// @(#)root/matrix:$Name: $:$Id: TMatrix.cxx,v 1.39 2003/05/07 17:52:27 brun Exp $
// Author: Fons Rademakers 03/11/97
/*************************************************************************
* Copyright (C) 1995-2000, Rene Brun and Fons Rademakers. *
* All rights reserved. *
* *
* For the licensing terms see $ROOTSYS/LICENSE. *
* For the list of contributors see $ROOTSYS/README/CREDITS. *
*************************************************************************/
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// //
// Linear Algebra Package //
// //
// The present package implements all the basic algorithms dealing //
// with vectors, matrices, matrix columns, rows, diagonals, etc. //
// //
// Matrix elements are arranged in memory in a COLUMN-wise //
// fashion (in FORTRAN's spirit). In fact, it makes it very easy to //
// feed the matrices to FORTRAN procedures, which implement more //
// elaborate algorithms. //
// //
// Unless otherwise specified, matrix and vector indices always start //
// with 0, spanning up to the specified limit-1. However, there are //
// constructors to which one can specify aribtrary lower and upper //
// bounds, e.g. TMatrix m(1,10,1,5) defines a matrix that ranges, and //
// that can be addresses, from 1..10, 1..5 (a(1,1)..a(10,5)). //
// //
// The present package provides all facilities to completely AVOID //
// returning matrices. Use "TMatrix A(TMatrix::kTransposed,B);" and //
// other fancy constructors as much as possible. If one really needs //
// to return a matrix, return a TLazyMatrix object instead. The //
// conversion is completely transparent to the end user, e.g. //
// "TMatrix m = THaarMatrix(5);" and _is_ efficient. //
// //
// Since TMatrix et al. are fully integrated in ROOT they of course //
// can be stored in a ROOT database. //
// //
// //
// How to efficiently use this package //
// ----------------------------------- //
// //
// 1. Never return complex objects (matrices or vectors) //
// Danger: For example, when the following snippet: //
// TMatrix foo(int n) //
// { //
// TMatrix foom(n,n); fill_in(foom); return foom; //
// } //
// TMatrix m = foo(5); //
// runs, it constructs matrix foo:foom, copies it onto stack as a //
// return value and destroys foo:foom. Return value (a matrix) //
// from foo() is then copied over to m (via a copy constructor), //
// and the return value is destroyed. So, the matrix constructor is //
// called 3 times and the destructor 2 times. For big matrices, //
// the cost of multiple constructing/copying/destroying of objects //
// may be very large. *Some* optimized compilers can cut down on 1 //
// copying/destroying, but still it leaves at least two calls to //
// the constructor. Note, TLazyMatrices (see below) can construct //
// TMatrix m "inplace", with only a _single_ call to the //
// constructor. //
// //
// 2. Use "two-address instructions" //
// "void TMatrix::operator += (const TMatrix &B);" //
// as much as possible. //
// That is, to add two matrices, it's much more efficient to write //
// A += B; //
// than //
// TMatrix C = A + B; //
// (if both operand should be preserved, //
// TMatrix C = A; C += B; //
// is still better). //
// //
// 3. Use glorified constructors when returning of an object seems //
// inevitable: //
// "TMatrix A(TMatrix::kTransposed,B);" //
// "TMatrix C(A,TMatrix::kTransposeMult,B);" //
// //
// like in the following snippet (from $ROOTSYS/test/vmatrix.cxx) //
// that verifies that for an orthogonal matrix T, T'T = TT' = E. //
// //
// TMatrix haar = THaarMatrix(5); //
// TMatrix unit(TMatrix::kUnit,haar); //
// TMatrix haar_t(TMatrix::kTransposed,haar); //
// TMatrix hth(haar,TMatrix::kTransposeMult,haar); //
// TMatrix hht(haar,TMatrix::kMult,haar_t); //
// TMatrix hht1 = haar; hht1 *= haar_t; //
// VerifyMatrixIdentity(unit,hth); //
// VerifyMatrixIdentity(unit,hht); //
// VerifyMatrixIdentity(unit,hht1); //
// //
// 4. Accessing row/col/diagonal of a matrix without much fuss //
// (and without moving a lot of stuff around): //
// //
// TMatrix m(n,n); TVector v(n); TMatrixDiag(m) += 4; //
// v = TMatrixRow(m,0); //
// TMatrixColumn m1(m,1); m1(2) = 3; // the same as m(2,1)=3; //
// Note, constructing of, say, TMatrixDiag does *not* involve any //
// copying of any elements of the source matrix. //
// //
// 5. It's possible (and encouraged) to use "nested" functions //
// For example, creating of a Hilbert matrix can be done as follows: //
// //
// void foo(const TMatrix &m) //
// { //
// TMatrix m1(TMatrix::kZero,m); //
// struct MakeHilbert : public TElementPosAction { //
// void Operation(Real_t &element) { element = 1./(fI+fJ-1); } //
// }; //
// m1.Apply(MakeHilbert()); //
// } //
// //
// of course, using a special method THilbertMatrix() is //
// still more optimal, but not by a whole lot. And that's right, //
// class MakeHilbert is declared *within* a function and local to //
// that function. It means one can define another MakeHilbert class //
// (within another function or outside of any function, that is, in //
// the global scope), and it still will be OK. Note, this currently //
// is not yet supported by the interpreter CINT. //
// //
// Another example is applying of a simple function to each matrix //
// element: //
// //
// void foo(TMatrix &m, TMatrix &m1) //
// { //
// typedef double (*dfunc_t)(double); //
// class ApplyFunction : public TElementAction { //
// dfunc_t fFunc; //
// void Operation(Real_t &element) { element=fFunc(element); } //
// public: //
// ApplyFunction(dfunc_t func):fFunc(func) {} //
// }; //
// ApplyFunction x(TMath::Sin); //
// m.Apply(x); //
// } //
// //
// Validation code $ROOTSYS/test/vmatrix.cxx and vvector.cxx contain //
// a few more examples of that kind. //
// //
// 6. Lazy matrices: instead of returning an object return a "recipe" //
// how to make it. The full matrix would be rolled out only when //
// and where it's needed: //
// TMatrix haar = THaarMatrix(5); //
// THaarMatrix() is a *class*, not a simple function. However //
// similar this looks to a returning of an object (see note #1 //
// above), it's dramatically different. THaarMatrix() constructs a //
// TLazyMatrix, an object of just a few bytes long. A
// "TMatrix(const TLazyMatrix &recipe)" constructor follows the //
// recipe and makes the matrix haar() right in place. No matrix //
// element is moved whatsoever! //
// //
// The implementation is based on original code by //
// Oleg E. Kiselyov (oleg@pobox.com). //
// //
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include "TMatrix.h"
#include "TROOT.h"
#include "TClass.h"
#include "TPluginManager.h"
#include "TVirtualUtilHist.h"
ClassImp(TMatrix)
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::Allocate(Int_t no_rows, Int_t no_cols, Int_t row_lwb, Int_t col_lwb)
{
// Allocate new matrix. Arguments are number of rows, columns, row
// lowerbound (0 default) and column lowerbound (0 default).
Invalidate();
if (no_rows <= 0) {
Error("Allocate", "no of rows has to be positive");
return;
}
if (no_cols <= 0) {
Error("Allocate", "no of columns has to be positive");
return;
}
fNrows = no_rows;
fNcols = no_cols;
fRowLwb = row_lwb;
fColLwb = col_lwb;
fNelems = fNrows * fNcols;
fElements = new Real_t[fNelems];
if (fElements)
memset(fElements, 0, fNelems*sizeof(Real_t));
if (fNcols == 1) { // Only one col - fIndex is dummy actually
fIndex = &fElements;
return;
}
fIndex = new Real_t*[fNcols];
if (fIndex)
memset(fIndex, 0, fNcols*sizeof(Real_t*));
Int_t i;
Real_t *col_p;
for (i = 0, col_p = &fElements[0]; i < fNcols; i++, col_p += fNrows)
fIndex[i] = col_p;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix::~TMatrix()
{
// TMatrix destructor.
if (IsValid()) {
if (fNcols != 1)
delete [] fIndex;
delete [] fElements;
}
Invalidate();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::Draw(Option_t *option)
{
// Draw this matrix using an intermediate histogram
// The histogram is named "TMatrix" by default and no title
//create the hist utility manager (a plugin)
TVirtualUtilHist *util = (TVirtualUtilHist*)gROOT->GetListOfSpecials()->FindObject("R__TVirtualUtilHist");
if (!util) {
TPluginHandler *h;
if ((h = gROOT->GetPluginManager()->FindHandler("TVirtualUtilHist"))) {
if (h->LoadPlugin() == -1)
return;
h->ExecPlugin(0);
util = (TVirtualUtilHist*)gROOT->GetListOfSpecials()->FindObject("R__TVirtualUtilHist");
}
}
util->PaintMatrix(*this,option);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::ResizeTo(Int_t nrows, Int_t ncols)
{
// Erase the old matrix and create a new one according to new boundaries
// with indexation starting at 0.
if (IsValid()) {
if (fNrows == nrows && fNcols == ncols)
return;
if (fNcols != 1)
delete [] fIndex;
delete [] fElements;
}
Allocate(nrows, ncols);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::ResizeTo(Int_t row_lwb, Int_t row_upb, Int_t col_lwb, Int_t col_upb)
{
// Erase the old matrix and create a new one according to new boudaries.
Int_t new_nrows = row_upb - row_lwb + 1;
Int_t new_ncols = col_upb - col_lwb + 1;
if (IsValid()) {
fRowLwb = row_lwb;
fColLwb = col_lwb;
if (fNrows == new_nrows && fNcols == new_ncols)
return;
if (fNcols != 1)
delete [] fIndex;
delete [] fElements;
}
Allocate(new_nrows, new_ncols, row_lwb, col_lwb);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix::TMatrix(EMatrixCreatorsOp1 op, const TMatrix &prototype)
{
// Create a matrix applying a specific operation to the prototype.
