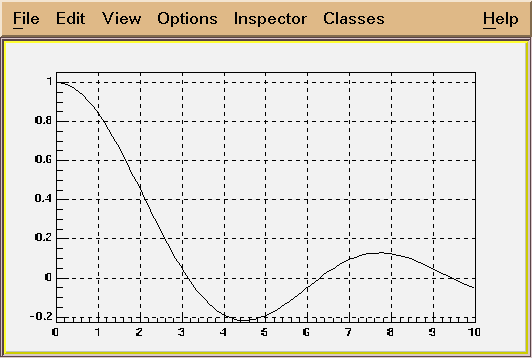
 */
//
//
// Example of a function of type B
// TF1 *f1 = new TF1("f1","[0]*x*sin([1]*x)",-3,3);
// This creates a function of variable x with 2 parameters.
// The parameters must be initialized via:
// f1->SetParameter(0,value_first_parameter);
// f1->SetParameter(1,value_second_parameter);
// Parameters may be given a name:
// f1->SetParName(0,"Constant");
//
// Example of function of type C
// Consider the macro myfunc.C below
//-------------macro myfunc.C-----------------------------
//Double_t myfunction(Double_t *x, Double_t *par)
//{
// Float_t xx =x[0];
// Double_t f = TMath::Abs(par[0]*sin(par[1]*xx)/xx);
// return f;
//}
//void myfunc()
//{
// TF1 *f1 = new TF1("myfunc",myfunction,0,10,2);
// f1->SetParameters(2,1);
// f1->SetParNames("constant","coefficient");
// f1->Draw();
//}
//void myfit()
//{
// TH1F *h1=new TH1F("h1","test",100,0,10);
// h1->FillRandom("myfunc",20000);
// TF1 *f1=gROOT->GetFunction("myfunc");
// f1->SetParameters(800,1);
// h1.Fit("myfunc");
//}
//--------end of macro myfunc.C---------------------------------
//
// In an interactive session you can do:
// Root > .L myfunc.C
// Root > myfunc();
// Root > myfit();
//
//
// TF1 objects can reference other TF1 objects (thanks John Odonnell)
// of type A or B defined above.This excludes CINT interpreted functions
// and compiled functions.
// However, there is a restriction. A function cannot reference a basic
// function if the basic function is a polynomial polN.
// Example:
//{
// TF1 *fcos = new TF1 ("fcos", "[0]*cos(x)", 0., 10.);
// fcos->SetParNames( "cos");
// fcos->SetParameter( 0, 1.1);
//
// TF1 *fsin = new TF1 ("fsin", "[0]*sin(x)", 0., 10.);
// fsin->SetParNames( "sin");
// fsin->SetParameter( 0, 2.1);
//
// TF1 *fsincos = new TF1 ("fsc", "fcos+fsin");
//
// TF1 *fs2 = new TF1 ("fs2", "fsc+fsc");
//}
//
// WHY TF1 CANNOT ACCEPT A CLASS MEMBER FUNCTION ?
// ===============================================
// This is a frequently asked question.
// C++ is a strongly typed language. There is no way for TF1 (without
// recompiling this class) to know about all possible user defined data types.
// This also apply to the case of a static class function.
//
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
TF1 *TF1::fgCurrent = 0;
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(): TFormula(), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 default constructor*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ======================
fXmin = 0;
fXmax = 0;
fNpx = 100;
fType = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fNDF = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fFunction = 0;
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
fAlpha = 0;
fBeta = 0;
fGamma = 0;
fParent = 0;
fSave = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fMethodCall = 0;
SetFillStyle(0);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const char *name,const char *formula, Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax)
:TFormula(name,formula), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 constructor using a formula definition*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =========================================
//*-*
//*-* See TFormula constructor for explanation of the formula syntax.
//*-*
//*-* See tutorials: fillrandom, first, fit1, formula1, multifit
//*-* for real examples.
//*-*
//*-* Creates a function of type A or B between xmin and xmax
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fXmin = xmin;
fXmax = xmax;
fNpx = 100;
fType = 0;
fFunction = 0;
if (fNpar) {
fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
for (int i = 0; i < fNpar; i++) {
fParErrors[i] = 0;
fParMin[i] = 0;
fParMax[i] = 0;
}
} else {
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
}
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fAlpha = 0;
fBeta = 0;
fGamma = 0;
fParent = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fNDF = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fSave = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fMethodCall = 0;
if (!gStyle) return;
SetLineColor(gStyle->GetFuncColor());
SetLineWidth(gStyle->GetFuncWidth());
SetLineStyle(gStyle->GetFuncStyle());
SetFillStyle(0);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const char *name, Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax, Int_t npar)
:TFormula(), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 constructor using name an interpreted function*-*-*-*
//*-* =======================================================
//*-*
//*-* Creates a function of type C between xmin and xmax.
//*-* name is the name of an interpreted CINT cunction.
//*-* The function is defined with npar parameters
//*-* fcn must be a function of type:
//*-* Double_t fcn(Double_t *x, Double_t *params)
//*-*
//*-* This constructor is called for functions of type C by CINT.
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fXmin = xmin;
fXmax = xmax;
fNpx = 100;
fType = 2;
fFunction = 0;
if (npar > 0 ) fNpar = npar;
if (fNpar) {
fNames = new TString[fNpar];
fParams = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
for (int i = 0; i < fNpar; i++) {
fParams[i] = 0;
fParErrors[i] = 0;
fParMin[i] = 0;
fParMax[i] = 0;
}
} else {
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
}
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fAlpha = 0;
fBeta = 0;
fGamma = 0;
fParent = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fNDF = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fSave = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fMethodCall = 0;
fNdim = 1;
TF1 *f1old = (TF1*)gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->FindObject(name);
if (f1old) delete f1old;
SetName(name);
gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->Add(this);
if (gStyle) {
SetLineColor(gStyle->GetFuncColor());
SetLineWidth(gStyle->GetFuncWidth());
SetLineStyle(gStyle->GetFuncStyle());
}
SetFillStyle(0);
SetTitle(name);
if (name) {
if (*name == '*') return; //case happens via SavePrimitive
fMethodCall = new TMethodCall();
fMethodCall->InitWithPrototype(name,"Double_t*,Double_t*");
fNumber = -1;
} else {
Printf("Function:%s cannot be compiled",name);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const char *name,void *fcn, Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax, Int_t npar)
:TFormula(), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 constructor using pointer to an interpreted function*-*-*-*
//*-* =======================================================
//*-*
//*-* See TFormula constructor for explanation of the formula syntax.
//*-*
//*-* Creates a function of type C between xmin and xmax.
//*-* The function is defined with npar parameters
//*-* fcn must be a function of type:
//*-* Double_t fcn(Double_t *x, Double_t *params)
//*-*
//*-* see tutorial; myfit for an example of use
//*-* also test/stress.cxx (see function stress1)
//*-*
//*-*
//*-* This constructor is called for functions of type C by CINT.
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fXmin = xmin;
fXmax = xmax;
fNpx = 100;
fType = 2;
fFunction = 0;
if (npar > 0 ) fNpar = npar;
if (fNpar) {
fNames = new TString[fNpar];
fParams = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
for (int i = 0; i < fNpar; i++) {
fParams[i] = 0;
fParErrors[i] = 0;
fParMin[i] = 0;
fParMax[i] = 0;
}
} else {
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
}
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fAlpha = 0;
fBeta = 0;
fGamma = 0;
fParent = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fNDF = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fSave = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fMethodCall = 0;
fNdim = 1;
TF1 *f1old = (TF1*)gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->FindObject(name);
if (f1old) delete f1old;
SetName(name);
gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->Add(this);
if (gStyle) {
SetLineColor(gStyle->GetFuncColor());
SetLineWidth(gStyle->GetFuncWidth());
SetLineStyle(gStyle->GetFuncStyle());
}
SetFillStyle(0);
if (!fcn) return;
char *funcname = G__p2f2funcname(fcn);
SetTitle(funcname);
if (funcname) {
fMethodCall = new TMethodCall();
fMethodCall->InitWithPrototype(funcname,"Double_t*,Double_t*");
fNumber = -1;
} else {
Printf("Function:%s cannot be compiled",name);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const char *name,Double_t (*fcn)(Double_t *, Double_t *), Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax, Int_t npar)
:TFormula(), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 constructor using a pointer to real function*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ===============================================
//*-*
//*-* npar is the number of free parameters used by the function
//*-*
//*-* This constructor creates a function of type C when invoked
//*-* with the normal C++ compiler.
//*-*
//*-* see test program test/stress.cxx (function stress1) for an example.
//*-* note the interface with an intermediate pointer.
//*-*
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fXmin = xmin;
fXmax = xmax;
fNpx = 100;
char *funcname = G__p2f2funcname((void*)fcn);
if (funcname) {
fType = 2;
SetTitle(funcname);
fMethodCall = new TMethodCall();
fMethodCall->InitWithPrototype(funcname,"Double_t*,Double_t*");
fNumber = -1;
fFunction = 0;
} else {
fType = 1;
fMethodCall = 0;
fFunction = fcn;
}
if (npar > 0 ) fNpar = npar;
if (fNpar) {
fNames = new TString[fNpar];
fParams = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
for (int i = 0; i < fNpar; i++) {
fParams[i] = 0;
fParErrors[i] = 0;
fParMin[i] = 0;
fParMax[i] = 0;
}
} else {
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
}
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fAlpha = 0;
fBeta = 0;
fGamma = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fSave = 0;
fParent = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fNDF = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fNdim = 1;
//*-*- Store formula in linked list of formula in ROOT
SetName(name);
if (gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->FindObject(name)) return;
gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->Add(this);
if (!gStyle) return;
SetLineColor(gStyle->GetFuncColor());
SetLineWidth(gStyle->GetFuncWidth());
SetLineStyle(gStyle->GetFuncStyle());
SetFillStyle(0);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::~TF1()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 default destructor*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =====================
if (fParMin) delete [] fParMin;
if (fParMax) delete [] fParMax;
if (fParErrors) delete [] fParErrors;
if (fIntegral) delete [] fIntegral;
if (fAlpha) delete [] fAlpha;
if (fBeta) delete [] fBeta;
if (fGamma) delete [] fGamma;
if (fSave) delete [] fSave;
delete fHistogram;
delete fMethodCall;
if (fParent) {
if (fParent->InheritsFrom(TH1::Class())) {
((TH1*)fParent)->GetListOfFunctions()->Remove(this);
return;
}
//parent may be a graph, or ??
//The pad utility manager is required (a plugin)
TVirtualUtilPad *util = (TVirtualUtilPad*)gROOT->GetListOfSpecials()->FindObject("R__TVirtualUtilPad");
if (!util) {
TPluginHandler *h;
if ((h = gROOT->GetPluginManager()->FindHandler("TVirtualUtilPad"))) {
if (h->LoadPlugin() == -1)
return;
h->ExecPlugin(0);
util = (TVirtualUtilPad*)gROOT->GetListOfSpecials()->FindObject("R__TVirtualUtilPad");
}
}
util->RemoveObject(fParent,this);
fParent = 0;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const TF1 &f1) : TFormula(f1), TAttLine(f1), TAttFill(f1), TAttMarker(f1)
{
((TF1&)f1).Copy(*this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Browse(TBrowser *)
{
Draw();
gPad->Update();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Copy(TObject &obj) const
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Copy this F1 to a new F1*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ========================
TFormula::Copy(obj);
TAttLine::Copy((TF1&)obj);
TAttFill::Copy((TF1&)obj);
TAttMarker::Copy((TF1&)obj);
((TF1&)obj).fXmin = fXmin;
((TF1&)obj).fXmax = fXmax;
((TF1&)obj).fNpx = fNpx;
((TF1&)obj).fType = fType;
((TF1&)obj).fFunction = fFunction;
((TF1&)obj).fChisquare = fChisquare;
((TF1&)obj).fNpfits = fNpfits;
((TF1&)obj).fNDF = fNDF;
((TF1&)obj).fMinimum = fMinimum;
((TF1&)obj).fMaximum = fMaximum;
((TF1&)obj).fParErrors = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fParMin = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fParMax = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fIntegral = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fAlpha = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fBeta = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fGamma = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fParent = fParent;
((TF1&)obj).fNsave = fNsave;
((TF1&)obj).fSave = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fHistogram = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fMethodCall = 0;
if (fNsave) {
((TF1&)obj).fSave = new Double_t[fNsave];
for (Int_t j=0;j<fNsave;j++) ((TF1&)obj).fSave[j] = fSave[j];
}
if (fNpar) {
((TF1&)obj).fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
((TF1&)obj).fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
((TF1&)obj).fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
Int_t i;
for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) ((TF1&)obj).fParErrors[i] = fParErrors[i];
for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) ((TF1&)obj).fParMin[i] = fParMin[i];
for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) ((TF1&)obj).fParMax[i] = fParMax[i];
}
if (fMethodCall) {
TMethodCall *m = new TMethodCall();
m->InitWithPrototype(fMethodCall->GetMethodName(),fMethodCall->GetProto());
((TF1&)obj).fMethodCall = m;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::Derivative(Double_t x, Double_t *params, Double_t epsilon)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return derivative of function at point x*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//
// The derivative is computed by computing the value of the function
// at points x-epsilon*range and x+epsilon*range (range=fXmax-fXmin).
