.
![]() . Its eigenvectors and
eigenvalues are computed by standard methods, and thus a new basis is
obtained for the original 8-dimensional space the expansion of the
prototypes,
. Its eigenvectors and
eigenvalues are computed by standard methods, and thus a new basis is
obtained for the original 8-dimensional space the expansion of the
prototypes,

![]() for all
the tracks of the sample. The eigenvectors which are insignificant for
the trajectory description in the expansion will have their
corresponding coefficients
for all
the tracks of the sample. The eigenvectors which are insignificant for
the trajectory description in the expansion will have their
corresponding coefficients ![]() close to zero for all the
prototypes.
close to zero for all the
prototypes.
![]() ), thus providing
to the user all the means of understanding his data.
), thus providing
to the user all the means of understanding his data.
![]() prototypes each being characterized by
prototypes each being characterized by
![]() variables
variables
![]() . Each prototype is a point, or a
column vector, in a
. Each prototype is a point, or a
column vector, in a ![]() -dimensional pattern space.
-dimensional pattern space.
![\begin{displaymath}
\mathbf{x} = \left[\begin{array}{c}
x_0\\ x_1\\ \vdots\\ x_{P-1}\end{array}\right]\,,
\end{displaymath}](gif/principal_img8.gif)
![]() variables are the quantities accessible to the
experimentalist, but are not necessarily the most significant for the
classification purpose.
variables are the quantities accessible to the
experimentalist, but are not necessarily the most significant for the
classification purpose.
![]() is real, positive definite, symmetric, and will
have all its eigenvalues greater then zero. It will now be show that
among the family of all the complete orthonormal bases of the pattern
space, the base formed by the eigenvectors of the covariance matrix
and belonging to the largest eigenvalues, corresponds to the most
significant features of the description of the original prototypes.
is real, positive definite, symmetric, and will
have all its eigenvalues greater then zero. It will now be show that
among the family of all the complete orthonormal bases of the pattern
space, the base formed by the eigenvectors of the covariance matrix
and belonging to the largest eigenvalues, corresponds to the most
significant features of the description of the original prototypes.
![]() basis vectors
basis vectors
![]() ,
,
![]() , spanning a feature
space, will be obtained by minimizing the error due to this
truncated expansion, i.e.,
, spanning a feature
space, will be obtained by minimizing the error due to this
truncated expansion, i.e.,
![]() using (5),
we get
using (5),
we get
![]() is minimum, since
is minimum, since ![]() is
positive definite. By the method of Lagrange multipliers, and the
condition (5), we get
is
positive definite. By the method of Lagrange multipliers, and the
condition (5), we get
![]() for its columns
for its columns


![\begin{displaymath}
\min\left(E_N\right) =
\min\left[\left\langle\left(\mathb...
...\sum^N_{i=0} a_{i_n} \mathbf{e}_n\right)^2\right\rangle\right]
\end{displaymath}](gif/principal_img16.gif)
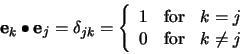
![$\displaystyle \left\langle\left[\sum_{n=N+1}^{P-1} a_{i_n}\mathbf{e}_n\right]^2\right\rangle$](gif/principal_img22.gif)
![$\displaystyle \left\langle\left[\sum_{n=N+1}^{P-1} \mathbf{y}_i^T\bullet\mathbf{e}_n\mathbf{e}_n\right]^2\right\rangle$](gif/principal_img23.gif)


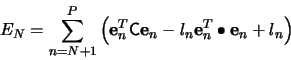
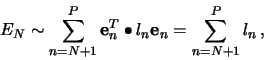
![\begin{displaymath}
\mathsf{T} = \left[
\begin{array}{cccc}
\mathbf{e}_0 &
\...
...bf{e}_{1_{P-1}} & \cdots & \mathbf{e}_{{P-1}_{P-1}}\\
\end{array}\right]
\end{displaymath}](gif/principal_img35.gif)