// Example: TMatrix a(10,12); ...; TMatrix b(TMatrix::kTransposed, a);
// Supported operations are: kZero, kUnit, kTransposed, kInverted and kInvertedPosDef.
Invalidate();
if (!prototype.IsValid()) {
Error("TMatrix(EMatrixCreatorOp1)", "prototype matrix not initialized");
return;
}
switch(op) {
case kZero:
Allocate(prototype.fNrows, prototype.fNcols,
prototype.fRowLwb, prototype.fColLwb);
break;
case kUnit:
Allocate(prototype.fNrows, prototype.fNcols,
prototype.fRowLwb, prototype.fColLwb);
UnitMatrix();
break;
case kTransposed:
Transpose(prototype);
break;
case kInverted:
Invert(prototype);
break;
case kInvertedPosDef:
InvertPosDef(prototype);
break;
default:
Error("TMatrix(EMatrixCreatorOp1)", "operation %d not yet implemented", op);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix::TMatrix(const TMatrix &a, EMatrixCreatorsOp2 op, const TMatrix &b)
{
// Create a matrix applying a specific operation to two prototypes.
// Example: TMatrix a(10,12), b(12,5); ...; TMatrix c(a, TMatrix::kMult, b);
// Supported operations are: kMult (a*b), kTransposeMult (a'*b),
// kInvMult,kInvPosDefMult (a^(-1)*b) and kAtBA (a'*b*a).
Invalidate();
if (!a.IsValid()) {
Error("TMatrix(EMatrixCreatorOp2)", "matrix a not initialized");
return;
}
if (!b.IsValid()) {
Error("TMatrix(EMatrixCreatorOp2)", "matrix b not initialized");
return;
}
switch(op) {
case kMult:
AMultB(a, b);
break;
case kTransposeMult:
AtMultB(a, b);
break;
default:
Error("TMatrix(EMatrixCreatorOp2)", "operation %d not yet implemented", op);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::MakeSymmetric()
{
// symmetrize matrix (matrix needs to be a square one).
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("MakeSymmetric", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (fNrows != fNcols) {
Error("MakeSymmetric", "matrix to symmetrize must be square");
return *this;
}
Int_t irow;
for (irow = 0; irow < fNrows; irow++) {
Int_t icol;
for (icol = 0; icol < irow; icol++) {
fElements[irow*fNrows+icol] += fElements[icol*fNrows+irow];
fElements[irow*fNrows+icol] /= 2.0;
fElements[icol*fNrows+irow] = fElements[irow*fNrows+icol];
}
}
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::UnitMatrix()
{
// make a unit matrix (matrix need not be a square one). The matrix
// is traversed in the natural (that is, column by column) order.
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("UnitMatrix", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
Real_t *ep = fElements;
Int_t i, j;
for (j = 0; j < fNcols; j++)
for (i = 0; i < fNrows; i++)
*ep++ = (i==j ? 1.0 : 0.0);
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::operator=(Real_t val)
{
// Assign val to every element of the matrix.
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator=", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
Real_t *ep = fElements;
while (ep < fElements+fNelems)
*ep++ = val;
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::operator+=(Double_t val)
{
// Add val to every element of the matrix.
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator+=", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
Real_t *ep = fElements;
while (ep < fElements+fNelems)
*ep++ += val;
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::operator-=(Double_t val)
{
// Subtract val from every element of the matrix.
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator-=", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
Real_t *ep = fElements;
while (ep < fElements+fNelems)
*ep++ -= val;
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::operator*=(Double_t val)
{
// Multiply every element of the matrix with val.
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator*=", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
Real_t *ep = fElements;
while (ep < fElements+fNelems)
*ep++ *= val;
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMatrix::operator==(Real_t val) const
{
// Are all matrix elements equal to val?
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator==", "matrix not initialized");
return kFALSE;
}
Real_t *ep = fElements;
while (ep < fElements+fNelems)
if (!(*ep++ == val))
return kFALSE;
return kTRUE;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMatrix::operator!=(Real_t val) const
{
// Are all matrix elements not equal to val?
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator!=", "matrix not initialized");
return kFALSE;
}
Real_t *ep = fElements;
while (ep < fElements+fNelems)
if (!(*ep++ != val))
return kFALSE;
return kTRUE;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMatrix::operator<(Real_t val) const
{
// Are all matrix elements < val?
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator<", "matrix not initialized");
return kFALSE;
}
Real_t *ep = fElements;
while (ep < fElements+fNelems)
if (!(*ep++ < val))
return kFALSE;
return kTRUE;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMatrix::operator<=(Real_t val) const
{
// Are all matrix elements <= val?
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator<=", "matrix not initialized");
return kFALSE;
}
Real_t *ep = fElements;
while (ep < fElements+fNelems)
if (!(*ep++ <= val))
return kFALSE;
return kTRUE;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMatrix::operator>(Real_t val) const
{
// Are all matrix elements > val?
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator>", "matrix not initialized");
return kFALSE;
}
Real_t *ep = fElements;
while (ep < fElements+fNelems)
if (!(*ep++ > val))
return kFALSE;
return kTRUE;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMatrix::operator>=(Real_t val) const
{
// Are all matrix elements >= val?
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator>=", "matrix not initialized");
return kFALSE;
}
Real_t *ep = fElements;
while (ep < fElements+fNelems)
if (!(*ep++ >= val))
return kFALSE;
return kTRUE;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::Abs()
{
// Take an absolute value of a matrix, i.e. apply Abs() to each element.
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("Abs", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
Real_t *ep;
for (ep = fElements; ep < fElements+fNelems; ep++)
*ep = TMath::Abs(*ep);
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::Sqr()
{
// Square each element of the matrix.
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("Sqr", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
Real_t *ep;
for (ep = fElements; ep < fElements+fNelems; ep++)
*ep = (*ep) * (*ep);
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::Sqrt()
{
// Take square root of all elements.
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("Sqrt", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
Real_t *ep;
for (ep = fElements; ep < fElements+fNelems; ep++)
if (*ep >= 0)
*ep = TMath::Sqrt(*ep);
else
Error("Sqrt", "(%d,%d)-th element, %g, is negative, can't take the square root",
(ep-fElements) % fNrows + fRowLwb,
(ep-fElements) / fNrows + fColLwb, *ep);
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t operator==(const TMatrix &im1, const TMatrix &im2)
{
// Check to see if two matrices are identical.
if (!AreCompatible(im1, im2)) return kFALSE;
return (memcmp(im1.fElements, im2.fElements, im1.fNelems*sizeof(Real_t)) == 0);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &operator+=(TMatrix &target, const TMatrix &source)
{
// Add the source matrix to the target matrix.
if (!AreCompatible(target, source)) {
Error("operator+=", "matrices are not compatible");
return target;
}
Real_t *sp = source.fElements;
Real_t *tp = target.fElements;
for ( ; tp < target.fElements+target.fNelems; )
*tp++ += *sp++;
return target;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &operator-=(TMatrix &target, const TMatrix &source)
{
// Subtract the source matrix from the target matrix.
if (!AreCompatible(target, source)) {
Error("operator-=", "matrices are not compatible");
return target;
}
Real_t *sp = source.fElements;
Real_t *tp = target.fElements;
for ( ; tp < target.fElements+target.fNelems; )
*tp++ -= *sp++;
return target;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &Add(TMatrix &target, Double_t scalar, const TMatrix &source)
{
// Modify addition: target += scalar * source.
if (!AreCompatible(target, source)) {
Error("Add", "matrices are not compatible");
return target;
}
Real_t *sp = source.fElements;
Real_t *tp = target.fElements;
for ( ; tp < target.fElements+target.fNelems; )
*tp++ += scalar * (*sp++);
return target;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix operator+(const TMatrix &source1, const TMatrix &source2)
{
TMatrix target(source1);
target += source2;
return target;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix operator-(const TMatrix &source1, const TMatrix &source2)
{
TMatrix target(source1);
target -= source2;
return target;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix operator*(const TMatrix &source1, const TMatrix &source2)
{
TMatrix target(source1,TMatrix::kMult,source2);
return target;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &ElementMult(TMatrix &target, const TMatrix &source)
{
// Multiply target by the source, element-by-element.
if (!AreCompatible(target, source)) {
Error("ElementMult", "matrices are not compatible");
return target;
}
Real_t *sp = source.fElements;
Real_t *tp = target.fElements;
for ( ; tp < target.fElements+target.fNelems; )
*tp++ *= *sp++;
return target;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &ElementDiv(TMatrix &target, const TMatrix &source)
{
// Divide target by the source, element-by-element.
if (!AreCompatible(target, source)) {
Error("ElementDiv", "matrices are not compatible");
return target;
}
Real_t *sp = source.fElements;
Real_t *tp = target.fElements;
for ( ; tp < target.fElements+target.fNelems; )
*tp++ /= *sp++;
return target;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMatrix::RowNorm() const
{
// Row matrix norm, MAX{ SUM{ |M(i,j)|, over j}, over i}.
// The norm is induced by the infinity vector norm.
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("RowNorm", "matrix not initialized");
return 0.0;
}
Real_t *ep = fElements;
Double_t norm = 0;
// Scan the matrix row-after-row
while (ep < fElements+fNrows) {
Int_t j;
Double_t sum = 0;
// Scan a row to compute the sum
for (j = 0; j < fNcols; j++, ep += fNrows)
sum += TMath::Abs(*ep);
ep -= fNelems - 1; // Point ep to the beginning of the next row
norm = TMath::Max(norm, sum);
}
Assert(ep == fElements + fNrows);
return norm;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMatrix::ColNorm() const
{
// Column matrix norm, MAX{ SUM{ |M(i,j)|, over i}, over j}.
// The norm is induced by the 1 vector norm.
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("ColNorm", "matrix not initialized");
return 0.0;
}
Real_t *ep = fElements;
Double_t norm = 0;
// Scan the matrix col-after-col (i.e. in the natural order of elems)
while (ep < fElements+fNelems) {
Int_t i;
Double_t sum = 0;
// Scan a col to compute the sum
for (i = 0; i < fNrows; i++)
sum += TMath::Abs(*ep++);
norm = TMath::Max(norm, sum);
}
Assert(ep == fElements + fNelems);
return norm;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMatrix::E2Norm() const
{
// Square of the Euclidian norm, SUM{ m(i,j)^2 }.