// if params is NULL, use the current values of parameters
Double_t xx[2];
if (epsilon <= 0) epsilon = 0.001;
epsilon *= fXmax-fXmin;
xx[0] = x - epsilon;
xx[1] = x + epsilon;
if (xx[0] < fXmin) xx[0] = fXmin;
if (xx[1] > fXmax) xx[1] = fXmax;
Double_t f1,f2,deriv;
InitArgs(&xx[0],params);
f1 = EvalPar(&xx[0],params);
InitArgs(&xx[1],params);
f2 = EvalPar(&xx[1],params);
deriv = (f2-f1)/(xx[1]-xx[0]);
return deriv;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TF1::DistancetoPrimitive(Int_t px, Int_t py)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Compute distance from point px,py to a function*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ===============================================
//*-* Compute the closest distance of approach from point px,py to this function.
//*-* The distance is computed in pixels units.
//*-*
//*-* Algorithm:
//*-*
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
if (!fHistogram) return 9999;
Int_t distance = fHistogram->DistancetoPrimitive(px,py);
if (distance <= 1) return distance;
Double_t xx[1];
Double_t x = gPad->AbsPixeltoX(px);
xx[0] = gPad->PadtoX(x);
if (xx[0] < fXmin || xx[0] > fXmax) return distance;
Double_t fval = Eval(xx[0]);
Double_t y = gPad->YtoPad(fval);
Int_t pybin = gPad->YtoAbsPixel(y);
return TMath::Abs(py - pybin);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Draw(Option_t *option)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Draw this function with its current attributes*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==============================================
//*-*
//*-* Possible option values are:
//*-* "SAME" superimpose on top of existing picture
//*-* "L" connect all computed points with a straight line
//*-* "C" connect all computed points with a smooth curve.
//*-* "FC" draw a fill area below a smooth curve
//*-*
//*-* Note that the default value is "L". Therefore to draw on top
//*-* of an existing picture, specify option "LSAME"
//*-*
//*-* NB. You must use DrawCopy if you want to draw several times the same
//*-* function in the current canvas.
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
TString opt = option;
opt.ToLower();
if (gPad && !opt.Contains("same")) gPad->Clear();
AppendPad(option);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1 *TF1::DrawCopy(Option_t *option) const
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Draw a copy of this function with its current attributes*-*-*
//*-* ========================================================
//*-*
//*-* This function MUST be used instead of Draw when you want to draw
//*-* the same function with different parameters settings in the same canvas.
//*-*
//*-* Possible option values are:
//*-* "SAME" superimpose on top of existing picture
//*-* "L" connect all computed points with a straight line
//*-* "C" connect all computed points with a smooth curve.
//*-* "FC" draw a fill area below a smooth curve
//*-*
//*-* Note that the default value is "L". Therefore to draw on top
//*-* of an existing picture, specify option "LSAME"
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
TF1 *newf1 = new TF1();
Copy(*newf1);
newf1->AppendPad(option);
newf1->SetBit(kCanDelete);
return newf1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::DrawDerivative(Option_t *option)
{
// Draw derivative of this function
//
// An intermediate TGraph object is built and drawn with option.
//
// The resulting graph will be drawn into the current pad.
// If this function is used via the context menu, it recommended
// to create a new canvas/pad before invoking this function.
TVirtualPad *pad = gROOT->GetSelectedPad();
TVirtualPad *padsav = gPad;
if (pad) pad->cd();
char cmd[512];
sprintf(cmd,"{TGraph *R__%s_Derivative = new TGraph((TF1*)0x%lx,"d");R__%s_Derivative->Draw("%s");}",GetName(),(Long_t)this,GetName(),option);
gROOT->ProcessLine(cmd);
if (padsav) padsav->cd();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::DrawIntegral(Option_t *option)
{
// Draw integral of this function
//
// An intermediate TGraph object is built and drawn with option.
//
// The resulting graph will be drawn into the current pad.
// If this function is used via the context menu, it recommended
// to create a new canvas/pad before invoking this function.
TVirtualPad *pad = gROOT->GetSelectedPad();
TVirtualPad *padsav = gPad;
if (pad) pad->cd();
char cmd[512];
sprintf(cmd,"{TGraph *R__%s_Integral = new TGraph((TF1*)0x%lx,"i");R__%s_Integral->Draw("%s");}",GetName(),(Long_t)this,GetName(),option);
gROOT->ProcessLine(cmd);
if (padsav) padsav->cd();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::DrawF1(const char *formula, Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax, Option_t *option)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Draw formula between xmin and xmax*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==================================
//*-*
if (Compile(formula)) return;
SetRange(xmin, xmax);
Draw(option);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::DrawPanel()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*Display a panel with all function drawing options*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =================================================
//*-*
//*-* See class TDrawPanelHist for example
if (gPad) {
gROOT->SetSelectedPrimitive(this);
gROOT->SetSelectedPad(gPad);
}
//The pad utility manager is required (a plugin)
TVirtualUtilPad *util = (TVirtualUtilPad*)gROOT->GetListOfSpecials()->FindObject("R__TVirtualUtilPad");
if (!util) {
TPluginHandler *h;
if ((h = gROOT->GetPluginManager()->FindHandler("TVirtualUtilPad"))) {
if (h->LoadPlugin() == -1)
return;
h->ExecPlugin(0);
util = (TVirtualUtilPad*)gROOT->GetListOfSpecials()->FindObject("R__TVirtualUtilPad");
}
}
util->DrawPanel();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::Eval(Double_t x, Double_t y, Double_t z, Double_t t)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Evaluate this formula*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =====================
//*-*
//*-* Computes the value of this function (general case for a 3-d function)
//*-* at point x,y,z.
//*-* For a 1-d function give y=0 and z=0
//*-* The current value of variables x,y,z is passed through x, y and z.
//*-* The parameters used will be the ones in the array params if params is given
//*-* otherwise parameters will be taken from the stored data members fParams
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
Double_t xx[4];
xx[0] = x;
xx[1] = y;
xx[2] = z;
xx[3] = t;
InitArgs(xx,fParams);
return TF1::EvalPar(xx,fParams);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::EvalPar(const Double_t *x, const Double_t *params)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*Evaluate function with given coordinates and parameters*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =======================================================
//*-*
// Compute the value of this function at point defined by array x
// and current values of parameters in array params.
// If argument params is omitted or equal 0, the internal values
// of parameters (array fParams) will be used instead.
// For a 1-D function only x[0] must be given.
// In case of a multi-dimemsional function, the arrays x must be
// filled with the corresponding number of dimensions.
//
// WARNING. In case of an interpreted function (fType=2), it is the
// user's responsability to initialize the parameters via InitArgs
// before calling this function.
// InitArgs should be called at least once to specify the addresses
// of the arguments x and params.
// InitArgs should be called everytime these addresses change.
//
fgCurrent = this;
if (fType == 0) return TFormula::EvalPar(x,params);
Double_t result = 0;
if (fType == 1) {
if (fFunction) {
if (params) result = (*fFunction)((Double_t*)x,(Double_t*)params);
else result = (*fFunction)((Double_t*)x,fParams);
}else result = GetSave(x);
}
if (fType == 2) {
if (fMethodCall) fMethodCall->Execute(result);
else result = GetSave(x);
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::ExecuteEvent(Int_t event, Int_t px, Int_t py)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Execute action corresponding to one event*-*-*-*
//*-* =========================================
//*-* This member function is called when a F1 is clicked with the locator
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fHistogram->ExecuteEvent(event,px,py);
if (!gPad->GetView()) {
if (event == kMouseMotion) gPad->SetCursor(kHand);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::FixParameter(Int_t ipar, Double_t value)
{
// Fix the value of a parameter
// The specified value will be used in a fit operation
if (ipar < 0 || ipar > fNpar-1) return;
SetParameter(ipar,value);
if (value != 0) SetParLimits(ipar,value,value);
else SetParLimits(ipar,1,1);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1 *TF1::GetCurrent()
{
// static function returning the current function being processed
return fgCurrent;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TH1 *TF1::GetHistogram() const
{
// return a pointer to the histogram used to vusualize the function
if (fHistogram) return fHistogram;
// may be function has not yet be painted. force a pad update
//gPad->Modified();
//gPad->Update();
((TF1*)this)->Paint();
return fHistogram;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetMaximum(Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax) const
{
// return the maximum value of the function
// Method:
// the function is computed at fNpx points between xmin and xmax
// xxmax is the X value corresponding to the maximum function value
// An iterative procedure computes the maximum around xxmax
// until dx is less than 1e-9 *(fXmax-fXmin)
Double_t x,y;
if (xmin >= xmax) {xmin = fXmin; xmax = fXmax;}
Double_t dx = (xmax-xmin)/fNpx;
Double_t xxmax = xmin;
Double_t yymax = ((TF1*)this)->Eval(xmin+dx);
for (Int_t i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
x = xmin + (i+0.5)*dx;
y = ((TF1*)this)->Eval(x);
if (y > yymax) {xxmax = x; yymax = y;}
}
if (dx < 1.e-9*(fXmax-fXmin)) return yymax;
else return GetMaximum(TMath::Max(xmin,xxmax-dx), TMath::Min(xmax,xxmax+dx));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetMaximumX(Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax) const
{
// return the X value corresponding to the maximum value of the function
// Method:
// the function is computed at fNpx points between xmin and xmax
// xxmax is the X value corresponding to the maximum function value
// An iterative procedure computes the maximum around xxmax
// until dx is less than 1e-9 *(fXmax-fXmin)
Double_t x,y;
if (xmin >= xmax) {xmin = fXmin; xmax = fXmax;}
Double_t dx = (xmax-xmin)/fNpx;
Double_t xxmax = xmin;
Double_t yymax = ((TF1*)this)->Eval(xmin+dx);
for (Int_t i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
x = xmin + (i+0.5)*dx;
y = ((TF1*)this)->Eval(x);
if (y > yymax) {xxmax = x; yymax = y;}
}
if (dx < 1.e-9*(fXmax-fXmin)) return TMath::Min(xmax,xxmax);
else return GetMaximumX(TMath::Max(xmin,xxmax-dx), TMath::Min(xmax,xxmax+dx));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetMinimum(Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax) const
{
// return the minimum value of the function
// Method:
// the function is computed at fNpx points between xmin and xmax
// xxmax is the X value corresponding to the minimum function value
// An iterative procedure computes the minimum around xxmax
// until dx is less than 1e-9 *(fXmax-fXmin)
Double_t x,y;
if (xmin >= xmax) {xmin = fXmin; xmax = fXmax;}
Double_t dx = (xmax-xmin)/fNpx;
Double_t xxmin = xmin;
Double_t yymin = ((TF1*)this)->Eval(xmin+dx);
for (Int_t i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
x = xmin + (i+0.5)*dx;
y = ((TF1*)this)->Eval(x);
if (y < yymin) {xxmin = x; yymin = y;}
}
if (dx < 1.e-9*(fXmax-fXmin)) return yymin;
else return GetMinimum(TMath::Max(xmin,xxmin-dx), TMath::Min(xmax,xxmin+dx));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetMinimumX(Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax) const
{
// return the X value corresponding to the minimum value of the function
// Method:
// the function is computed at fNpx points between xmin and xmax
// xxmax is the X value corresponding to the minimum function value
// An iterative procedure computes the minimum around xxmax
// until dx is less than 1e-9 *(fXmax-fXmin)
Double_t x,y;
if (xmin >= xmax) {xmin = fXmin; xmax = fXmax;}
Double_t dx = (xmax-xmin)/fNpx;
Double_t xxmin = xmin;
Double_t yymin = ((TF1*)this)->Eval(xmin+dx);
for (Int_t i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
x = xmin + (i+0.5)*dx;
y = ((TF1*)this)->Eval(x);
if (y < yymin) {xxmin = x; yymin = y;}
}
if (dx < 1.e-9*(fXmax-fXmin)) return TMath::Min(xmax,xxmin);
else return GetMinimumX(TMath::Max(xmin,xxmin-dx), TMath::Min(xmax,xxmin+dx));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetX(Double_t fy, Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax) const
{
// return the X value corresponding to the function value fy for (xmin<x<xmax).
