Model JLC Detector
Quantities to Measure
For each of produced particles
- (t,x) : time and position
- (E,p) : energy and momentum
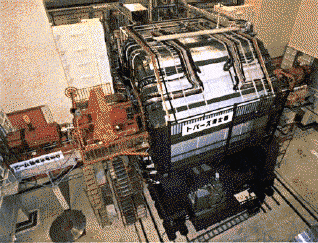 TOPAZ detector (TRISTAN)
TOPAZ detector (TRISTAN)
Configuration of Model JLC Detector
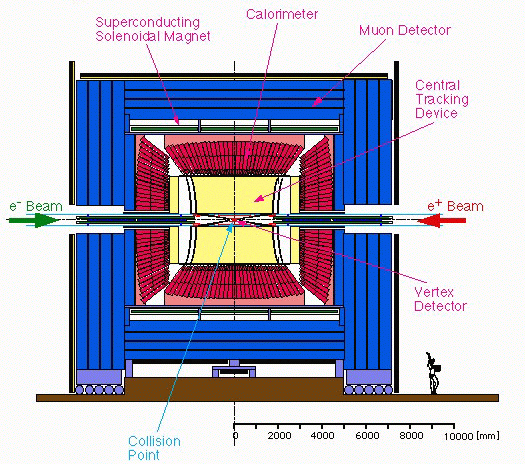
Role of Each Detector Component
- Vertex Detector : Particle Identification
- Detects production or decay points of particles. Since quasi-stable particles such as tau leptons, c- and b-quarks decay after flying a few mm from their production points, we can identify them by detecting their decay vertices.
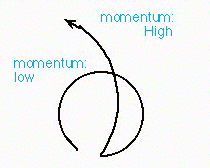
- Central Tracking Device : Momentum Measurement
- Detects tracks of long-lived charged particles (electrons, muons, charged pi or K mesons, and protons). The trajectories of these charged particles are bent by the magnetic field in the superconducting solenoid. The curvatures of their tracks measure their momenta.
- Calorimeter : Energy Measurement
- Measures energies of particles such as electrons and photons, which produce electromagnetic shower or those of particles such as charged pi mesons, charged and neutral K mesons, protons, and neutrons.

- Muon Detector : Muon Identification
- Muons penetrate the calorimeter without showering. Those charged particles which reach the muon detector surrounding the calorimeter are identified as muons.
To next page,
To previous page,
To contents
webmaster@www-jlc.kek.jp Feb 08, 1995


 TOPAZ detector (TRISTAN)
TOPAZ detector (TRISTAN)