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("E2Norm", "matrix not initialized");
return 0.0;
}
Real_t *ep;
Double_t sum = 0;
for (ep = fElements; ep < fElements+fNelems; ep++)
sum += (*ep) * (*ep);
return sum;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t E2Norm(const TMatrix &m1, const TMatrix &m2)
{
// Square of the Euclidian norm of the difference between two matrices.
if (!AreCompatible(m1, m2)) {
Error("E2Norm", "matrices are not compatible");
return 0.0;
}
Real_t *mp1 = m1.fElements;
Real_t *mp2 = m2.fElements;
Double_t sum = 0;
for (; mp1 < m1.fElements+m1.fNelems; mp1++, mp2++)
sum += (*mp1 - *mp2) * (*mp1 - *mp2);
return sum;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::NormByDiag(const TVector &v, Option_t *option)
{
// b(i,j) = a(i,j)/sqrt(abs*(v(i)*v(j)))
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("NormByDiag", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (!v.IsValid()) {
Error("NormByDiag", "vector is not initialized");
return *this;
}
const Int_t nMax = TMath::Max(fNrows,fNcols);
if (v.fNrows < nMax) {
Error("NormByDiag", "norm vector is too short");
return *this;
}
TString opt(option);
opt.ToUpper();
const Int_t divide = (opt.Contains("D")) ? 1 : 0;
const Real_t* pv = v.fElements;
Real_t* mp = fElements;
Int_t irow;
if (divide) {
for (irow = 0; irow < fNrows; irow++) {
Int_t icol;
for (icol = 0; icol < fNcols; icol++) {
Double_t val = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(pv[irow]*pv[icol]));
Assert(val != 0.0);
mp[irow*fNcols+icol] /= val;
}
}
} else {
for (irow = 0; irow < fNrows; irow++) {
Int_t icol;
for (icol = 0; icol < fNcols; icol++) {
Double_t val = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(pv[irow]*pv[icol]));
mp[irow*fNcols+icol] *= val;
}
}
}
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::NormByColumn(const TVector &v, Option_t *option)
{
// Multiply/divide a matrix columns with a vector:
// matrix(i,j) *= v(i)
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("NormByColumn", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (!v.IsValid()) {
Error("NormByColumn", "vector is not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (fNcols != v.fNrows) {
Error("NormByColumn", "matrix cannot be normed column-wise by this vector");
return *this;
}
TString opt(option);
opt.ToUpper();
const Int_t divide = (opt.Contains("D")) ? 1 : 0;
const Real_t* pv = v.fElements;
Real_t *mp = fElements;
Int_t i;
if (divide) {
for ( ; mp < fElements + fNelems; pv++)
for (i = 0; i < fNrows; i++) {
Assert(*pv != 0.0);
*mp++ /= *pv;
}
} else {
for ( ; mp < fElements + fNelems; pv++)
for (i = 0; i < fNrows; i++)
*mp++ *= *pv;
}
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::NormByRow(const TVector &v, Option_t *option)
{
// Multiply/divide a matrix row with a vector:
// matrix(i,j) *= v(j)
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("NormByRow", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (!v.IsValid()) {
Error("NormByRow", "vector is not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (fNcols != v.fNrows) {
Error("NormByRow", "matrix cannot be normed column-wise by this vector");
return *this;
}
TString opt(option);
opt.ToUpper();
const Int_t divide = (opt.Contains("D")) ? 1 : 0;
const Real_t* pv = v.fElements;
Real_t *mp = fElements;
Int_t i;
if (divide) {
for ( ; mp < fElements + fNelems; pv = v.fElements) {
for (i = 0; i < fNrows; i++)
{
Assert(*pv != 0.0);
*mp++ /= *pv++;
}
}
} else {
for ( ; mp < fElements + fNelems; pv = v.fElements)
for (i = 0; i < fNrows; i++)
*mp++ *= *pv++;
}
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::Print(Option_t *) const
{
// Print the matrix as a table of elements (zeros are printed as dots).
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("Print", "matrix not initialized");
return;
}
printf("nMatrix %dx%d is as follows", fNrows, fNcols);
Int_t cols_per_sheet = 5;
Int_t sheet_counter;
for (sheet_counter = 1; sheet_counter <= fNcols; sheet_counter += cols_per_sheet) {
printf("n\n |");
Int_t i, j;
for (j = sheet_counter; j < sheet_counter+cols_per_sheet && j <= fNcols; j++)
printf(" %6d |", j+fColLwb-1);
printf("n%sn",
"------------------------------------------------------------------");
for (i = 1; i <= fNrows; i++) {
printf("%4d |", i+fRowLwb-1);
for (j = sheet_counter; j < sheet_counter+cols_per_sheet && j <= fNcols; j++)
printf("%11.4g ", (*this)(i+fRowLwb-1, j+fColLwb-1));
printf("n");
}
}
printf("n");
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::Transpose(const TMatrix &prototype)
{
// Transpose a matrix.
if (!prototype.IsValid()) {
Error("Transpose", "prototype matrix not initialized");
return;
}
Allocate(prototype.fNcols, prototype.fNrows,
prototype.fColLwb, prototype.fRowLwb);
Real_t *rsp = prototype.fElements; // Row source pointer
Real_t *tp = fElements;
// (This: target) matrix is traversed in the natural, column-wise way,
// whilst the source (prototype) matrix is scanned row-by-row
while (tp < fElements + fNelems) {
Real_t *sp = rsp++; // sp = @ms[j,i] for i=0
// Move tp to the next elem in the col and sp to the next el in the curr row
while (sp < prototype.fElements + prototype.fNelems)
*tp++ = *sp, sp += prototype.fNrows;
}
Assert(tp == fElements + fNelems &&
rsp == prototype.fElements + prototype.fNrows);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::Invert(Double_t *determ_ptr)
{
// The most general (Gauss-Jordan) matrix inverse
//
// This method works for any matrix (which of course must be square and
// non-singular). Use this method only if none of specialized algorithms
// (for symmetric, tridiagonal, etc) matrices isn't applicable/available.
// Also, the matrix to invert has to be _well_ conditioned:
// Gauss-Jordan eliminations (even with pivoting) perform poorly for
// near-singular matrices (e.g., Hilbert matrices).
//
// The method inverts matrix inplace and returns the determinant if
// determ_ptr was specified as not 0. Determinant will be exactly zero
// if the matrix turns out to be (numerically) singular. If determ_ptr is
// 0 and matrix happens to be singular, throw up.
//
// The algorithm perform inplace Gauss-Jordan eliminations with
// full pivoting. It was adapted from my Algol-68 "translation" (ca 1986)
// of the FORTRAN code described in
// Johnson, K. Jeffrey, "Numerical methods in chemistry", New York,
// N.Y.: Dekker, c1980, 503 pp, p.221
//
// Note, since it's much more efficient to perform operations on matrix
// columns rather than matrix rows (due to the layout of elements in the
// matrix), the present method implements a "transposed" algorithm.