// Method:
// the function z = abs(f-fy) is computed at fNpx points between xmin and xmax
// xxmax is the X value corresponding to the minimum function value
// An iterative procedure computes the minimum around xxmax
// until dx is less than 1e-9 *(fXmax-fXmin).
// In case the problem has several solutions in X, the higher X solution is returned
// If the problem has no solution, the function returns the value of X
// where f(X) is closer to fy.
Double_t x,y;
if (xmin >= xmax) {xmin = fXmin; xmax = fXmax;}
Double_t dx = (xmax-xmin)/fNpx;
Double_t xxmin = xmin;
Double_t yymin = TMath::Abs(((TF1*)this)->Eval(xmin+dx) -fy);
for (Int_t i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
x = xmin + (i+0.5)*dx;
y = TMath::Abs(((TF1*)this)->Eval(x) -fy);
if (y < yymin) {xxmin = x; yymin = y;}
}
if (dx < 1.e-9*(fXmax-fXmin)) return TMath::Min(xmax,xxmin);
else return GetX(fy,TMath::Max(xmin,xxmin-dx), TMath::Min(xmax,xxmin+dx));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TF1::GetNDF() const
{
// return the number of degrees of freedom in the fit
// the fNDF parameter has been previously computed during a fit.
// The number of degrees of freedom corresponds to the number of points
// used in the fit minus the number of free parameters.
if (fNDF == 0) return fNpfits-fNpar;
return fNDF;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
char *TF1::GetObjectInfo(Int_t px, Int_t /* py */) const
{
// Redefines TObject::GetObjectInfo.
// Displays the function info (x, function value
// corresponding to cursor position px,py
//
static char info[64];
Double_t x = gPad->PadtoX(gPad->AbsPixeltoX(px));
sprintf(info,"(x=%g, f=%g)",x,((TF1*)this)->Eval(x));
return info;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetParError(Int_t ipar) const
{
//return value of parameter number ipar
if (ipar < 0 || ipar > fNpar-1) return 0;
return fParErrors[ipar];
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::GetParLimits(Int_t ipar, Double_t &parmin, Double_t &parmax)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*Return limits for parameter ipar*-*-*-*
//*-* ================================
parmin = 0;
parmax = 0;
if (ipar < 0 || ipar > fNpar-1) return;
if (fParMin) parmin = fParMin[ipar];
if (fParMax) parmax = fParMax[ipar];
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetProb() const
{
// return the fit probability
Int_t ndf = fNpfits - fNpar;
if (ndf <= 0) return 0;
return TMath::Prob(fChisquare,ndf);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TF1::GetQuantiles(Int_t nprobSum, Double_t *q, const Double_t *probSum)
{
// Compute Quantiles for density distribution of this function
// Quantile x_q of a probability distribution Function F is defined as
//
// F(x_q) = Integral_{xmin}^(x_q) f dx = q with 0 <= q <= 1.
//
// For instance the median x_0.5 of a distribution is defined as that value
// of the random variable for which the distribution function equals 0.5:
//
// F(x_0.5) = Probability(x < x_0.5) = 0.5
//
// code from Eddy Offermann, Renaissance
//
// input parameters
// - this TF1 function
// - nprobSum maximum size of array q and size of array probSum
// - probSum array of positions where quantiles will be computed.
// It is assumed to contain at least nprobSum values.
// output
// - return value nq (<=nprobSum) with the number of quantiles computed
// - array q filled with nq quantiles
//
// Getting quantiles from two histograms and storing results in a TGraph,
// a so-called QQ-plot
//
// TGraph *gr = new TGraph(nprob);
// f1->GetQuantiles(nprob,gr->GetX());
// f2->GetQuantiles(nprob,gr->GetY());
// gr->Draw("alp");
const Int_t npx = TMath::Min(250,TMath::Max(50,2*nprobSum));
const Double_t xMin = GetXmin();
const Double_t xMax = GetXmax();
const Double_t dx = (xMax-xMin)/npx;
TArrayD integral(npx+1);
TArrayD alpha(npx);
TArrayD beta(npx);
TArrayD gamma(npx);
integral[0] = 0;
Int_t intNegative = 0;
Int_t i;
for (i = 0; i < npx; i++) {
const Double_t *params = 0;
Double_t integ = Integral(Double_t(xMin+i*dx),Double_t(xMin+i*dx+dx),params);
if (integ < 0) {intNegative++; integ = -integ;}
integral[i+1] = integral[i] + integ;
}
if (intNegative > 0)
Warning("GetQuantiles","function:%s has %d negative values: abs assumed",
GetName(),intNegative);
if (integral[npx] == 0) {
Error("GetQuantiles","Integral of function is zero");
return 0;
}
const Double_t total = integral[npx];
for (i = 1; i <= npx; i++) integral[i] /= total;
//the integral r for each bin is approximated by a parabola
// x = alpha + beta*r +gamma*r**2
// compute the coefficients alpha, beta, gamma for each bin
for (i = 0; i < npx; i++) {
const Double_t x0 = xMin+dx*i;
const Double_t r2 = integral[i+1]-integral[i];
const Double_t r1 = Integral(x0,x0+0.5*dx)/total;
gamma[i] = (2*r2-4*r1)/(dx*dx);
beta[i] = r2/dx-gamma[i]*dx;
alpha[i] = x0;
gamma[i] *= 2;
}
// Be careful because of finite precision in the integral; Use the fact that the integral
// is monotone increasing
for (i = 0; i < nprobSum; i++) {
const Double_t r = probSum[i];
Int_t bin = TMath::Max(TMath::BinarySearch(npx+1,integral.GetArray(),r)-1,0);
while (bin < npx-1 && integral[bin+1] == r) {
if (integral[bin+2] == r) bin++;
else break;
}
const Double_t rr = r-integral[bin];
if (rr != 0.0) {
Double_t xx;
if (gamma[bin] && beta[bin]*beta[bin]+2*gamma[bin]*rr >= 0.0)
xx = (-beta[bin]+TMath::Sqrt(beta[bin]*beta[bin]+2*gamma[bin]*rr))/gamma[bin];
else
xx = rr/beta[bin];
q[i] = alpha[bin]+xx;
} else {
q[i] = alpha[bin];
if (integral[bin+1] == r) q[i] += dx;
}
}
return nprobSum;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetRandom()
{
// Return a random number following this function shape
//*-*
//*-* The distribution contained in the function fname (TF1) is integrated
//*-* over the channel contents.
//*-* It is normalized to 1.
//*-* For each bin the integral is approximated by a parabola.
//*-* The parabola coefficients are stored as non persistent data members
//*-* Getting one random number implies:
//*-* - Generating a random number between 0 and 1 (say r1)
//*-* - Look in which bin in the normalized integral r1 corresponds to
//*-* - Evaluate the parabolic curve in the selected bin to find
//*-* the corresponding X value.
//*-* The parabolic approximation is very good as soon as the number
//*-* of bins is greater than 50.
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-**-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
// Check if integral array must be build
if (fIntegral == 0) {
Double_t dx = (fXmax-fXmin)/fNpx;
fIntegral = new Double_t[fNpx+1];
fAlpha = new Double_t[fNpx];
fBeta = new Double_t[fNpx];
fGamma = new Double_t[fNpx];
fIntegral[0] = 0;
Double_t integ;
Int_t intNegative = 0;
Int_t i;
for (i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
integ = Integral(Double_t(fXmin+i*dx), Double_t(fXmin+i*dx+dx));
if (integ < 0) {intNegative++; integ = -integ;}
fIntegral[i+1] = fIntegral[i] + integ;
}
if (intNegative > 0) {
Warning("GetRandom","function:%s has %d negative values: abs assumed",GetName(),intNegative);
}
if (fIntegral[fNpx] == 0) {
Error("GetRandom","Integral of function is zero");
return 0;
}
Double_t total = fIntegral[fNpx];
for (i=1;i<=fNpx;i++) { // normalize integral to 1
fIntegral[i] /= total;
}
//the integral r for each bin is approximated by a parabola
// x = alpha + beta*r +gamma*r**2
// compute the coefficients alpha, beta, gamma for each bin
Double_t x0,r1,r2;
for (i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
x0 = fXmin+i*dx;
r2 = fIntegral[i+1] - fIntegral[i];
r1 = Integral(x0,x0+0.5*dx)/total;
fGamma[i] = (2*r2 - 4*r1)/(dx*dx);
fBeta[i] = r2/dx - fGamma[i]*dx;
fAlpha[i] = x0;
fGamma[i] *= 2;
}
}
// return random number
Double_t r = gRandom->Rndm();
Int_t bin = TMath::BinarySearch(fNpx,fIntegral,r);
Double_t rr = r - fIntegral[bin];
Double_t xx;
if(fGamma[bin])
xx = (-fBeta[bin] + TMath::Sqrt(fBeta[bin]*fBeta[bin]+2*fGamma[bin]*rr))/fGamma[bin];
else
xx = rr/fBeta[bin];
Double_t x = fAlpha[bin] + xx;
return x;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetRandom(Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax)
{
// Return a random number following this function shape in [xmin,xmax]
//*-*
//*-* The distribution contained in the function fname (TF1) is integrated
//*-* over the channel contents.
//*-* It is normalized to 1.
//*-* For each bin the integral is approximated by a parabola.
//*-* The parabola coefficients are stored as non persistent data members
//*-* Getting one random number implies:
//*-* - Generating a random number between 0 and 1 (say r1)
//*-* - Look in which bin in the normalized integral r1 corresponds to
//*-* - Evaluate the parabolic curve in the selected bin to find
//*-* the corresponding X value.
//*-* The parabolic approximation is very good as soon as the number
//*-* of bins is greater than 50.
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-**-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
// Check if integral array must be build
if (fIntegral == 0) {
Double_t dx = (fXmax-fXmin)/fNpx;
fIntegral = new Double_t[fNpx+1];
fAlpha = new Double_t[fNpx];
fBeta = new Double_t[fNpx];
fGamma = new Double_t[fNpx];
fIntegral[0] = 0;
Double_t integ;
Int_t intNegative = 0;
Int_t i;
for (i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
integ = Integral(Double_t(fXmin+i*dx), Double_t(fXmin+i*dx+dx));
if (integ < 0) {intNegative++; integ = -integ;}
fIntegral[i+1] = fIntegral[i] + integ;
}
if (intNegative > 0) {
Warning("GetRandom","function:%s has %d negative values: abs assumed",GetName(),intNegative);
}
if (fIntegral[fNpx] == 0) {
Error("GetRandom","Integral of function is zero");
return 0;
}
Double_t total = fIntegral[fNpx];
for (i=1;i<=fNpx;i++) { // normalize integral to 1
fIntegral[i] /= total;
}
//the integral r for each bin is approximated by a parabola
// x = alpha + beta*r +gamma*r**2
// compute the coefficients alpha, beta, gamma for each bin
Double_t x0,r1,r2;
for (i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
x0 = fXmin+i*dx;
r2 = fIntegral[i+1] - fIntegral[i];
r1 = Integral(x0,x0+0.5*dx)/total;
fGamma[i] = (2*r2 - 4*r1)/(dx*dx);
fBeta[i] = r2/dx - fGamma[i]*dx;
fAlpha[i] = x0;
fGamma[i] *= 2;
}
}
// return random number
Double_t dx = (fXmax-fXmin)/fNpx;
Int_t nbinmin = (Int_t)((xmin-fXmin)/dx);
Int_t nbinmax = (Int_t)((xmax-fXmin)/dx)+2;
if(nbinmax>fNpx) nbinmax=fNpx;
Double_t pmin=fIntegral[nbinmin];
Double_t pmax=fIntegral[nbinmax];
Double_t r,x,xx,rr;
do {
r = gRandom->Uniform(pmin,pmax);
Int_t bin = TMath::BinarySearch(fNpx,fIntegral,r);
rr = r - fIntegral[bin];
if(fGamma[bin])
xx = (-fBeta[bin] + TMath::Sqrt(fBeta[bin]*fBeta[bin]+2*fGamma[bin]*rr))/fGamma[bin];
else
xx = rr/fBeta[bin];
x = fAlpha[bin] + xx;
} while(x<xmin || x>xmax);
return x;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::GetRange(Double_t &xmin, Double_t &xmax) const
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return range of a 1-D function*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==============================
xmin = fXmin;
xmax = fXmax;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::GetRange(Double_t &xmin, Double_t &ymin, Double_t &xmax, Double_t &ymax) const
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return range of a 2-D function*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==============================
xmin = fXmin;
xmax = fXmax;
ymin = 0;
ymax = 0;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::GetRange(Double_t &xmin, Double_t &ymin, Double_t &zmin, Double_t &xmax, Double_t &ymax, Double_t &zmax) const
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return range of function*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ========================
xmin = fXmin;
xmax = fXmax;
ymin = 0;
ymax = 0;
zmin = 0;
zmax = 0;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetSave(const Double_t *xx)
{
// Get value corresponding to X in array of fSave values
if (fNsave <= 0) return 0;
if (fSave == 0) return 0;
Int_t np = fNsave - 3;
Double_t xmin = Double_t(fSave[np+1]);
Double_t xmax = Double_t(fSave[np+2]);
Double_t x = Double_t(xx[0]);
Double_t dx = (xmax-xmin)/np;
if (x < xmin || x > xmax) return 0;
if (dx <= 0) return 0;
Int_t bin = Int_t((x-xmin)/dx);
Double_t xlow = xmin + bin*dx;
Double_t xup = xlow + dx;
Double_t ylow = fSave[bin];
Double_t yup = fSave[bin+1];
Double_t y = ((xup*ylow-xlow*yup) + x*(yup-ylow))/dx;
return y;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TAxis *TF1::GetXaxis() const
{
// Get x axis of the function.