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("Invert(Double_t*)", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (fNrows != fNcols) {
Error("Invert(Double_t*)", "matrix to invert must be square");
return *this;
}
Double_t determinant = 1;
const Double_t singularity_tolerance = 1e-35;
if (fNrows <= 3) {
Real_t *m = fElements;
if (fNrows == 1) {
determinant = m[0];
} else if (fNrows == 2) {
determinant = m[0]*m[3]-m[1]*m[2];
} else if (fNrows == 3) {
determinant = m[0]*(m[4]*m[8]-m[7]*m[5])
-m[3]*(m[1]*m[8]-m[7]*m[2])
+m[6]*(m[1]*m[5]-m[4]*m[2]);
}
if (TMath::Abs(determinant) < singularity_tolerance) {
if (determ_ptr) {
*determ_ptr = 0;
return *this;
} else {
Error("Invert(Double_t*)", "matrix turns out to be singular: can't invert");
return *this;
}
}
if (fNrows == 1) {
m[0] = 1/m[0];
} else if (fNrows == 2) {
Real_t *o = new Real_t[fNelems];
memcpy(o,m,fNelems*sizeof(Real_t));
m[0] = o[3]/determinant;
m[1] = -o[1]/determinant;
m[2] = -o[2]/determinant;
m[3] = o[0]/determinant;
delete [] o;
} else if (fNrows == 3) {
Real_t *o = new Real_t[fNelems];
memcpy(o,m,fNelems*sizeof(Real_t));
m[0] = +(o[4]*o[8]-o[5]*o[7])/determinant;
m[1] = -(o[1]*o[8]-o[2]*o[7])/determinant;
m[2] = +(o[1]*o[5]-o[2]*o[4])/determinant;
m[3] = -(o[3]*o[8]-o[5]*o[6])/determinant;
m[4] = +(o[0]*o[8]-o[2]*o[6])/determinant;
m[5] = -(o[0]*o[5]-o[2]*o[3])/determinant;
m[6] = +(o[3]*o[7]-o[4]*o[6])/determinant;
m[7] = -(o[0]*o[7]-o[1]*o[6])/determinant;
m[8] = +(o[0]*o[4]-o[1]*o[3])/determinant;
delete [] o;
}
if (determ_ptr)
*determ_ptr = determinant;
return *this;
}
const Int_t symmetric = IsSymmetric();
// condition the matrix
TVector diag(fNrows);
if (symmetric) {
diag = TMatrixDiag(*this);
for (Int_t idx = 0; idx < diag.fNrows; idx++) {
if (diag.fElements[idx] == 0.0) diag.fElements[idx] = 1.0;
}
this->NormByDiag(diag);
}
// Locations of pivots (indices start with 0)
struct Pivot_t { int row, col; } *const pivots = new Pivot_t[fNcols];
Bool_t *const was_pivoted = new Bool_t[fNrows];
memset(was_pivoted, 0, fNrows*sizeof(Bool_t));
Pivot_t *pivotp;
for (pivotp = &pivots[0]; pivotp < &pivots[fNcols]; pivotp++) {
Int_t prow = 0, pcol = 0; // Location of a pivot to be
{ // Look through all non-pivoted cols
Real_t max_value = 0; // (and rows) for a pivot (max elem)
for (Int_t j = 0; j < fNcols; j++)
if (!was_pivoted[j]) {
Real_t *cp;
Int_t k;
Real_t curr_value = 0;
for (k = 0, cp = fIndex[j]; k < fNrows; k++, cp++)
if (!was_pivoted[k] && (curr_value = TMath::Abs(*cp)) > max_value)
max_value = curr_value, prow = k, pcol = j;
}
if (max_value < singularity_tolerance) {
// free allocated heap memory before returning
delete [] pivots;
delete [] was_pivoted;
if (determ_ptr) {
*determ_ptr = 0;
return *this;
} else {
Error("Invert(Double_t*)", "matrix turns out to be singular: can't invert");
return *this;
}
}
pivotp->row = prow;
pivotp->col = pcol;
}
// Swap prow-th and pcol-th columns to bring the pivot to the diagonal
if (prow != pcol) {
Real_t *cr = fIndex[prow];
Real_t *cc = fIndex[pcol];
for (Int_t k = 0; k < fNrows; k++) {
Real_t temp = *cr; *cr++ = *cc; *cc++ = temp;
}
}
was_pivoted[prow] = kTRUE;
{ // Normalize the pivot column and
Real_t *pivot_cp = fIndex[prow];
Double_t pivot_val = pivot_cp[prow]; // pivot is at the diagonal
determinant *= pivot_val; // correct the determinant
pivot_cp[prow] = kTRUE;
for (Int_t k=0; k < fNrows; k++)
*pivot_cp++ /= pivot_val;
}
{ // Perform eliminations
Real_t *pivot_rp = fElements + prow; // pivot row
for (Int_t k = 0; k < fNrows; k++, pivot_rp += fNrows)
if (k != prow) {
Double_t temp = *pivot_rp;
*pivot_rp = 0;
Real_t *pivot_cp = fIndex[prow]; // pivot column
Real_t *elim_cp = fIndex[k]; // elimination column
for (Int_t l = 0; l < fNrows; l++)
*elim_cp++ -= temp * *pivot_cp++;
}
}
}
Int_t no_swaps = 0; // Swap exchanged *rows* back in place
for (pivotp = &pivots[fNcols-1]; pivotp >= &pivots[0]; pivotp--)
if (pivotp->row != pivotp->col) {
no_swaps++;
Real_t *rp = fElements + pivotp->row;
Real_t *cp = fElements + pivotp->col;
for (Int_t k = 0; k < fNcols; k++, rp += fNrows, cp += fNrows) {
Real_t temp = *rp; *rp = *cp; *cp = temp;
}
}
// revert our scaling
if (symmetric) {
this->NormByDiag(diag);
if (determ_ptr) {
Int_t irow;
for (irow = 0; irow < fNrows; irow++)
determinant *= TMath::Abs(diag(irow));
}
}
if (determ_ptr)
*determ_ptr = (no_swaps & 1 ? -determinant : determinant);
delete [] was_pivoted;
delete [] pivots;
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TMatrix::IsSymmetric() const
{
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("IsSymmetric", "matrix not initialized");
return 0;
}
if (fNrows != fNcols) {
Error("IsSymmetric", "matrix is not square");
return 0;
}
if (fRowLwb != fColLwb) {
Error("IsSymmetric", "row and column start at different values");
return 0;
}
Int_t irow;
for (irow = 0; irow < fNrows; irow++) {
Int_t icol;
for (icol = 0; icol < irow; icol++) {
if (fElements[irow*fNrows+icol] != fElements[icol*fNrows+irow]) {
return 0;
}
}
}
return 1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::Invert(const TMatrix &m)
{
// Allocate new matrix and set it to inv(m).
if (!m.IsValid()) {
Error("Invert(const TMatrix&)", "matrix m not initialized");
return;
}
ResizeTo(m);
*this = m; // assignment operator
Invert(0);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::InvertPosDef()
{
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("InvertPosDef(Real_t*)", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (fNrows != fNcols) {
Error("InvertPosDef(Real_t*)", "matrix to invert must be square");
return *this;
}
if (fNrows <= 3) {
const Double_t singularity_tolerance = 1e-35;
Double_t determinant = 1;
Real_t *m = fElements;
if (fNrows == 1) {
determinant = m[0];
} else if (fNrows == 2) {
determinant = m[0]*m[3]-m[1]*m[2];
} else if (fNrows == 3) {
determinant = m[0]*(m[4]*m[8]-m[7]*m[5])
-m[3]*(m[1]*m[8]-m[7]*m[2])
+m[6]*(m[1]*m[5]-m[4]*m[2]);
}
if (TMath::Abs(determinant) < singularity_tolerance) {
Error("InvertPosDef", "matrix turns out to be singular: can't invert");
return *this;
}
if (fNrows == 1) {
m[0] = 1/m[0];
} else if (fNrows == 2) {
Real_t *o = new Real_t[fNelems];
memcpy(o,m,fNelems*sizeof(Real_t));
m[0] = o[3]/determinant;
m[1] = -o[1]/determinant;
m[2] = m[1];
m[3] = o[0]/determinant;
delete [] o;
} else if (fNrows == 3) {
Real_t *o = new Real_t[fNelems];
memcpy(o,m,fNelems*sizeof(Real_t));
m[0] = +(o[4]*o[8]-o[5]*o[7])/determinant;
m[1] = -(o[3]*o[8]-o[5]*o[6])/determinant;
m[2] = +(o[3]*o[7]-o[4]*o[6])/determinant;
m[3] = m[1];
m[4] = +(o[0]*o[8]-o[2]*o[6])/determinant;
m[5] = -(o[0]*o[7]-o[1]*o[6])/determinant;
m[6] = m[2];
m[7] = m[5];
m[8] = +(o[0]*o[4]-o[1]*o[3])/determinant;
delete [] o;
}
return *this;
}
const Int_t n = fNrows;
Real_t *pa = fElements;
Real_t *pu = new Real_t[n*n];
// step 1: Cholesky decomposition
if (Pdcholesky(pa,pu,n))
{
Error("InvertPosDef","matrix not positive definite ?, Gauss-Jordan inversion applied");
delete [] pu;
Invert(0);
return *this;
}
const Int_t off_n = (n-1)*n;
Int_t i,l;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
const Int_t off_i = i*n;
// step 2: Forward substitution
for (l = i; l < n; l++)
{
if (l == i)
pa[off_n+l] = 1./pu[l*n+l];
else
{
pa[off_n+l] = 0.;
for (Int_t k = i; k <= l-1; k++)
pa[off_n+l] = pa[off_n+l]-pu[k*n+l]*pa[off_n+k];
pa[off_n+l] = pa[off_n+l]/pu[l*n+l];
}
}
// step 3: Back substitution
for (l = n-1; l >= i; l--)
{
const Int_t off_l = l*n;
if (l == n-1)
pa[off_i+l] = pa[off_n+l]/pu[off_l+l];
else
{
pa[off_i+l] = pa[off_n+l];
for (Int_t k = n-1; k >= l+1; k--)
pa[off_i+l] = pa[off_i+l]-pu[off_l+k]*pa[off_i+k];
pa[off_i+l] = pa[off_i+l]/pu[off_l+l];
}
}
}
// Fill lower triangle symmetrically
if (n > 1)
{
for (Int_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (Int_t l = 0; l <= i-1; l++)
pa[i*n+l] = pa[l*n+i];
}
}
delete [] pu;
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TMatrix::Pdcholesky(const Real_t *a, Real_t *u, const Int_t n)
{
// Program Pdcholesky inverts a positiv definite (n x n) - matrix A,
// using the Cholesky decomposition
//
// Input: a - (n x n)- Matrix A
// n - dimensions n of matrices
//
// Output: u - (n x n)- Matrix U so that U^T . U = A
// return - 0 decomposition succesful
// - 1 decomposition failed
memset(u,0,n*n*sizeof(Real_t));
Int_t status = 0;
for (Int_t k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
Double_t s = 0.;
const Int_t off_k = k*n;
for (Int_t j = k; j < n; j++)
{
if (k > 0)
{
s = 0.;
for (Int_t l = 0; l <= k-1; l++)
{
const Int_t off_l = l*n;
s += u[off_l+k]*u[off_l+j];
}
}
u[off_k+j] = a[off_k+j]-s;
if (k == j)
{
if (u[off_k+j] < 0) status = 1;
u[off_k+j] = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Abs(u[off_k+j]));
}
else
u[off_k+j] = u[off_k+j]/u[off_k+k];
}
}
return status;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::InvertPosDef(const TMatrix &m)
{
// Allocate new matrix and set it to inv(m).
if (!m.IsValid()) {
Error("InvertPosDef(const TMatrix&)", "matrix m not initialized");
return;
}
ResizeTo(m);
*this = m; // assignment operator
InvertPosDef();
}
//____________________________________________________________________
const TMatrix TMatrix::EigenVectors(TVector &eigenValues) const
{
// Return a matrix containing the eigen-vectors; also fill the
// supplied vector with the eigen values.
if (IsSymmetric()) {
TMatrix eigenVectors = *this;
eigenValues.ResizeTo(fNrows);
TVector offDiag(fNrows);
// Tridiagonalize matrix
MakeTridiagonal(eigenVectors,eigenValues,offDiag);
// Make eigenvectors and -values
MakeEigenVectors(eigenValues,offDiag,eigenVectors);
// Order eigenvalues and -vectors
EigenSort(eigenVectors,eigenValues);
return eigenVectors;
}
else {
Error("EigenVectors","Not yet implemented for non-symmetric matrix");
return *this;
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::MakeTridiagonal(TMatrix &a, TVector &d, TVector &e)
{
// The comments in this algorithm are modified version of those in
// "Numerical ...". Please refer to that book (web-page) for more on
// the algorithm.