//if (!gPad) return 0;
TH1 *h = GetHistogram();
if (!h) return 0;
return h->GetXaxis();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TAxis *TF1::GetYaxis() const
{
// Get y axis of the function.
//if (!gPad) return 0;
TH1 *h = GetHistogram();
if (!h) return 0;
return h->GetYaxis();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::InitArgs(const Double_t *x, const Double_t *params)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Initialize parameters addresses*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ===============================
if (fMethodCall) {
Long_t args[2];
args[0] = (Long_t)x;
if (params) args[1] = (Long_t)params;
else args[1] = (Long_t)fParams;
fMethodCall->SetParamPtrs(args);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::InitStandardFunctions()
{
// Create the basic function objects
TF1 *f1;
if (!gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->FindObject("gaus")) {
f1 = new TF1("gaus","gaus",-1,1); f1->SetParameters(1,0,1);
f1 = new TF1("landau","landau",-1,1); f1->SetParameters(1,0,1);
f1 = new TF1("expo","expo",-1,1); f1->SetParameters(1,1);
for (Int_t i=0;i<10;i++) {
f1 = new TF1(Form("pol%d",i),Form("pol%d",i),-1,1);
f1->SetParameters(1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1);
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::Integral(Double_t a, Double_t b, const Double_t *params, Double_t epsilon)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return Integral of function between a and b*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//
// based on original CERNLIB routine DGAUSS by Sigfried Kolbig
// converted to C++ by Rene Brun
//
//
/*
*/
//
//
// Example of a function of type B
// TF1 *f1 = new TF1("f1","[0]*x*sin([1]*x)",-3,3);
// This creates a function of variable x with 2 parameters.
// The parameters must be initialized via:
// f1->SetParameter(0,value_first_parameter);
// f1->SetParameter(1,value_second_parameter);
// Parameters may be given a name:
// f1->SetParName(0,"Constant");
//
// Example of function of type C
// Consider the macro myfunc.C below
//-------------macro myfunc.C-----------------------------
//Double_t myfunction(Double_t *x, Double_t *par)
//{
// Float_t xx =x[0];
// Double_t f = TMath::Abs(par[0]*sin(par[1]*xx)/xx);
// return f;
//}
//void myfunc()
//{
// TF1 *f1 = new TF1("myfunc",myfunction,0,10,2);
// f1->SetParameters(2,1);
// f1->SetParNames("constant","coefficient");
// f1->Draw();
//}
//void myfit()
//{
// TH1F *h1=new TH1F("h1","test",100,0,10);
// h1->FillRandom("myfunc",20000);
// TF1 *f1=gROOT->GetFunction("myfunc");
// f1->SetParameters(800,1);
// h1.Fit("myfunc");
//}
//--------end of macro myfunc.C---------------------------------
//
// In an interactive session you can do:
// Root > .L myfunc.C
// Root > myfunc();
// Root > myfit();
//
//
// TF1 objects can reference other TF1 objects (thanks John Odonnell)
// of type A or B defined above.This excludes CINT interpreted functions
// and compiled functions.
// However, there is a restriction. A function cannot reference a basic
// function if the basic function is a polynomial polN.
// Example:
//{
// TF1 *fcos = new TF1 ("fcos", "[0]*cos(x)", 0., 10.);
// fcos->SetParNames( "cos");
// fcos->SetParameter( 0, 1.1);
//
// TF1 *fsin = new TF1 ("fsin", "[0]*sin(x)", 0., 10.);
// fsin->SetParNames( "sin");
// fsin->SetParameter( 0, 2.1);
//
// TF1 *fsincos = new TF1 ("fsc", "fcos+fsin");
//
// TF1 *fs2 = new TF1 ("fs2", "fsc+fsc");
//}
//
// WHY TF1 CANNOT ACCEPT A CLASS MEMBER FUNCTION ?
// ===============================================
// This is a frequently asked question.
// C++ is a strongly typed language. There is no way for TF1 (without
// recompiling this class) to know about all possible user defined data types.
// This also apply to the case of a static class function.
//
//------------------------------------------------------------------------
TF1 *TF1::fgCurrent = 0;
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(): TFormula(), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 default constructor*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ======================
fXmin = 0;
fXmax = 0;
fNpx = 100;
fType = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fNDF = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fFunction = 0;
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
fAlpha = 0;
fBeta = 0;
fGamma = 0;
fParent = 0;
fSave = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fMethodCall = 0;
SetFillStyle(0);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const char *name,const char *formula, Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax)
:TFormula(name,formula), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 constructor using a formula definition*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =========================================
//*-*
//*-* See TFormula constructor for explanation of the formula syntax.
//*-*
//*-* See tutorials: fillrandom, first, fit1, formula1, multifit
//*-* for real examples.
//*-*
//*-* Creates a function of type A or B between xmin and xmax
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fXmin = xmin;
fXmax = xmax;
fNpx = 100;
fType = 0;
fFunction = 0;
if (fNpar) {
fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
for (int i = 0; i < fNpar; i++) {
fParErrors[i] = 0;
fParMin[i] = 0;
fParMax[i] = 0;
}
} else {
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
}
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fAlpha = 0;
fBeta = 0;
fGamma = 0;
fParent = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fNDF = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fSave = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fMethodCall = 0;
if (!gStyle) return;
SetLineColor(gStyle->GetFuncColor());
SetLineWidth(gStyle->GetFuncWidth());
SetLineStyle(gStyle->GetFuncStyle());
SetFillStyle(0);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const char *name, Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax, Int_t npar)
:TFormula(), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 constructor using name an interpreted function*-*-*-*
//*-* =======================================================
//*-*
//*-* Creates a function of type C between xmin and xmax.
//*-* name is the name of an interpreted CINT cunction.
//*-* The function is defined with npar parameters
//*-* fcn must be a function of type:
//*-* Double_t fcn(Double_t *x, Double_t *params)
//*-*
//*-* This constructor is called for functions of type C by CINT.
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fXmin = xmin;
fXmax = xmax;
fNpx = 100;
fType = 2;
fFunction = 0;
if (npar > 0 ) fNpar = npar;
if (fNpar) {
fNames = new TString[fNpar];
fParams = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
for (int i = 0; i < fNpar; i++) {
fParams[i] = 0;
fParErrors[i] = 0;
fParMin[i] = 0;
fParMax[i] = 0;
}
} else {
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
}
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fAlpha = 0;
fBeta = 0;
fGamma = 0;
fParent = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fNDF = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fSave = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fMethodCall = 0;
fNdim = 1;
TF1 *f1old = (TF1*)gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->FindObject(name);
if (f1old) delete f1old;
SetName(name);
gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->Add(this);
if (gStyle) {
SetLineColor(gStyle->GetFuncColor());
SetLineWidth(gStyle->GetFuncWidth());
SetLineStyle(gStyle->GetFuncStyle());
}
SetFillStyle(0);
SetTitle(name);
if (name) {
if (*name == '*') return; //case happens via SavePrimitive
fMethodCall = new TMethodCall();
fMethodCall->InitWithPrototype(name,"Double_t*,Double_t*");
fNumber = -1;
} else {
Printf("Function:%s cannot be compiled",name);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const char *name,void *fcn, Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax, Int_t npar)
:TFormula(), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 constructor using pointer to an interpreted function*-*-*-*
//*-* =======================================================
//*-*
//*-* See TFormula constructor for explanation of the formula syntax.
//*-*
//*-* Creates a function of type C between xmin and xmax.
//*-* The function is defined with npar parameters
//*-* fcn must be a function of type:
//*-* Double_t fcn(Double_t *x, Double_t *params)
//*-*
//*-* see tutorial; myfit for an example of use
//*-* also test/stress.cxx (see function stress1)
//*-*
//*-*
//*-* This constructor is called for functions of type C by CINT.
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fXmin = xmin;
fXmax = xmax;
fNpx = 100;
fType = 2;
fFunction = 0;
if (npar > 0 ) fNpar = npar;
if (fNpar) {
fNames = new TString[fNpar];
fParams = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
for (int i = 0; i < fNpar; i++) {
fParams[i] = 0;
fParErrors[i] = 0;
fParMin[i] = 0;
fParMax[i] = 0;
}
} else {
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
}
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fAlpha = 0;
fBeta = 0;
fGamma = 0;
fParent = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fNDF = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fSave = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fMethodCall = 0;
fNdim = 1;
TF1 *f1old = (TF1*)gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->FindObject(name);
if (f1old) delete f1old;
SetName(name);
gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->Add(this);
if (gStyle) {
SetLineColor(gStyle->GetFuncColor());
SetLineWidth(gStyle->GetFuncWidth());
SetLineStyle(gStyle->GetFuncStyle());
}
SetFillStyle(0);
if (!fcn) return;
char *funcname = G__p2f2funcname(fcn);
SetTitle(funcname);
if (funcname) {
fMethodCall = new TMethodCall();
fMethodCall->InitWithPrototype(funcname,"Double_t*,Double_t*");
fNumber = -1;
} else {
Printf("Function:%s cannot be compiled",name);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const char *name,Double_t (*fcn)(Double_t *, Double_t *), Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax, Int_t npar)
:TFormula(), TAttLine(), TAttFill(), TAttMarker()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 constructor using a pointer to real function*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ===============================================
//*-*
//*-* npar is the number of free parameters used by the function
//*-*
//*-* This constructor creates a function of type C when invoked
//*-* with the normal C++ compiler.
//*-*
//*-* see test program test/stress.cxx (function stress1) for an example.
//*-* note the interface with an intermediate pointer.
//*-*
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fXmin = xmin;
fXmax = xmax;
fNpx = 100;
char *funcname = G__p2f2funcname((void*)fcn);
if (funcname) {
fType = 2;
SetTitle(funcname);
fMethodCall = new TMethodCall();
fMethodCall->InitWithPrototype(funcname,"Double_t*,Double_t*");
fNumber = -1;
fFunction = 0;
} else {
fType = 1;
fMethodCall = 0;
fFunction = fcn;
}
if (npar > 0 ) fNpar = npar;
if (fNpar) {
fNames = new TString[fNpar];
fParams = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
for (int i = 0; i < fNpar; i++) {
fParams[i] = 0;
fParErrors[i] = 0;
fParMin[i] = 0;
fParMax[i] = 0;
}
} else {
fParErrors = 0;
fParMin = 0;
fParMax = 0;
}
fChisquare = 0;
fIntegral = 0;
fAlpha = 0;
fBeta = 0;
fGamma = 0;
fNsave = 0;
fSave = 0;
fParent = 0;
fNpfits = 0;
fNDF = 0;
fHistogram = 0;
fMinimum = -1111;
fMaximum = -1111;
fNdim = 1;
//*-*- Store formula in linked list of formula in ROOT
SetName(name);
if (gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->FindObject(name)) return;
gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->Add(this);
if (!gStyle) return;
SetLineColor(gStyle->GetFuncColor());
SetLineWidth(gStyle->GetFuncWidth());
SetLineStyle(gStyle->GetFuncStyle());
SetFillStyle(0);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::~TF1()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*F1 default destructor*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =====================
if (fParMin) delete [] fParMin;
if (fParMax) delete [] fParMax;
if (fParErrors) delete [] fParErrors;
if (fIntegral) delete [] fIntegral;
if (fAlpha) delete [] fAlpha;
if (fBeta) delete [] fBeta;
if (fGamma) delete [] fGamma;
if (fSave) delete [] fSave;
delete fHistogram;
delete fMethodCall;
if (fParent) {
if (fParent->InheritsFrom(TH1::Class())) {
((TH1*)fParent)->GetListOfFunctions()->Remove(this);
return;
}
//parent may be a graph, or ??
//The pad utility manager is required (a plugin)
TVirtualUtilPad *util = (TVirtualUtilPad*)gROOT->GetListOfSpecials()->FindObject("R__TVirtualUtilPad");
if (!util) {
TPluginHandler *h;
if ((h = gROOT->GetPluginManager()->FindHandler("TVirtualUtilPad"))) {
if (h->LoadPlugin() == -1)
return;
h->ExecPlugin(0);
util = (TVirtualUtilPad*)gROOT->GetListOfSpecials()->FindObject("R__TVirtualUtilPad");
}
}
util->RemoveObject(fParent,this);
fParent = 0;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1::TF1(const TF1 &f1) : TFormula(f1), TAttLine(f1), TAttFill(f1), TAttMarker(f1)
{
((TF1&)f1).Copy(*this);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Browse(TBrowser *)
{
Draw();
gPad->Update();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Copy(TObject &obj) const
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Copy this F1 to a new F1*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ========================
TFormula::Copy(obj);
TAttLine::Copy((TF1&)obj);
TAttFill::Copy((TF1&)obj);
TAttMarker::Copy((TF1&)obj);
((TF1&)obj).fXmin = fXmin;
((TF1&)obj).fXmax = fXmax;
((TF1&)obj).fNpx = fNpx;
((TF1&)obj).fType = fType;
((TF1&)obj).fFunction = fFunction;
((TF1&)obj).fChisquare = fChisquare;
((TF1&)obj).fNpfits = fNpfits;
((TF1&)obj).fNDF = fNDF;
((TF1&)obj).fMinimum = fMinimum;
((TF1&)obj).fMaximum = fMaximum;
((TF1&)obj).fParErrors = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fParMin = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fParMax = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fIntegral = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fAlpha = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fBeta = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fGamma = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fParent = fParent;
((TF1&)obj).fNsave = fNsave;
((TF1&)obj).fSave = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fHistogram = 0;
((TF1&)obj).fMethodCall = 0;
if (fNsave) {
((TF1&)obj).fSave = new Double_t[fNsave];
for (Int_t j=0;j<fNsave;j++) ((TF1&)obj).fSave[j] = fSave[j];
}
if (fNpar) {
((TF1&)obj).fParErrors = new Double_t[fNpar];
((TF1&)obj).fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar];
((TF1&)obj).fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar];
Int_t i;
for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) ((TF1&)obj).fParErrors[i] = fParErrors[i];
for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) ((TF1&)obj).fParMin[i] = fParMin[i];
for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) ((TF1&)obj).fParMax[i] = fParMax[i];
}
if (fMethodCall) {
TMethodCall *m = new TMethodCall();
m->InitWithPrototype(fMethodCall->GetMethodName(),fMethodCall->GetProto());
((TF1&)obj).fMethodCall = m;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::Derivative(Double_t x, Double_t *params, Double_t epsilon)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return derivative of function at point x*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//
// The derivative is computed by computing the value of the function
// at points x-epsilon*range and x+epsilon*range (range=fXmax-fXmin).
// if params is NULL, use the current values of parameters
Double_t xx[2];
if (epsilon <= 0) epsilon = 0.001;
epsilon *= fXmax-fXmin;
xx[0] = x - epsilon;
xx[1] = x + epsilon;
if (xx[0] < fXmin) xx[0] = fXmin;
if (xx[1] > fXmax) xx[1] = fXmax;
Double_t f1,f2,deriv;
InitArgs(&xx[0],params);
f1 = EvalPar(&xx[0],params);
InitArgs(&xx[1],params);
f2 = EvalPar(&xx[1],params);
deriv = (f2-f1)/(xx[1]-xx[0]);
return deriv;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TF1::DistancetoPrimitive(Int_t px, Int_t py)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Compute distance from point px,py to a function*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ===============================================
//*-* Compute the closest distance of approach from point px,py to this function.
//*-* The distance is computed in pixels units.
//*-*
//*-* Algorithm:
//*-*
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
if (!fHistogram) return 9999;
Int_t distance = fHistogram->DistancetoPrimitive(px,py);
if (distance <= 1) return distance;
Double_t xx[1];
Double_t x = gPad->AbsPixeltoX(px);
xx[0] = gPad->PadtoX(x);
if (xx[0] < fXmin || xx[0] > fXmax) return distance;
Double_t fval = Eval(xx[0]);
Double_t y = gPad->YtoPad(fval);
Int_t pybin = gPad->YtoAbsPixel(y);
return TMath::Abs(py - pybin);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Draw(Option_t *option)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Draw this function with its current attributes*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==============================================
//*-*
//*-* Possible option values are:
//*-* "SAME" superimpose on top of existing picture
//*-* "L" connect all computed points with a straight line
//*-* "C" connect all computed points with a smooth curve.
//*-* "FC" draw a fill area below a smooth curve
//*-*
//*-* Note that the default value is "L". Therefore to draw on top
//*-* of an existing picture, specify option "LSAME"
//*-*
//*-* NB. You must use DrawCopy if you want to draw several times the same
//*-* function in the current canvas.
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
TString opt = option;
opt.ToLower();
if (gPad && !opt.Contains("same")) gPad->Clear();
AppendPad(option);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1 *TF1::DrawCopy(Option_t *option) const
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Draw a copy of this function with its current attributes*-*-*
//*-* ========================================================
//*-*
//*-* This function MUST be used instead of Draw when you want to draw
//*-* the same function with different parameters settings in the same canvas.
//*-*
//*-* Possible option values are:
//*-* "SAME" superimpose on top of existing picture
//*-* "L" connect all computed points with a straight line
//*-* "C" connect all computed points with a smooth curve.
//*-* "FC" draw a fill area below a smooth curve
//*-*
//*-* Note that the default value is "L". Therefore to draw on top
//*-* of an existing picture, specify option "LSAME"
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
TF1 *newf1 = new TF1();
Copy(*newf1);
newf1->AppendPad(option);
newf1->SetBit(kCanDelete);
return newf1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::DrawDerivative(Option_t *option)
{
// Draw derivative of this function
//
// An intermediate TGraph object is built and drawn with option.
//
// The resulting graph will be drawn into the current pad.
// If this function is used via the context menu, it recommended
// to create a new canvas/pad before invoking this function.
TVirtualPad *pad = gROOT->GetSelectedPad();
TVirtualPad *padsav = gPad;
if (pad) pad->cd();
char cmd[512];
sprintf(cmd,"{TGraph *R__%s_Derivative = new TGraph((TF1*)0x%lx,"d");R__%s_Derivative->Draw("%s");}",GetName(),(Long_t)this,GetName(),option);
gROOT->ProcessLine(cmd);
if (padsav) padsav->cd();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::DrawIntegral(Option_t *option)
{
// Draw integral of this function
//
// An intermediate TGraph object is built and drawn with option.
//
// The resulting graph will be drawn into the current pad.
// If this function is used via the context menu, it recommended
// to create a new canvas/pad before invoking this function.
TVirtualPad *pad = gROOT->GetSelectedPad();
TVirtualPad *padsav = gPad;
if (pad) pad->cd();
char cmd[512];
sprintf(cmd,"{TGraph *R__%s_Integral = new TGraph((TF1*)0x%lx,"i");R__%s_Integral->Draw("%s");}",GetName(),(Long_t)this,GetName(),option);
gROOT->ProcessLine(cmd);
if (padsav) padsav->cd();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::DrawF1(const char *formula, Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax, Option_t *option)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Draw formula between xmin and xmax*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==================================
//*-*
if (Compile(formula)) return;
SetRange(xmin, xmax);
Draw(option);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::DrawPanel()
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*Display a panel with all function drawing options*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =================================================
//*-*
//*-* See class TDrawPanelHist for example
if (gPad) {
gROOT->SetSelectedPrimitive(this);
gROOT->SetSelectedPad(gPad);
}
//The pad utility manager is required (a plugin)
TVirtualUtilPad *util = (TVirtualUtilPad*)gROOT->GetListOfSpecials()->FindObject("R__TVirtualUtilPad");
if (!util) {
TPluginHandler *h;
if ((h = gROOT->GetPluginManager()->FindHandler("TVirtualUtilPad"))) {
if (h->LoadPlugin() == -1)
return;
h->ExecPlugin(0);
util = (TVirtualUtilPad*)gROOT->GetListOfSpecials()->FindObject("R__TVirtualUtilPad");
}
}
util->DrawPanel();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::Eval(Double_t x, Double_t y, Double_t z, Double_t t)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Evaluate this formula*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =====================
//*-*
//*-* Computes the value of this function (general case for a 3-d function)
//*-* at point x,y,z.
//*-* For a 1-d function give y=0 and z=0
//*-* The current value of variables x,y,z is passed through x, y and z.
//*-* The parameters used will be the ones in the array params if params is given
//*-* otherwise parameters will be taken from the stored data members fParams
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
Double_t xx[4];
xx[0] = x;
xx[1] = y;
xx[2] = z;
xx[3] = t;
InitArgs(xx,fParams);
return TF1::EvalPar(xx,fParams);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::EvalPar(const Double_t *x, const Double_t *params)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*Evaluate function with given coordinates and parameters*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =======================================================
//*-*
// Compute the value of this function at point defined by array x
// and current values of parameters in array params.
// If argument params is omitted or equal 0, the internal values
// of parameters (array fParams) will be used instead.
// For a 1-D function only x[0] must be given.
// In case of a multi-dimemsional function, the arrays x must be
// filled with the corresponding number of dimensions.
//
// WARNING. In case of an interpreted function (fType=2), it is the
// user's responsability to initialize the parameters via InitArgs
// before calling this function.
// InitArgs should be called at least once to specify the addresses
// of the arguments x and params.
// InitArgs should be called everytime these addresses change.