//
/*
PRIVATE METHOD:
Tridiagonalise the covariance matrix according to the Householder
method as described in
Numerical Recipes in C
section 11.2.
The basic idea is to perform 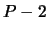 orthogonal transformation, where
each transformation eat away the off-diagonal elements, except the
inner most.
*/
//
const Int_t n = a.fNrows;
if (!a.IsValid()) {
gROOT->Error("Maketridiagonal", "matrix not initialized");
return;
}
if (a.fNrows != a.fNcols) {
gROOT->Error("Maketridiagonal", "matrix to tridiagonalize must be square");
return;
}
if (!a.IsSymmetric()) {
gROOT->Error("MakeTridiagonal", "Can only tridiagonalise symmetric matrix");
a.Zero();
d.Zero();
e.Zero();
return;
}
Real_t *pa = a.fElements;
Real_t *pd = d.fElements;
Real_t *pe = e.fElements;
Int_t i;
for (i = n-1; i > 0; i--) {
const Int_t l = i-1;
Double_t h = 0;
Double_t scale = 0;
if (l > 0) {
for (Int_t k = 0; k <= l; k++)
scale += TMath::Abs(pa[i+k*n]);
if (scale == 0)
// Skip transformation
pe[i] = pa[i+l*n];
else {
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k <= l; k++) {
// Use scaled elements of a for transformation
pa[i+k*n] /= scale;
// Calculate sigma in h
h += pa[i+k*n]*pa[i+k*n];
}
Double_t f = pa[i+l*n];
Double_t g = (f >= 0. ? -TMath::Sqrt(h) : TMath::Sqrt(h));
pe[i] = scale*g;
h -= f*g; // Now h is eq. (11.2.4) in "Numerical ..."
pa[i+l*n] = f-g;
f = 0;
Int_t j;
for (j = 0; j <= l; j++) {
// Store the u/H in ith column of a;
pa[j+i*n] = pa[i+j*n]/h;
// Form element A dot u in g;
g = 0;
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k <= j; k++)
g += pa[j+k*n]*pa[i+k*n];
for (k = j+1; k <= l; k++)
g += pa[k+j*n]*pa[i+k*n];
// Form element of vector p in temporarily unused element of
// e
pe[j] = g/h;
f += pe[j]*pa[i+j*n];
}
// Form K eq (11.2.11)
const Double_t hh = f/(h+h);
// Form vector q and store in e overwriting p
for (j = 0; j <= l; j++) {
f = pa[i+j*n];
pe[j] = g = pe[j]-hh*f;
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k <= j; k++)
// Reduce a, eq (11.2.13)
pa[j+k*n] -= (f*pe[k]+g*pa[i+k*n]);
}
}
}
else
pe[i] = pa[i+l*n];
pd[i] = h;
}
pd[0] = 0;
pe[0] = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Begin accumulation of transformation matrix
const Int_t l = i-1;
if (pd[i]) {
// This block is skipped if i = 0;
Int_t j;
for (j = 0; j <= l; j++) {
Double_t g = 0;
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k <= l; k++)
// Use vector u/H stored in a to form P dot Q
g += pa[i+k*n]*pa[k+j*n];
for (k = 0; k <= l; k++)
pa[k+j*n] -= g*pa[k+i*n];
}
}
pd[i] = pa[i+i*n];
pa[i+i*n] = 1;
Int_t j;
for (j = 0; j <= l; j++) {
pa[j+i*n] = pa[i+j*n] = 0;
}
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::MakeEigenVectors(TVector &d, TVector &e, TMatrix &z)
{
//
/*
PRIVATE METHOD:
orthogonal transformation, where
each transformation eat away the off-diagonal elements, except the
inner most.
*/
//
const Int_t n = a.fNrows;
if (!a.IsValid()) {
gROOT->Error("Maketridiagonal", "matrix not initialized");
return;
}
if (a.fNrows != a.fNcols) {
gROOT->Error("Maketridiagonal", "matrix to tridiagonalize must be square");
return;
}
if (!a.IsSymmetric()) {
gROOT->Error("MakeTridiagonal", "Can only tridiagonalise symmetric matrix");
a.Zero();
d.Zero();
e.Zero();
return;
}
Real_t *pa = a.fElements;
Real_t *pd = d.fElements;
Real_t *pe = e.fElements;
Int_t i;
for (i = n-1; i > 0; i--) {
const Int_t l = i-1;
Double_t h = 0;
Double_t scale = 0;
if (l > 0) {
for (Int_t k = 0; k <= l; k++)
scale += TMath::Abs(pa[i+k*n]);
if (scale == 0)
// Skip transformation
pe[i] = pa[i+l*n];
else {
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k <= l; k++) {
// Use scaled elements of a for transformation
pa[i+k*n] /= scale;
// Calculate sigma in h
h += pa[i+k*n]*pa[i+k*n];
}
Double_t f = pa[i+l*n];
Double_t g = (f >= 0. ? -TMath::Sqrt(h) : TMath::Sqrt(h));
pe[i] = scale*g;
h -= f*g; // Now h is eq. (11.2.4) in "Numerical ..."
pa[i+l*n] = f-g;
f = 0;
Int_t j;
for (j = 0; j <= l; j++) {
// Store the u/H in ith column of a;
pa[j+i*n] = pa[i+j*n]/h;
// Form element A dot u in g;
g = 0;
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k <= j; k++)
g += pa[j+k*n]*pa[i+k*n];
for (k = j+1; k <= l; k++)
g += pa[k+j*n]*pa[i+k*n];
// Form element of vector p in temporarily unused element of
// e
pe[j] = g/h;
f += pe[j]*pa[i+j*n];
}
// Form K eq (11.2.11)
const Double_t hh = f/(h+h);
// Form vector q and store in e overwriting p
for (j = 0; j <= l; j++) {
f = pa[i+j*n];
pe[j] = g = pe[j]-hh*f;
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k <= j; k++)
// Reduce a, eq (11.2.13)
pa[j+k*n] -= (f*pe[k]+g*pa[i+k*n]);
}
}
}
else
pe[i] = pa[i+l*n];
pd[i] = h;
}
pd[0] = 0;
pe[0] = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Begin accumulation of transformation matrix
const Int_t l = i-1;
if (pd[i]) {
// This block is skipped if i = 0;
Int_t j;
for (j = 0; j <= l; j++) {
Double_t g = 0;
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k <= l; k++)
// Use vector u/H stored in a to form P dot Q
g += pa[i+k*n]*pa[k+j*n];
for (k = 0; k <= l; k++)
pa[k+j*n] -= g*pa[k+i*n];
}
}
pd[i] = pa[i+i*n];
pa[i+i*n] = 1;
Int_t j;
for (j = 0; j <= l; j++) {
pa[j+i*n] = pa[i+j*n] = 0;
}
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::MakeEigenVectors(TVector &d, TVector &e, TMatrix &z)
{
//
/*
PRIVATE METHOD:
Find eigenvalues and vectors of tridiagonalised covariance matrix
according to the QL with implicit shift algorithm from
Numerical Recipes in C
section 11.3.
The basic idea is to find matrices 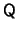 and
and 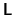 so that
so that
 , where
, where 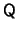 is orthogonal and
is orthogonal and
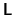 is lower triangular. The QL algorithm
consist of a
sequence of orthogonal transformations
is lower triangular. The QL algorithm
consist of a
sequence of orthogonal transformations
(1) If 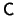 have eigenvalues with different absolute value
have eigenvalues with different absolute value
 , then
, then
 [lower triangular form] as
[lower triangular form] as
 . The eigenvalues appear on the diagonal in
increasing order of absolute magnitude. (2) If If
. The eigenvalues appear on the diagonal in
increasing order of absolute magnitude. (2) If If 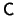 has an
eigenvalue
has an
eigenvalue  of multiplicty of order
of multiplicty of order  ,
,
 [lower triangular form] as
[lower triangular form] as
 , except for a diagona block matrix of order
, except for a diagona block matrix of order  ,
whose eigenvalues
,
whose eigenvalues
 .
*/
//
const Int_t n = z.fNrows;
Real_t *pd = d.fElements;
Real_t *pe = e.fElements;
Real_t *pz = z.fElements;
// It's convenient to renumber the e vector elements
Int_t l;
for (l = 1; l < n; l++)
pe[l-1] = pe[l];
pe[n-1] = 0;
for (l = 0; l < n; l++) {
Int_t iter = 0;
Int_t m = 0;
do {
for (m = l; m < n-1; m++) {
// Look for a single small sub-diagonal element to split the
// matrix
const Double_t dd = TMath::Abs(pd[m])+TMath::Abs(pd[m+1]);
if ((Double_t)(TMath::Abs(pe[m])+dd) == dd)
break;
}
if (m != l) {
if (iter++ == 30) {
gROOT->Error("MakeEigenVectors","too many iterationsn");
return;
}
// Form shift
Double_t g = (pd[l+1]-pd[l])/(2*pe[l]);
Double_t r = TMath::Sqrt(g*g+1);
// This is d_m-k_s
g = pd[m]-pd[l]+pe[l]/(g+TMath::Sign(r,g));
Double_t s = 1;
Double_t c = 1;
Double_t p = 0;
Int_t i = 0;
for (i = m-1; i >= l; i--) {
// A plane rotation as in the original QL, followed by
// Givens rotations to restore tridiagonal form
Double_t f = s*pe[i];
const Double_t b = c*pe[i];
r = TMath::Sqrt(f*f+g*g);
pe[i+1] = r;
if (r == 0) {
// Recover from underflow
pd[i+1] -= p;
pe[m] = 0;
break;
}
s = f/r;
c = g/r;
g = pd[i+1]-p;
r = (pd[i]-g)*s+2*c*b;
p = s*r;
pd[i+1] = g+p;
g = c*r-b;
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k < n; k++) {
// Form Eigenvectors
f = pz[k+(i+1)*n];
pz[k+(i+1)*n] = s*pz[k+i*n]+c*f;
pz[k+i*n] = c*pz[k+i*n]-s*f;
}
} // for (i = m)
if (r == 0 && i >= l)
continue;
pd[l] -= p;
pe[l] = g;
pe[m] = 0;
} // if (m != l)
} while (m != l);
} // for (l = 0)
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::EigenSort(TMatrix &eigenVectors, TVector &eigenValues)
{
//
/*
PRIVATE METHOD:
.