//
fgCurrent = this;
if (fType == 0) return TFormula::EvalPar(x,params);
Double_t result = 0;
if (fType == 1) {
if (fFunction) {
if (params) result = (*fFunction)((Double_t*)x,(Double_t*)params);
else result = (*fFunction)((Double_t*)x,fParams);
}else result = GetSave(x);
}
if (fType == 2) {
if (fMethodCall) fMethodCall->Execute(result);
else result = GetSave(x);
}
return result;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::ExecuteEvent(Int_t event, Int_t px, Int_t py)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Execute action corresponding to one event*-*-*-*
//*-* =========================================
//*-* This member function is called when a F1 is clicked with the locator
//*-*
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
fHistogram->ExecuteEvent(event,px,py);
if (!gPad->GetView()) {
if (event == kMouseMotion) gPad->SetCursor(kHand);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::FixParameter(Int_t ipar, Double_t value)
{
// Fix the value of a parameter
// The specified value will be used in a fit operation
if (ipar < 0 || ipar > fNpar-1) return;
SetParameter(ipar,value);
if (value != 0) SetParLimits(ipar,value,value);
else SetParLimits(ipar,1,1);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TF1 *TF1::GetCurrent()
{
// static function returning the current function being processed
return fgCurrent;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TH1 *TF1::GetHistogram() const
{
// return a pointer to the histogram used to vusualize the function
if (fHistogram) return fHistogram;
// may be function has not yet be painted. force a pad update
//gPad->Modified();
//gPad->Update();
((TF1*)this)->Paint();
return fHistogram;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetMaximum(Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax) const
{
// return the maximum value of the function
// Method:
// the function is computed at fNpx points between xmin and xmax
// xxmax is the X value corresponding to the maximum function value
// An iterative procedure computes the maximum around xxmax
// until dx is less than 1e-9 *(fXmax-fXmin)
Double_t x,y;
if (xmin >= xmax) {xmin = fXmin; xmax = fXmax;}
Double_t dx = (xmax-xmin)/fNpx;
Double_t xxmax = xmin;
Double_t yymax = ((TF1*)this)->Eval(xmin+dx);
for (Int_t i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
x = xmin + (i+0.5)*dx;
y = ((TF1*)this)->Eval(x);
if (y > yymax) {xxmax = x; yymax = y;}
}
if (dx < 1.e-9*(fXmax-fXmin)) return yymax;
else return GetMaximum(TMath::Max(xmin,xxmax-dx), TMath::Min(xmax,xxmax+dx));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetMaximumX(Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax) const
{
// return the X value corresponding to the maximum value of the function
// Method:
// the function is computed at fNpx points between xmin and xmax
// xxmax is the X value corresponding to the maximum function value
// An iterative procedure computes the maximum around xxmax
// until dx is less than 1e-9 *(fXmax-fXmin)
Double_t x,y;
if (xmin >= xmax) {xmin = fXmin; xmax = fXmax;}
Double_t dx = (xmax-xmin)/fNpx;
Double_t xxmax = xmin;
Double_t yymax = ((TF1*)this)->Eval(xmin+dx);
for (Int_t i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
x = xmin + (i+0.5)*dx;
y = ((TF1*)this)->Eval(x);
if (y > yymax) {xxmax = x; yymax = y;}
}
if (dx < 1.e-9*(fXmax-fXmin)) return TMath::Min(xmax,xxmax);
else return GetMaximumX(TMath::Max(xmin,xxmax-dx), TMath::Min(xmax,xxmax+dx));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetMinimum(Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax) const
{
// return the minimum value of the function
// Method:
// the function is computed at fNpx points between xmin and xmax
// xxmax is the X value corresponding to the minimum function value
// An iterative procedure computes the minimum around xxmax
// until dx is less than 1e-9 *(fXmax-fXmin)
Double_t x,y;
if (xmin >= xmax) {xmin = fXmin; xmax = fXmax;}
Double_t dx = (xmax-xmin)/fNpx;
Double_t xxmin = xmin;
Double_t yymin = ((TF1*)this)->Eval(xmin+dx);
for (Int_t i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
x = xmin + (i+0.5)*dx;
y = ((TF1*)this)->Eval(x);
if (y < yymin) {xxmin = x; yymin = y;}
}
if (dx < 1.e-9*(fXmax-fXmin)) return yymin;
else return GetMinimum(TMath::Max(xmin,xxmin-dx), TMath::Min(xmax,xxmin+dx));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetMinimumX(Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax) const
{
// return the X value corresponding to the minimum value of the function
// Method:
// the function is computed at fNpx points between xmin and xmax
// xxmax is the X value corresponding to the minimum function value
// An iterative procedure computes the minimum around xxmax
// until dx is less than 1e-9 *(fXmax-fXmin)
Double_t x,y;
if (xmin >= xmax) {xmin = fXmin; xmax = fXmax;}
Double_t dx = (xmax-xmin)/fNpx;
Double_t xxmin = xmin;
Double_t yymin = ((TF1*)this)->Eval(xmin+dx);
for (Int_t i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
x = xmin + (i+0.5)*dx;
y = ((TF1*)this)->Eval(x);
if (y < yymin) {xxmin = x; yymin = y;}
}
if (dx < 1.e-9*(fXmax-fXmin)) return TMath::Min(xmax,xxmin);
else return GetMinimumX(TMath::Max(xmin,xxmin-dx), TMath::Min(xmax,xxmin+dx));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetX(Double_t fy, Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax) const
{
// return the X value corresponding to the function value fy for (xmin<x<xmax).
// Method:
// the function z = abs(f-fy) is computed at fNpx points between xmin and xmax
// xxmax is the X value corresponding to the minimum function value
// An iterative procedure computes the minimum around xxmax
// until dx is less than 1e-9 *(fXmax-fXmin).
// In case the problem has several solutions in X, the higher X solution is returned
// If the problem has no solution, the function returns the value of X
// where f(X) is closer to fy.
Double_t x,y;
if (xmin >= xmax) {xmin = fXmin; xmax = fXmax;}
Double_t dx = (xmax-xmin)/fNpx;
Double_t xxmin = xmin;
Double_t yymin = TMath::Abs(((TF1*)this)->Eval(xmin+dx) -fy);
for (Int_t i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
x = xmin + (i+0.5)*dx;
y = TMath::Abs(((TF1*)this)->Eval(x) -fy);
if (y < yymin) {xxmin = x; yymin = y;}
}
if (dx < 1.e-9*(fXmax-fXmin)) return TMath::Min(xmax,xxmin);
else return GetX(fy,TMath::Max(xmin,xxmin-dx), TMath::Min(xmax,xxmin+dx));
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TF1::GetNDF() const
{
// return the number of degrees of freedom in the fit
// the fNDF parameter has been previously computed during a fit.
// The number of degrees of freedom corresponds to the number of points
// used in the fit minus the number of free parameters.
if (fNDF == 0) return fNpfits-fNpar;
return fNDF;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
char *TF1::GetObjectInfo(Int_t px, Int_t /* py */) const
{
// Redefines TObject::GetObjectInfo.
// Displays the function info (x, function value
// corresponding to cursor position px,py
//
static char info[64];
Double_t x = gPad->PadtoX(gPad->AbsPixeltoX(px));
sprintf(info,"(x=%g, f=%g)",x,((TF1*)this)->Eval(x));
return info;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetParError(Int_t ipar) const
{
//return value of parameter number ipar
if (ipar < 0 || ipar > fNpar-1) return 0;
return fParErrors[ipar];
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::GetParLimits(Int_t ipar, Double_t &parmin, Double_t &parmax)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*Return limits for parameter ipar*-*-*-*
//*-* ================================
parmin = 0;
parmax = 0;
if (ipar < 0 || ipar > fNpar-1) return;
if (fParMin) parmin = fParMin[ipar];
if (fParMax) parmax = fParMax[ipar];
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetProb() const
{
// return the fit probability
Int_t ndf = fNpfits - fNpar;
if (ndf <= 0) return 0;
return TMath::Prob(fChisquare,ndf);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Int_t TF1::GetQuantiles(Int_t nprobSum, Double_t *q, const Double_t *probSum)
{
// Compute Quantiles for density distribution of this function
// Quantile x_q of a probability distribution Function F is defined as
//
// F(x_q) = Integral_{xmin}^(x_q) f dx = q with 0 <= q <= 1.
//
// For instance the median x_0.5 of a distribution is defined as that value
// of the random variable for which the distribution function equals 0.5:
//
// F(x_0.5) = Probability(x < x_0.5) = 0.5
//
// code from Eddy Offermann, Renaissance
//
// input parameters
// - this TF1 function
// - nprobSum maximum size of array q and size of array probSum
// - probSum array of positions where quantiles will be computed.
// It is assumed to contain at least nprobSum values.
// output
// - return value nq (<=nprobSum) with the number of quantiles computed
// - array q filled with nq quantiles
//
// Getting quantiles from two histograms and storing results in a TGraph,
// a so-called QQ-plot
//
// TGraph *gr = new TGraph(nprob);
// f1->GetQuantiles(nprob,gr->GetX());
// f2->GetQuantiles(nprob,gr->GetY());
// gr->Draw("alp");
const Int_t npx = TMath::Min(250,TMath::Max(50,2*nprobSum));
const Double_t xMin = GetXmin();
const Double_t xMax = GetXmax();
const Double_t dx = (xMax-xMin)/npx;
TArrayD integral(npx+1);
TArrayD alpha(npx);
TArrayD beta(npx);
TArrayD gamma(npx);
integral[0] = 0;
Int_t intNegative = 0;
Int_t i;
for (i = 0; i < npx; i++) {
const Double_t *params = 0;
Double_t integ = Integral(Double_t(xMin+i*dx),Double_t(xMin+i*dx+dx),params);
if (integ < 0) {intNegative++; integ = -integ;}
integral[i+1] = integral[i] + integ;
}
if (intNegative > 0)
Warning("GetQuantiles","function:%s has %d negative values: abs assumed",
GetName(),intNegative);
if (integral[npx] == 0) {
Error("GetQuantiles","Integral of function is zero");
return 0;
}
const Double_t total = integral[npx];
for (i = 1; i <= npx; i++) integral[i] /= total;
//the integral r for each bin is approximated by a parabola
// x = alpha + beta*r +gamma*r**2
// compute the coefficients alpha, beta, gamma for each bin
for (i = 0; i < npx; i++) {
const Double_t x0 = xMin+dx*i;
const Double_t r2 = integral[i+1]-integral[i];
const Double_t r1 = Integral(x0,x0+0.5*dx)/total;
gamma[i] = (2*r2-4*r1)/(dx*dx);
beta[i] = r2/dx-gamma[i]*dx;
alpha[i] = x0;
gamma[i] *= 2;
}
// Be careful because of finite precision in the integral; Use the fact that the integral
// is monotone increasing
for (i = 0; i < nprobSum; i++) {
const Double_t r = probSum[i];
Int_t bin = TMath::Max(TMath::BinarySearch(npx+1,integral.GetArray(),r)-1,0);
while (bin < npx-1 && integral[bin+1] == r) {
if (integral[bin+2] == r) bin++;
else break;
}
const Double_t rr = r-integral[bin];
if (rr != 0.0) {
Double_t xx;
if (gamma[bin] && beta[bin]*beta[bin]+2*gamma[bin]*rr >= 0.0)
xx = (-beta[bin]+TMath::Sqrt(beta[bin]*beta[bin]+2*gamma[bin]*rr))/gamma[bin];
else
xx = rr/beta[bin];
q[i] = alpha[bin]+xx;
} else {
q[i] = alpha[bin];
if (integral[bin+1] == r) q[i] += dx;
}
}
return nprobSum;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetRandom()
{
// Return a random number following this function shape
//*-*
//*-* The distribution contained in the function fname (TF1) is integrated
//*-* over the channel contents.
//*-* It is normalized to 1.
//*-* For each bin the integral is approximated by a parabola.
//*-* The parabola coefficients are stored as non persistent data members
//*-* Getting one random number implies:
//*-* - Generating a random number between 0 and 1 (say r1)
//*-* - Look in which bin in the normalized integral r1 corresponds to
//*-* - Evaluate the parabolic curve in the selected bin to find
//*-* the corresponding X value.
//*-* The parabolic approximation is very good as soon as the number
//*-* of bins is greater than 50.
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-**-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
// Check if integral array must be build
if (fIntegral == 0) {
Double_t dx = (fXmax-fXmin)/fNpx;
fIntegral = new Double_t[fNpx+1];
fAlpha = new Double_t[fNpx];
fBeta = new Double_t[fNpx];
fGamma = new Double_t[fNpx];
fIntegral[0] = 0;
Double_t integ;
Int_t intNegative = 0;
Int_t i;
for (i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
integ = Integral(Double_t(fXmin+i*dx), Double_t(fXmin+i*dx+dx));
if (integ < 0) {intNegative++; integ = -integ;}
fIntegral[i+1] = fIntegral[i] + integ;
}
if (intNegative > 0) {
Warning("GetRandom","function:%s has %d negative values: abs assumed",GetName(),intNegative);
}
if (fIntegral[fNpx] == 0) {
Error("GetRandom","Integral of function is zero");
return 0;
}
Double_t total = fIntegral[fNpx];
for (i=1;i<=fNpx;i++) { // normalize integral to 1
fIntegral[i] /= total;
}
//the integral r for each bin is approximated by a parabola
// x = alpha + beta*r +gamma*r**2
// compute the coefficients alpha, beta, gamma for each bin
Double_t x0,r1,r2;
for (i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
x0 = fXmin+i*dx;
r2 = fIntegral[i+1] - fIntegral[i];
r1 = Integral(x0,x0+0.5*dx)/total;
fGamma[i] = (2*r2 - 4*r1)/(dx*dx);
fBeta[i] = r2/dx - fGamma[i]*dx;
fAlpha[i] = x0;
fGamma[i] *= 2;
}
}
// return random number
Double_t r = gRandom->Rndm();
Int_t bin = TMath::BinarySearch(fNpx,fIntegral,r);
Double_t rr = r - fIntegral[bin];
Double_t xx;
if(fGamma[bin])
xx = (-fBeta[bin] + TMath::Sqrt(fBeta[bin]*fBeta[bin]+2*fGamma[bin]*rr))/fGamma[bin];
else
xx = rr/fBeta[bin];
Double_t x = fAlpha[bin] + xx;
return x;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetRandom(Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax)
{
// Return a random number following this function shape in [xmin,xmax]
//*-*
//*-* The distribution contained in the function fname (TF1) is integrated
//*-* over the channel contents.
//*-* It is normalized to 1.
//*-* For each bin the integral is approximated by a parabola.
//*-* The parabola coefficients are stored as non persistent data members
//*-* Getting one random number implies:
//*-* - Generating a random number between 0 and 1 (say r1)
//*-* - Look in which bin in the normalized integral r1 corresponds to
//*-* - Evaluate the parabolic curve in the selected bin to find
//*-* the corresponding X value.
//*-* The parabolic approximation is very good as soon as the number
//*-* of bins is greater than 50.
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-**-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
// Check if integral array must be build
if (fIntegral == 0) {
Double_t dx = (fXmax-fXmin)/fNpx;
fIntegral = new Double_t[fNpx+1];
fAlpha = new Double_t[fNpx];
fBeta = new Double_t[fNpx];
fGamma = new Double_t[fNpx];
fIntegral[0] = 0;
Double_t integ;
Int_t intNegative = 0;
Int_t i;
for (i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
integ = Integral(Double_t(fXmin+i*dx), Double_t(fXmin+i*dx+dx));
if (integ < 0) {intNegative++; integ = -integ;}
fIntegral[i+1] = fIntegral[i] + integ;
}
if (intNegative > 0) {
Warning("GetRandom","function:%s has %d negative values: abs assumed",GetName(),intNegative);
}
if (fIntegral[fNpx] == 0) {
Error("GetRandom","Integral of function is zero");
return 0;
}
Double_t total = fIntegral[fNpx];
for (i=1;i<=fNpx;i++) { // normalize integral to 1
fIntegral[i] /= total;
}
//the integral r for each bin is approximated by a parabola
// x = alpha + beta*r +gamma*r**2
// compute the coefficients alpha, beta, gamma for each bin
Double_t x0,r1,r2;
for (i=0;i<fNpx;i++) {
x0 = fXmin+i*dx;
r2 = fIntegral[i+1] - fIntegral[i];
r1 = Integral(x0,x0+0.5*dx)/total;
fGamma[i] = (2*r2 - 4*r1)/(dx*dx);
fBeta[i] = r2/dx - fGamma[i]*dx;
fAlpha[i] = x0;
fGamma[i] *= 2;
}
}
// return random number
Double_t dx = (fXmax-fXmin)/fNpx;
Int_t nbinmin = (Int_t)((xmin-fXmin)/dx);
Int_t nbinmax = (Int_t)((xmax-fXmin)/dx)+2;
if(nbinmax>fNpx) nbinmax=fNpx;
Double_t pmin=fIntegral[nbinmin];
Double_t pmax=fIntegral[nbinmax];
Double_t r,x,xx,rr;
do {
r = gRandom->Uniform(pmin,pmax);
Int_t bin = TMath::BinarySearch(fNpx,fIntegral,r);
rr = r - fIntegral[bin];
if(fGamma[bin])
xx = (-fBeta[bin] + TMath::Sqrt(fBeta[bin]*fBeta[bin]+2*fGamma[bin]*rr))/fGamma[bin];
else
xx = rr/fBeta[bin];
x = fAlpha[bin] + xx;
} while(x<xmin || x>xmax);
return x;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::GetRange(Double_t &xmin, Double_t &xmax) const
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return range of a 1-D function*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==============================
xmin = fXmin;
xmax = fXmax;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::GetRange(Double_t &xmin, Double_t &ymin, Double_t &xmax, Double_t &ymax) const
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return range of a 2-D function*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==============================
xmin = fXmin;
xmax = fXmax;
ymin = 0;
ymax = 0;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::GetRange(Double_t &xmin, Double_t &ymin, Double_t &zmin, Double_t &xmax, Double_t &ymax, Double_t &zmax) const
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return range of function*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ========================
xmin = fXmin;
xmax = fXmax;
ymin = 0;
ymax = 0;
zmin = 0;
zmax = 0;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::GetSave(const Double_t *xx)
{
// Get value corresponding to X in array of fSave values
if (fNsave <= 0) return 0;
if (fSave == 0) return 0;
Int_t np = fNsave - 3;
Double_t xmin = Double_t(fSave[np+1]);
Double_t xmax = Double_t(fSave[np+2]);
Double_t x = Double_t(xx[0]);
Double_t dx = (xmax-xmin)/np;
if (x < xmin || x > xmax) return 0;
if (dx <= 0) return 0;
Int_t bin = Int_t((x-xmin)/dx);
Double_t xlow = xmin + bin*dx;
Double_t xup = xlow + dx;
Double_t ylow = fSave[bin];
Double_t yup = fSave[bin+1];
Double_t y = ((xup*ylow-xlow*yup) + x*(yup-ylow))/dx;
return y;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TAxis *TF1::GetXaxis() const
{
// Get x axis of the function.
//if (!gPad) return 0;
TH1 *h = GetHistogram();
if (!h) return 0;
return h->GetXaxis();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
TAxis *TF1::GetYaxis() const
{
// Get y axis of the function.
//if (!gPad) return 0;
TH1 *h = GetHistogram();
if (!h) return 0;
return h->GetYaxis();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::InitArgs(const Double_t *x, const Double_t *params)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Initialize parameters addresses*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ===============================
if (fMethodCall) {
Long_t args[2];
args[0] = (Long_t)x;
if (params) args[1] = (Long_t)params;
else args[1] = (Long_t)fParams;
fMethodCall->SetParamPtrs(args);
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::InitStandardFunctions()
{
// Create the basic function objects
TF1 *f1;
if (!gROOT->GetListOfFunctions()->FindObject("gaus")) {
f1 = new TF1("gaus","gaus",-1,1); f1->SetParameters(1,0,1);
f1 = new TF1("landau","landau",-1,1); f1->SetParameters(1,0,1);
f1 = new TF1("expo","expo",-1,1); f1->SetParameters(1,1);
for (Int_t i=0;i<10;i++) {
f1 = new TF1(Form("pol%d",i),Form("pol%d",i),-1,1);
f1->SetParameters(1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1);
}
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Double_t TF1::Integral(Double_t a, Double_t b, const Double_t *params, Double_t epsilon)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Return Integral of function between a and b*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//
// based on original CERNLIB routine DGAUSS by Sigfried Kolbig
// converted to C++ by Rene Brun
//
//
/*
This function computes, to an attempted specified accuracy, the value of the integral
![]()
Usage:
In any arithmetic expression, this function has the approximate value of the integral I.
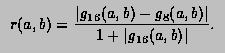
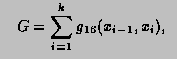
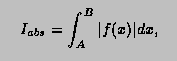
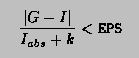
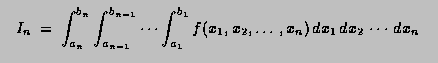 */
//
//
// Author(s): A.C. Genz, A.A. Malik
// converted/adapted by R.Brun to C++ from Fortran CERNLIB routine RADMUL (D120)
// The new code features many changes compared to the Fortran version.
// Note that this function is currently called only by TF2::Integral (n=2)
// and TF3::Integral (n=3).
//
// This function computes, to an attempted specified accuracy, the value of
// the integral over an n-dimensional rectangular region.
//
// N Number of dimensions.
// A,B One-dimensional arrays of length >= N . On entry A[i], and B[i],
// contain the lower and upper limits of integration, respectively.
// EPS Specified relative accuracy.
// RELERR Contains, on exit, an estimation of the relative accuray of RESULT.
//
// Method:
//
// An integration rule of degree seven is used together with a certain
// strategy of subdivision.
// For a more detailed description of the method see References.
//
// Notes:
//
// 1.Multi-dimensional integration is time-consuming. For each rectangular
// subregion, the routine requires function evaluations.
// Careful programming of the integrand might result in substantial saving
// of time.
// 2.Numerical integration usually works best for smooth functions.
// Some analysis or suitable transformations of the integral prior to
// numerical work may contribute to numerical efficiency.
//
// References:
//
// 1.A.C. Genz and A.A. Malik, Remarks on algorithm 006:
// An adaptive algorithm for numerical integration over
// an N-dimensional rectangular region, J. Comput. Appl. Math. 6 (1980) 295-302.
// 2.A. van Doren and L. de Ridder, An adaptive algorithm for numerical
// integration over an n-dimensional cube, J.Comput. Appl. Math. 2 (1976) 207-217.
//
//=========================================================================
Double_t ctr[15], wth[15], wthl[15], z[15];
const Double_t xl2 = 0.358568582800318073;
const Double_t xl4 = 0.948683298050513796;
const Double_t xl5 = 0.688247201611685289;
const Double_t w2 = 980./6561;
const Double_t w4 = 200./19683;
const Double_t wp2 = 245./486;
const Double_t wp4 = 25./729;
Double_t wn1[14] = { -0.193872885230909911, -0.555606360818980835,
-0.876695625666819078, -1.15714067977442459, -1.39694152314179743,
-1.59609815576893754, -1.75461057765584494, -1.87247878880251983,
-1.94970278920896201, -1.98628257887517146, -1.98221815780114818,
-1.93750952598689219, -1.85215668343240347, -1.72615963013768225};
Double_t wn3[14] = { 0.0518213686937966768, 0.0314992633236803330,
0.0111771579535639891,-0.00914494741655235473,-0.0294670527866686986,
-0.0497891581567850424,-0.0701112635269013768, -0.0904333688970177241,
-0.110755474267134071, -0.131077579637250419, -0.151399685007366752,
-0.171721790377483099, -0.192043895747599447, -0.212366001117715794};
Double_t wn5[14] = { 0.871183254585174982e-01, 0.435591627292587508e-01,
0.217795813646293754e-01, 0.108897906823146873e-01, 0.544489534115734364e-02,
0.272244767057867193e-02, 0.136122383528933596e-02, 0.680611917644667955e-03,
0.340305958822333977e-03, 0.170152979411166995e-03, 0.850764897055834977e-04,
0.425382448527917472e-04, 0.212691224263958736e-04, 0.106345612131979372e-04};
Double_t wpn1[14] = { -1.33196159122085045, -2.29218106995884763,
-3.11522633744855959, -3.80109739368998611, -4.34979423868312742,
-4.76131687242798352, -5.03566529492455417, -5.17283950617283939,
-5.17283950617283939, -5.03566529492455417, -4.76131687242798352,
-4.34979423868312742, -3.80109739368998611, -3.11522633744855959};
Double_t wpn3[14] = { 0.0445816186556927292, -0.0240054869684499309,
-0.0925925925925925875, -0.161179698216735251, -0.229766803840877915,
-0.298353909465020564, -0.366941015089163228, -0.435528120713305891,
-0.504115226337448555, -0.572702331961591218, -0.641289437585733882,
-0.709876543209876532, -0.778463648834019195, -0.847050754458161859};
Double_t result = 0;
Double_t abserr = 0;
Int_t ifail = 3;
if (n < 2 || n > 15) return 0;
Double_t twondm = TMath::Power(2,n);
Int_t ifncls = 0;
Bool_t ldv = kFALSE;
Int_t irgnst = 2*n+3;
Int_t irlcls = Int_t(twondm) +2*n*(n+1)+1;
Int_t isbrgn = irgnst;
Int_t isbrgs = irgnst;
// The original algorithm expected a parameter MAXPTS
// where MAXPTS = Maximum number of function evaluations to be allowed.
// Here we set MAXPTS to 1000*(the lowest possible value)
Int_t maxpts = 1000*irlcls;
Int_t minpts = 1;
// The original agorithm expected a working space array WK of length IWK
// with IWK Length ( >= (2N + 3) * (1 + MAXPTS/(2**N + 2N(N + 1) + 1))/2).