*/
//
const Int_t n = z.fNrows;
Real_t *pd = d.fElements;
Real_t *pe = e.fElements;
Real_t *pz = z.fElements;
// It's convenient to renumber the e vector elements
Int_t l;
for (l = 1; l < n; l++)
pe[l-1] = pe[l];
pe[n-1] = 0;
for (l = 0; l < n; l++) {
Int_t iter = 0;
Int_t m = 0;
do {
for (m = l; m < n-1; m++) {
// Look for a single small sub-diagonal element to split the
// matrix
const Double_t dd = TMath::Abs(pd[m])+TMath::Abs(pd[m+1]);
if ((Double_t)(TMath::Abs(pe[m])+dd) == dd)
break;
}
if (m != l) {
if (iter++ == 30) {
gROOT->Error("MakeEigenVectors","too many iterationsn");
return;
}
// Form shift
Double_t g = (pd[l+1]-pd[l])/(2*pe[l]);
Double_t r = TMath::Sqrt(g*g+1);
// This is d_m-k_s
g = pd[m]-pd[l]+pe[l]/(g+TMath::Sign(r,g));
Double_t s = 1;
Double_t c = 1;
Double_t p = 0;
Int_t i = 0;
for (i = m-1; i >= l; i--) {
// A plane rotation as in the original QL, followed by
// Givens rotations to restore tridiagonal form
Double_t f = s*pe[i];
const Double_t b = c*pe[i];
r = TMath::Sqrt(f*f+g*g);
pe[i+1] = r;
if (r == 0) {
// Recover from underflow
pd[i+1] -= p;
pe[m] = 0;
break;
}
s = f/r;
c = g/r;
g = pd[i+1]-p;
r = (pd[i]-g)*s+2*c*b;
p = s*r;
pd[i+1] = g+p;
g = c*r-b;
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k < n; k++) {
// Form Eigenvectors
f = pz[k+(i+1)*n];
pz[k+(i+1)*n] = s*pz[k+i*n]+c*f;
pz[k+i*n] = c*pz[k+i*n]-s*f;
}
} // for (i = m)
if (r == 0 && i >= l)
continue;
pd[l] -= p;
pe[l] = g;
pe[m] = 0;
} // if (m != l)
} while (m != l);
} // for (l = 0)
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::EigenSort(TMatrix &eigenVectors, TVector &eigenValues)
{
//
/*
PRIVATE METHOD:
Order the eigenvalues and vectors by ascending eigenvalue. The
algorithm is a straight insertion. It's taken from
Numerical Recipes in C
section 11.1.
*/
//
Int_t n = eigenVectors.fNrows;
Real_t *pVec = eigenVectors.fElements;
Real_t *pVal = eigenValues.fElements;
Int_t i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Int_t k = i;
Double_t p = pVal[i];
Int_t j;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (pVal[j] >= p) {
k = j;
p = pVal[j];
}
if (k != i) {
pVal[k] = pVal[i];
pVal[i] = p;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) {
p = pVec[j+i*n];
pVec[j+i*n] = pVec[j+k*n];
pVec[j+k*n] = p;
}
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
const Real_t &TMatrix::operator()(Int_t rown, Int_t coln) const
{
// Access a single matrix element.
static Real_t err;
err = 0.0;
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator()", "matrix is not initialized");
return err;
}
Int_t arown = rown - fRowLwb; // Effective indices
Int_t acoln = coln - fColLwb;
if (arown >= fNrows || arown < 0) {
Error("operator()", "row index %d is out of matrix boundaries [%d,%d]",
rown, fRowLwb, fNrows+fRowLwb-1);
return err;
}
if (acoln >= fNcols || acoln < 0) {
Error("operator()", "col index %d is out of matrix boundaries [%d,%d]",
coln, fColLwb, fNcols+fColLwb-1);
return err;
}
return (fIndex[acoln])[arown];
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::operator*=(const TMatrix &source)
{
// Compute target = target * source inplace. Strictly speaking, it can't be
// done inplace, though only the row of the target matrix needs
// to be saved. "Inplace" multiplication is only possible
// when the 'source' matrix is square.
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator*=(const TMatrix&)", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (!source.IsValid()) {
Error("operator*=(const TMatrix&)", "source matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (fRowLwb != source.fColLwb || fNcols != source.fNrows ||
fColLwb != source.fColLwb || fNcols != source.fNcols)
Error("operator*=(const TMatrix&)",
"matrices above are unsuitable for the inplace multiplication");
// One row of the old_target matrix
Real_t *const one_row = new Real_t[fNcols];
const Real_t *one_row_end = &one_row[fNcols];
Real_t *trp = fElements; // Pointer to the i-th row
for ( ; trp < &fElements[fNrows]; trp++) { // Go row-by-row in the target
Real_t *wrp, *orp; // work row pointers
for (wrp = trp, orp = one_row; orp < one_row_end; )
*orp++ = *wrp, wrp += fNrows; // Copy a row of old_target
Real_t *scp = source.fElements; // Source column pointer
for (wrp = trp; wrp < fElements+fNelems; wrp += fNrows) {
Double_t sum = 0; // Multiply a row of old_target
for (orp = one_row; orp < one_row_end; ) // by each col of source
sum += *orp++ * *scp++; // to get a row of new_target
*wrp = sum;
}
}
delete [] one_row;
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::operator*=(const TMatrixDiag &diag)
{
// Multiply a matrix by the diagonal of another matrix
// opt == "R" : matrix(i,j) *= diag(j) (default)
// else : matrix(i,j) *= diag(i)
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator*=(const TMatrixDiag&)", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (!diag.fMatrix->IsValid()) {
Error("operator*=(const TMatrixDiag&)", "diag matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (fNcols != diag.fNdiag) {
Error("operator*=(const TMatrixDiag&)", "matrix cannot be multiplied row-wise by the diagonal of the other matrix");
return *this;
}
Real_t *dp = diag.fPtr; // Diag ptr
Real_t *mp = fElements; // Matrix ptr
Int_t i;
for ( ; mp < fElements + fNelems; dp += diag.fInc)
for (i = 0; i < fNrows; i++)
*mp++ *= *dp;
Assert(dp < diag.fPtr + diag.fMatrix->fNelems + diag.fInc);
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::operator/=(const TMatrixDiag &diag)
{
// Divide a matrix by the diagonal of another matrix
// matrix(i,j) *= diag(j)
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator/=(const TMatrixDiag&)", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (!diag.fMatrix->IsValid()) {
Error("operator/=(const TMatrixDiag&)", "diag matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (fNcols != diag.fNdiag) {
Error("operator/=(const TMatrixDiag&)", "matrix cannot be divided by the diagonal of the other matrix");
return *this;
}
Real_t *dp = diag.fPtr; // Diag ptr
Real_t *mp = fElements; // Matrix ptr
Int_t i;
for ( ; mp < fElements + fNelems; dp += diag.fInc) {
Assert(*dp != 0.0);
for (i = 0; i < fNrows; i++)
*mp++ /= *dp;
}
Assert(dp < diag.fPtr + diag.fMatrix->fNelems + diag.fInc);
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::operator*=(const TMatrixColumn &col)
{
// Multiply a matrix by the column of another matrix
// matrix(i,j) *= another(i,k) for fixed k
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator*=(const TMatrixColumn&)", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (!col.fMatrix->IsValid()) {
Error("operator*=(const TMatrixColumn&)", "column matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (fNcols != col.fMatrix->fNcols) {
Error("operator*=(const TMatrixColumn&)", "matrix cannot be multiplied by the column of the other matrix");
return *this;
}
Real_t *cp = col.fPtr; // Column ptr
Real_t *mp = fElements; // Matrix ptr
Int_t i;
for ( ; mp < fElements + fNelems; cp++)
for (i = 0; i < fNrows; i++)
*mp++ *= *cp;
Assert(cp < col.fPtr + col.fMatrix->fNelems);
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::operator/=(const TMatrixColumn &col)
{
// Divide a matrix by the column of another matrix
// matrix(i,j) /= another(i,k) for fixed k
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator/=(const TMatrixColumn&)", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (!col.fMatrix->IsValid()) {
Error("operator/=(const TMatrixColumn&)", "column matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (fNcols != col.fMatrix->fNcols) {
Error("operator/=(const TMatrixColumn&)", "matrix cannot be divided by the column of the other matrix");
return *this;
}
Real_t *cp = col.fPtr; // Column ptr
Real_t *mp = fElements; // Matrix ptr
Int_t i;
for ( ; mp < fElements + fNelems; cp++) {
Assert(*cp != 0.0);
for (i = 0; i < fNrows; i++)
*mp++ /= *cp;
}
Assert(cp < col.fPtr + col.fMatrix->fNelems);
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::operator*=(const TMatrixRow &row)
{
// Multiply a matrix by the row of another matrix
// matrix(i,j) *= another(k,j) for fixed k
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator*=(const TMatrixRow&)", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (!row.fMatrix->IsValid()) {
Error("operator*=(const TMatrixRow&)", "row matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (fNrows != row.fMatrix->fNrows) {
Error("operator*=(const TMatrixRow&)", "matrix cannot be multiplied by the row of the other matrix");
return *this;
}
Real_t *rp = row.fPtr; // Row ptr
Real_t *mp = fElements; // Matrix ptr
Int_t i;
for ( ; mp < fElements + fNelems; rp = row.fPtr) {
for (i = 0; i < fNrows; i++) {
Assert(rp < row.fPtr+row.fMatrix->fNelems);
*mp++ *= *rp;
rp += row.fInc;
}
}
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TMatrix &TMatrix::operator/=(const TMatrixRow &row)
{
// Divide a matrix by the row of another matrix
// matrix(i,j) /= another(k,j) for fixed k
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("operator/=(const TMatrixRow&)", "matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (!row.fMatrix->IsValid()) {
Error("operator/=(const TMatrixRow&)", "row matrix not initialized");
return *this;
}
if (fNrows != row.fMatrix->fNrows) {
Error("operator/=(const TMatrixRow&)", "matrix cannot be divided by the row of the other matrix");
return *this;
}
Real_t *rp = row.fPtr; // Row ptr
Real_t *mp = fElements; // Matrix ptr
Int_t i;
for ( ; mp < fElements + fNelems; rp = row.fPtr) {
for (i = 0; i < fNrows; i++) {
Assert(rp < row.fPtr+row.fMatrix->fNelems);
Assert(*rp != 0.0);
*mp++ /= *rp;
rp += row.fInc;
}
}
return *this;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::AMultB(const TMatrix &a, const TMatrix &b)
{
// General matrix multiplication. Create a matrix C such that C = A * B.
// Note, matrix C needs to be allocated.
if (!a.IsValid()) {
Error("AMultB", "matrix a not initialized");
return;
}
if (!b.IsValid()) {
Error("AMultB", "matrix b not initialized");
return;
}
if (a.fNcols != b.fNrows || a.fColLwb != b.fRowLwb) {
Error("AMultB", "matrices a and b cannot be multiplied");
return;
}
Allocate(a.fNrows, b.fNcols, a.fRowLwb, b.fColLwb);
Real_t *arp; // Pointer to the i-th row of A
Real_t *bcp = b.fElements; // Pointer to the j-th col of B
Real_t *cp = fElements; // C is to be traversed in the natural
while (cp < fElements + fNelems) { // order, col-after-col
for (arp = a.fElements; arp < a.fElements + a.fNrows; ) {
Double_t cij = 0;
Real_t *bccp = bcp; // To scan the jth col of B
while (arp < a.fElements + a.fNelems) // Scan the i-th row of A and
cij += *bccp++ * *arp, arp += a.fNrows; // the j-th col of B
*cp++ = cij;
arp -= a.fNelems - 1; // arp points to (i+1)-th row
}
bcp += b.fNrows; // We're done with j-th col of both
} // B and C. Set bcp to the (j+1)-th col
Assert(cp == fElements + fNelems && bcp == b.fElements + b.fNelems);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::Mult(const TMatrix &a, const TMatrix &b)
{
// Compute C = A*B. The same as AMultB(), only matrix C is already
// allocated, and it is *this.
if (!a.IsValid()) {
Error("Mult", "matrix a not initialized");
return;
}
if (!b.IsValid()) {
Error("Mult", "matrix b not initialized");
return;
}
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("Mult", "matrix not initialized");
return;
}
if (a.fNcols != b.fNrows || a.fColLwb != b.fRowLwb) {
Error("Mult", "matrices a and b cannot be multiplied");
return;
}
if (fNrows != a.fNrows || fNcols != b.fNcols ||
fRowLwb != a.fRowLwb || fColLwb != b.fColLwb) {
Error("Mult", "product A*B is incompatible with the given matrix");
return;
}
Real_t *arp; // Pointer to the i-th row of A
Real_t *bcp = b.fElements; // Pointer to the j-th col of B
Real_t *cp = fElements; // C is to be traversed in the natural
while (cp < fElements + fNelems) { // order, col-after-col
for (arp = a.fElements; arp < a.fElements + a.fNrows; ) {
Double_t cij = 0;
Real_t *bccp = bcp; // To scan the jth col of B
while (arp < a.fElements + a.fNelems) // Scan the i-th row of A and
cij += *bccp++ * *arp, arp += a.fNrows; // the j-th col of B
*cp++ = cij;
arp -= a.fNelems - 1; // arp points to (i+1)-th row
}
bcp += b.fNrows; // We're done with j-th col of both
} // B and C. Set bcp to the (j+1)-th col
Assert(cp == fElements + fNelems && bcp == b.fElements + b.fNelems);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::AtMultB(const TMatrix &a, const TMatrix &b)
{
// Create a matrix C such that C = A' * B. In other words,
// c[i,j] = SUM{ a[k,i] * b[k,j] }. Note, matrix C needs to be allocated.
if (!a.IsValid()) {
Error("AtMultB", "matrix a not initialized");
return;
}
if (!b.IsValid()) {
Error("AtMultB", "matrix b not initialized");
return;
}
if (a.fNrows != b.fNrows || a.fRowLwb != b.fRowLwb) {
Error("AtMultB", "matrices above are unsuitable for A'B multiplication");
return;
}
Allocate(a.fNcols, b.fNcols, a.fColLwb, b.fColLwb);
Real_t *acp; // Pointer to the i-th col of A
Real_t *bcp = b.fElements; // Pointer to the j-th col of B
Real_t *cp = fElements; // C is to be traversed in the natural
while (cp < fElements + fNelems) { // order, col-after-col
for (acp = a.fElements; acp < a.fElements + a.fNelems; ) {
Double_t cij = 0; // Scan all cols of A
Real_t *bccp = bcp; // To scan the jth col of B
for (int i = 0; i < a.fNrows; i++) // Scan the i-th row of A and
cij += *bccp++ * *acp++; // the j-th col of B
*cp++ = cij;
}
bcp += b.fNrows; // We're done with j-th col of both
} // B and C. Set bcp to the (j+1)-th col
Assert(cp == fElements + fNelems && bcp == b.fElements + b.fNelems);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TMatrix::Determinant() const
{
// Compute the determinant of a general square matrix.
// Example: Matrix A; Double_t A.Determinant();
//
// Gauss-Jordan transformations of the matrix with a slight
// modification to take advantage of the *column*-wise arrangement
// of Matrix elements. Thus we eliminate matrix's columns rather than
// rows in the Gauss-Jordan transformations. Note that determinant
// is invariant to matrix transpositions.
// The matrix is copied to a special object of type TMatrixPivoting,
// where all Gauss-Jordan eliminations with full pivoting are to
// take place.
if (!IsValid()) {
Error("Determinant", "matrix not initialized");
return 0.0;
}
if (fNrows != fNcols) {
Error("Determinant", "can't obtain determinant of a non-square matrix");
return 0.0;
}
if (fRowLwb != fColLwb) {
Error("Determinant", "row and col lower bounds are inconsistent");
return 0.0;
}
Double_t det = 1;
const Real_t *m = fElements;
if (fNrows == 1) {
det = m[0];
} else if (fNrows == 2) {
det = m[0]*m[3]-m[1]*m[2];
} else if (fNrows == 3) {
det = m[0]*(m[4]*m[8]-m[7]*m[5])
-m[3]*(m[1]*m[8]-m[7]*m[2])
+m[6]*(m[1]*m[5]-m[4]*m[2]);
} else {
TMatrixPivoting mp(*this);
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k < fNcols && det != 0; k++)
det *= mp.PivotingAndElimination();
}
return det;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::Streamer(TBuffer &R__b)
{
// Stream an object of class TMatrix.
if (R__b.IsReading()) {
UInt_t R__s, R__c;
Version_t R__v = R__b.ReadVersion(&R__s, &R__c);
if (R__v > 1) {
TMatrix::Class()->ReadBuffer(R__b, this, R__v, R__s, R__c);
if (fNcols == 1) {
fIndex = &fElements;
} else {
if (fNcols <= 0) return;
fIndex = new Real_t*[fNcols];
if (fIndex)
memset(fIndex, 0, fNcols*sizeof(Real_t*));
Int_t i;
Real_t *col_p;
for (i = 0, col_p = &fElements[0]; i < fNcols; i++, col_p += fNrows)
fIndex[i] = col_p;
}
return;
}
//====process old versions before automatic schema evolution
TObject::Streamer(R__b);
R__b >> fNrows;
R__b >> fNcols;
R__b >> fRowLwb;
R__b >> fColLwb;
fNelems = R__b.ReadArray(fElements);
if (fNcols == 1) {
fIndex = &fElements;
} else {
fIndex = new Real_t*[fNcols];
if (fIndex)
memset(fIndex, 0, fNcols*sizeof(Real_t*));
Int_t i;
Real_t *col_p;
for (i = 0, col_p = &fElements[0]; i < fNcols; i++, col_p += fNrows)
fIndex[i] = col_p;
}
R__b.CheckByteCount(R__s, R__c, TMatrix::IsA());
//====end of old versions
} else {
TMatrix::Class()->WriteBuffer(R__b,this);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void Compare(const TMatrix &matrix1, const TMatrix &matrix2)
{
// Compare two matrices and print out the result of the comparison.
Int_t i, j;
if (!AreCompatible(matrix1, matrix2)) {
Error("Compare", "matrices are not compatible");
return;
}
printf("n\nComparison of two TMatrices:n");
Double_t norm1 = 0, norm2 = 0; // Norm of the Matrices
Double_t ndiff = 0; // Norm of the difference
Int_t imax = 0, jmax = 0; // For the elements that differ most
Real_t difmax = -1;
Real_t *mp1 = matrix1.fElements; // Matrix element pointers
Real_t *mp2 = matrix2.fElements;
for (j = 0; j < matrix1.fNcols; j++) // Due to the column-wise arrangement,
for (i = 0; i < matrix1.fNrows; i++) { // the row index changes first
Real_t mv1 = *mp1++;
Real_t mv2 = *mp2++;
Real_t diff = TMath::Abs(mv1-mv2);
if (diff > difmax) {
difmax = diff;
imax = i;
jmax = j;
}
norm1 += TMath::Abs(mv1);
norm2 += TMath::Abs(mv2);
ndiff += TMath::Abs(diff);
}
imax += matrix1.fRowLwb, jmax += matrix1.fColLwb;
printf("nMaximal discrepancy t\t%g", difmax);
printf("n occured at the pointt\t(%d,%d)", imax, jmax);
const Real_t mv1 = matrix1(imax,jmax);
const Real_t mv2 = matrix2(imax,jmax);
printf("n Matrix 1 element is t\t%g", mv1);
printf("n Matrix 2 element is t\t%g", mv2);
printf("n Absolute error v2[i]-v1[i]t\t%g", mv2-mv1);
printf("n Relative errort\tt\t%gn",
(mv2-mv1)/TMath::Max(TMath::Abs(mv2+mv1)/2,(Real_t)1e-7));
printf("n||Matrix 1|| t\tt%g", norm1);
printf("n||Matrix 2|| t\tt%g", norm2);
printf("n||Matrix1-Matrix2||t\tt\t%g", ndiff);
printf("n||Matrix1-Matrix2||/sqrt(||Matrix1|| ||Matrix2||)t%gn\n",
ndiff/TMath::Max(TMath::Sqrt(norm1*norm2), 1e-7));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void VerifyElementValue(const TMatrix &m, Real_t val)
{
// Validate that all elements of matrix have value val (within 1.e-5).
Int_t imax = 0, jmax = 0;
Double_t max_dev = 0;
Int_t i, j;
for (i = m.GetRowLwb(); i <= m.GetRowUpb(); i++)
for (j = m.GetColLwb(); j <= m.GetColUpb(); j++) {
Double_t dev = TMath::Abs(m(i,j)-val);
if (dev > max_dev)
imax = i, jmax = j, max_dev = dev;
}
if (max_dev == 0)
return;
else if(max_dev < 1e-5)
printf("Element (%d,%d) with value %g differs the most from whatn"
"was expected, %g, though the deviation %g is smalln",
imax,jmax,m(imax,jmax),val,max_dev);
else
Error("VerifyElementValue", "a significant difference from the expected value %gn"
"encountered for element (%d,%d) with value %g",
val,imax,jmax,m(imax,jmax));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void VerifyMatrixIdentity(const TMatrix &m1, const TMatrix &m2)
{
// Verify that elements of the two matrices are equal (within 1.e-5).
Int_t imax = 0, jmax = 0;
Double_t max_dev = 0;
Int_t i, j;
if (!AreCompatible(m1, m2)) {
Error("VerifyMatrixIdentity", "matrices are not compatible");
return;
}
for (i = m1.GetRowLwb(); i <= m1.GetRowUpb(); i++)
for (j = m1.GetColLwb(); j <= m1.GetColUpb(); j++) {
Double_t dev = TMath::Abs(m1(i,j)-m2(i,j));
if (dev > max_dev)
imax = i, jmax = j, max_dev = dev;
}
if (max_dev == 0)
return;
if (max_dev < 1e-5)
printf("Two (%d,%d) elements of matrices with values %g and %gn"
"differ the most, though the deviation %g is smalln",
imax,jmax,m1(imax,jmax),m2(imax,jmax),max_dev);
else
Error("VerifyMatrixIdentity", "a significant difference between the matrices encounteredn"
"at (%d,%d) element, with values %g and %g",
imax,jmax,m1(imax,jmax),m2(imax,jmax));
}
ROOT page - Class index - Top of the page
This page has been automatically generated. If you have any comments or suggestions about the page layout send a mail to ROOT support, or contact the developers with any questions or problems regarding ROOT.
![]() orthogonal transformation, where
each transformation eat away the off-diagonal elements, except the
inner most.
*/
//
const Int_t n = a.fNrows;
if (!a.IsValid()) {
gROOT->Error("Maketridiagonal", "matrix not initialized");
return;
}
if (a.fNrows != a.fNcols) {
gROOT->Error("Maketridiagonal", "matrix to tridiagonalize must be square");
return;
}
if (!a.IsSymmetric()) {
gROOT->Error("MakeTridiagonal", "Can only tridiagonalise symmetric matrix");
a.Zero();
d.Zero();
e.Zero();
return;
}
Real_t *pa = a.fElements;
Real_t *pd = d.fElements;
Real_t *pe = e.fElements;
Int_t i;
for (i = n-1; i > 0; i--) {
const Int_t l = i-1;
Double_t h = 0;
Double_t scale = 0;
if (l > 0) {
for (Int_t k = 0; k <= l; k++)
scale += TMath::Abs(pa[i+k*n]);
if (scale == 0)
// Skip transformation
pe[i] = pa[i+l*n];
else {
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k <= l; k++) {
// Use scaled elements of a for transformation
pa[i+k*n] /= scale;
// Calculate sigma in h
h += pa[i+k*n]*pa[i+k*n];
}
Double_t f = pa[i+l*n];
Double_t g = (f >= 0. ? -TMath::Sqrt(h) : TMath::Sqrt(h));
pe[i] = scale*g;
h -= f*g; // Now h is eq. (11.2.4) in "Numerical ..."
pa[i+l*n] = f-g;
f = 0;
Int_t j;
for (j = 0; j <= l; j++) {
// Store the u/H in ith column of a;
pa[j+i*n] = pa[i+j*n]/h;
// Form element A dot u in g;
g = 0;
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k <= j; k++)
g += pa[j+k*n]*pa[i+k*n];
for (k = j+1; k <= l; k++)
g += pa[k+j*n]*pa[i+k*n];
// Form element of vector p in temporarily unused element of
// e
pe[j] = g/h;
f += pe[j]*pa[i+j*n];
}
// Form K eq (11.2.11)
const Double_t hh = f/(h+h);
// Form vector q and store in e overwriting p
for (j = 0; j <= l; j++) {
f = pa[i+j*n];
pe[j] = g = pe[j]-hh*f;
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k <= j; k++)
// Reduce a, eq (11.2.13)
pa[j+k*n] -= (f*pe[k]+g*pa[i+k*n]);
}
}
}
else
pe[i] = pa[i+l*n];
pd[i] = h;
}
pd[0] = 0;
pe[0] = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Begin accumulation of transformation matrix
const Int_t l = i-1;
if (pd[i]) {
// This block is skipped if i = 0;
Int_t j;
for (j = 0; j <= l; j++) {
Double_t g = 0;
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k <= l; k++)
// Use vector u/H stored in a to form P dot Q
g += pa[i+k*n]*pa[k+j*n];
for (k = 0; k <= l; k++)
pa[k+j*n] -= g*pa[k+i*n];
}
}
pd[i] = pa[i+i*n];
pa[i+i*n] = 1;
Int_t j;
for (j = 0; j <= l; j++) {
pa[j+i*n] = pa[i+j*n] = 0;
}
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::MakeEigenVectors(TVector &d, TVector &e, TMatrix &z)
{
//
/*
PRIVATE METHOD:
orthogonal transformation, where
each transformation eat away the off-diagonal elements, except the
inner most.
*/
//
const Int_t n = a.fNrows;
if (!a.IsValid()) {
gROOT->Error("Maketridiagonal", "matrix not initialized");
return;
}
if (a.fNrows != a.fNcols) {
gROOT->Error("Maketridiagonal", "matrix to tridiagonalize must be square");
return;
}
if (!a.IsSymmetric()) {
gROOT->Error("MakeTridiagonal", "Can only tridiagonalise symmetric matrix");
a.Zero();
d.Zero();
e.Zero();
return;
}
Real_t *pa = a.fElements;
Real_t *pd = d.fElements;
Real_t *pe = e.fElements;
Int_t i;
for (i = n-1; i > 0; i--) {
const Int_t l = i-1;
Double_t h = 0;
Double_t scale = 0;
if (l > 0) {
for (Int_t k = 0; k <= l; k++)
scale += TMath::Abs(pa[i+k*n]);
if (scale == 0)
// Skip transformation
pe[i] = pa[i+l*n];
else {
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k <= l; k++) {
// Use scaled elements of a for transformation
pa[i+k*n] /= scale;
// Calculate sigma in h
h += pa[i+k*n]*pa[i+k*n];
}
Double_t f = pa[i+l*n];
Double_t g = (f >= 0. ? -TMath::Sqrt(h) : TMath::Sqrt(h));
pe[i] = scale*g;
h -= f*g; // Now h is eq. (11.2.4) in "Numerical ..."
pa[i+l*n] = f-g;
f = 0;
Int_t j;
for (j = 0; j <= l; j++) {
// Store the u/H in ith column of a;
pa[j+i*n] = pa[i+j*n]/h;
// Form element A dot u in g;
g = 0;
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k <= j; k++)
g += pa[j+k*n]*pa[i+k*n];
for (k = j+1; k <= l; k++)
g += pa[k+j*n]*pa[i+k*n];
// Form element of vector p in temporarily unused element of
// e
pe[j] = g/h;
f += pe[j]*pa[i+j*n];
}
// Form K eq (11.2.11)
const Double_t hh = f/(h+h);
// Form vector q and store in e overwriting p
for (j = 0; j <= l; j++) {
f = pa[i+j*n];
pe[j] = g = pe[j]-hh*f;
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k <= j; k++)
// Reduce a, eq (11.2.13)
pa[j+k*n] -= (f*pe[k]+g*pa[i+k*n]);
}
}
}
else
pe[i] = pa[i+l*n];
pd[i] = h;
}
pd[0] = 0;
pe[0] = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Begin accumulation of transformation matrix
const Int_t l = i-1;
if (pd[i]) {
// This block is skipped if i = 0;
Int_t j;
for (j = 0; j <= l; j++) {
Double_t g = 0;
Int_t k;
for (k = 0; k <= l; k++)
// Use vector u/H stored in a to form P dot Q
g += pa[i+k*n]*pa[k+j*n];
for (k = 0; k <= l; k++)
pa[k+j*n] -= g*pa[k+i*n];
}
}
pd[i] = pa[i+i*n];
pa[i+i*n] = 1;
Int_t j;
for (j = 0; j <= l; j++) {
pa[j+i*n] = pa[i+j*n] = 0;
}
}
}
//____________________________________________________________________
void TMatrix::MakeEigenVectors(TVector &d, TVector &e, TMatrix &z)
{
//
/*
PRIVATE METHOD:
![]() and
and ![]() so that
so that
![]() , where
, where ![]() is orthogonal and
is orthogonal and
![]() is lower triangular. The QL algorithm
consist of a
sequence of orthogonal transformations
is lower triangular. The QL algorithm
consist of a
sequence of orthogonal transformations