// Here, this array is allocated dynamically
Int_t iwk = irgnst*(1 +maxpts/irlcls)/2;
Double_t *wk = new Double_t[iwk+10];
Int_t j;
for (j=0;j<n;j++) {
ctr[j] = (b[j] + a[j])*0.5;
wth[j] = (b[j] - a[j])*0.5;
}
Double_t rgnvol, sum1, sum2, sum3, sum4, sum5, difmax, f2, f3, dif, aresult;
Double_t rgncmp=0, rgnval, rgnerr;
Int_t j1, k, l, m, idvaxn=0, idvax0=0, isbtmp, isbtpp;
InitArgs(z,fParams);
L20:
rgnvol = twondm;
for (j=0;j<n;j++) {
rgnvol *= wth[j];
z[j] = ctr[j];
}
sum1 = EvalPar(z,fParams); //evaluate function
difmax = 0;
sum2 = 0;
sum3 = 0;
for (j=0;j<n;j++) {
z[j] = ctr[j] - xl2*wth[j];
f2 = EvalPar(z,fParams);
z[j] = ctr[j] + xl2*wth[j];
f2 += EvalPar(z,fParams);
wthl[j] = xl4*wth[j];
z[j] = ctr[j] - wthl[j];
f3 = EvalPar(z,fParams);
z[j] = ctr[j] + wthl[j];
f3 += EvalPar(z,fParams);
sum2 += f2;
sum3 += f3;
dif = TMath::Abs(7*f2-f3-12*sum1);
if (dif >= difmax) {
difmax=dif;
idvaxn=j+1;
}
z[j] = ctr[j];
}
sum4 = 0;
for (j=1;j<n;j++) {
j1 = j-1;
for (k=j;k<n;k++) {
for (l=0;l<2;l++) {
wthl[j1] = -wthl[j1];
z[j1] = ctr[j1] + wthl[j1];
for (m=0;m<2;m++) {
wthl[k] = -wthl[k];
z[k] = ctr[k] + wthl[k];
sum4 += EvalPar(z,fParams);
}
}
z[k] = ctr[k];
}
z[j1] = ctr[j1];
}
sum5 = 0;
for (j=0;j<n;j++) {
wthl[j] = -xl5*wth[j];
z[j] = ctr[j] + wthl[j];
}
L90:
sum5 += EvalPar(z,fParams);
for (j=0;j<n;j++) {
wthl[j] = -wthl[j];
z[j] = ctr[j] + wthl[j];
if (wthl[j] > 0) goto L90;
}
rgncmp = rgnvol*(wpn1[n-2]*sum1+wp2*sum2+wpn3[n-2]*sum3+wp4*sum4);
rgnval = wn1[n-2]*sum1+w2*sum2+wn3[n-2]*sum3+w4*sum4+wn5[n-2]*sum5;
rgnval *= rgnvol;
rgnerr = TMath::Abs(rgnval-rgncmp);
result += rgnval;
abserr += rgnerr;
ifncls += irlcls;
aresult = TMath::Abs(result);
if (aresult < 1e-100) {
delete [] wk;
return result;
}
if (ldv) {
L110:
isbtmp = 2*isbrgn;
if (isbtmp > isbrgs) goto L160;
if (isbtmp < isbrgs) {
isbtpp = isbtmp + irgnst;
if (wk[isbtmp-1] < wk[isbtpp-1]) isbtmp = isbtpp;
}
if (rgnerr >= wk[isbtmp-1]) goto L160;
for (k=0;k<irgnst;k++) {
wk[isbrgn-k-1] = wk[isbtmp-k-1];
}
isbrgn = isbtmp;
goto L110;
}
L140:
isbtmp = (isbrgn/(2*irgnst))*irgnst;
if (isbtmp >= irgnst && rgnerr > wk[isbtmp-1]) {
for (k=0;k<irgnst;k++) {
wk[isbrgn-k-1] = wk[isbtmp-k-1];
}
isbrgn = isbtmp;
goto L140;
}
L160:
wk[isbrgn-1] = rgnerr;
wk[isbrgn-2] = rgnval;
wk[isbrgn-3] = Double_t(idvaxn);
for (j=0;j<n;j++) {
isbtmp = isbrgn-2*j-4;
wk[isbtmp] = ctr[j];
wk[isbtmp-1] = wth[j];
}
if (ldv) {
ldv = kFALSE;
ctr[idvax0-1] += 2*wth[idvax0-1];
isbrgs += irgnst;
isbrgn = isbrgs;
goto L20;
}
relerr = abserr/aresult;
if (relerr < 1e-1 && aresult < 1e-20) ifail = 0;
if (relerr < 1e-3 && aresult < 1e-10) ifail = 0;
if (relerr < 1e-5 && aresult < 1e-5) ifail = 0;
if (isbrgs+irgnst > iwk) ifail = 2;
if (ifncls+2*irlcls > maxpts) ifail = 1;
if (relerr < eps && ifncls >= minpts) ifail = 0;
if (ifail == 3) {
ldv = kTRUE;
isbrgn = irgnst;
abserr -= wk[isbrgn-1];
result -= wk[isbrgn-2];
idvax0 = Int_t(wk[isbrgn-3]);
for (j=0;j<n;j++) {
isbtmp = isbrgn-2*j-4;
ctr[j] = wk[isbtmp];
wth[j] = wk[isbtmp-1];
}
wth[idvax0-1] = 0.5*wth[idvax0-1];
ctr[idvax0-1] -= wth[idvax0-1];
goto L20;
}
// IFAIL On exit:
// 0 Normal exit. . At most MAXPTS calls to the function F were performed.
// 1 MAXPTS is too small for the specified accuracy EPS. RESULT and RELERR
// contain the values obtainable for the specified value of MAXPTS.
//
delete [] wk;
// Int_t nfnevl = ifncls; //number of function evaluations performed.
return result; //an approximate value of the integral
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TF1::IsInside(const Double_t *x) const
{
// Return kTRUE is the point is inside the function range
if (x[0] < fXmin || x[0] > fXmax) return kFALSE;
return kTRUE;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Paint(Option_t *option)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Paint this function with its current attributes*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ===============================================
Int_t i;
Double_t xv[1];
fgCurrent = this;
TString opt = option;
opt.ToLower();
Double_t xmin=fXmin, xmax=fXmax, pmin=fXmin, pmax=fXmax;
if (gPad) {
pmin = gPad->PadtoX(gPad->GetUxmin());
pmax = gPad->PadtoX(gPad->GetUxmax());
}
if (opt.Contains("same")) {
if (xmax < pmin) return; // Otto: completely outside
if (xmin > pmax) return;
if (xmin < pmin) xmin = pmin;
if (xmax > pmax) xmax = pmax;
}
// Create a temporary histogram and fill each channel with the function value
// Preserve axis titles
TString xtitle = "";
TString ytitle = "";
if (fHistogram) {
xtitle = fHistogram->GetXaxis()->GetTitle();
ytitle = fHistogram->GetYaxis()->GetTitle();
if (!gPad->GetLogx() && fHistogram->TestBit(TH1::kLogX)) { delete fHistogram; fHistogram = 0;}
if ( gPad->GetLogx() && !fHistogram->TestBit(TH1::kLogX)) { delete fHistogram; fHistogram = 0;}
}
if (fHistogram) {
// if (xmin != fXmin || xmax != fXmax) fHistogram->GetXaxis()->SetLimits(xmin,xmax);
fHistogram->GetXaxis()->SetLimits(xmin,xmax);
} else {
// if logx, we must bin in logx and not in x !!!
// otherwise if several decades, one gets crazy results
if (xmin > 0 && gPad && gPad->GetLogx()) {
Axis_t *xbins = new Axis_t[fNpx+1];
Double_t xlogmin = TMath::Log10(xmin);
Double_t xlogmax = TMath::Log10(xmax);
Double_t dlogx = (xlogmax-xlogmin)/((Double_t)fNpx);
for (i=0;i<=fNpx;i++) {
xbins[i] = gPad->PadtoX(xlogmin+ i*dlogx);
}
fHistogram = new TH1D("Func",GetTitle(),fNpx,xbins);
fHistogram->SetBit(TH1::kLogX);
delete [] xbins;
} else {
fHistogram = new TH1D("Func",GetTitle(),fNpx,xmin,xmax);
}
if (!fHistogram) return;
fHistogram->SetDirectory(0);
}
//restore axis titles
fHistogram->GetXaxis()->SetTitle(xtitle.Data());
fHistogram->GetYaxis()->SetTitle(ytitle.Data());
InitArgs(xv,fParams);
for (i=1;i<=fNpx;i++) {
xv[0] = fHistogram->GetBinCenter(i);
fHistogram->SetBinContent(i,EvalPar(xv,fParams));
}
//*-*- Copy Function attributes to histogram attributes
Double_t minimum = fHistogram->GetMinimumStored();
Double_t maximum = fHistogram->GetMaximumStored();
if (minimum == -1111) { //this can happen after unzooming
if (fHistogram->TestBit(TH1::kIsZoomed)) {
minimum = fHistogram->GetYaxis()->GetXmin();
} else {
minimum = fMinimum;
}
fHistogram->SetMinimum(minimum);
}
if (maximum == -1111) {
if (fHistogram->TestBit(TH1::kIsZoomed)) {
maximum = fHistogram->GetYaxis()->GetXmax();
} else {
maximum = fMaximum;
}
fHistogram->SetMaximum(maximum);
}
fHistogram->SetBit(TH1::kNoStats);
fHistogram->SetLineColor(GetLineColor());
fHistogram->SetLineStyle(GetLineStyle());
fHistogram->SetLineWidth(GetLineWidth());
fHistogram->SetFillColor(GetFillColor());
fHistogram->SetFillStyle(GetFillStyle());
fHistogram->SetMarkerColor(GetMarkerColor());
fHistogram->SetMarkerStyle(GetMarkerStyle());
fHistogram->SetMarkerSize(GetMarkerSize());
//*-*- Draw the histogram
if (!gPad) return;
if (opt.Length() == 0) fHistogram->Paint("lf");
else if (opt == "same") fHistogram->Paint("lfsame");
else fHistogram->Paint(option);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Print(Option_t *option) const
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Dump this function with its attributes*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==================================
TFormula::Print(option);
if (fHistogram) fHistogram->Print(option);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::ReleaseParameter(Int_t ipar)
{
// Release parameter number ipar If used in a fit, the parameter
// can vary freely. The parameter limits are reset to 0,0.
if (ipar < 0 || ipar > fNpar-1) return;
SetParLimits(ipar,0,0);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Save(Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax, Double_t, Double_t, Double_t, Double_t)
{
// Save values of function in array fSave
if (fSave != 0) {delete [] fSave; fSave = 0;}
fNsave = fNpx+3;
if (fNsave <= 3) {fNsave=0; return;}
fSave = new Double_t[fNsave];
Int_t i;
Double_t dx = (xmax-xmin)/fNpx;
if (dx <= 0) {
dx = (fXmax-fXmin)/fNpx;
fNsave--;
xmin = fXmin +0.5*dx;
xmax = fXmax -0.5*dx;
}
Double_t xv[1];
InitArgs(xv,fParams);
for (i=0;i<=fNpx;i++) {
xv[0] = xmin + dx*i;
fSave[i] = EvalPar(xv,fParams);
}
fSave[fNpx+1] = xmin;
fSave[fNpx+2] = xmax;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SavePrimitive(ofstream &out, Option_t *option)
{
// Save primitive as a C++ statement(s) on output stream out
Int_t i;
char quote = '"';
out<<" "<<endl;
if (!fMethodCall) {
out<<" TF1 *"<<GetName()<<" = new TF1("<<quote<<GetName()<<quote<<","<<quote<<GetTitle()<<quote<<","<<fXmin<<","<<fXmax<<");"<<endl;
if (fNpx != 100) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetNpx("<<fNpx<<");"<<endl;
}
} else {
out<<" TF1 *"<<GetName()<<" = new TF1("<<quote<<"*"<<GetName()<<quote<<","<<fXmin<<","<<fXmax<<","<<GetNpar()<<");"<<endl;
out<<" //The original function : "<<GetTitle()<<" had originally been created by:" <<endl;
out<<" //TF1 *"<<GetName()<<" = new TF1("<<quote<<GetName()<<quote<<","<<GetTitle()<<","<<fXmin<<","<<fXmax<<","<<GetNpar()<<");"<<endl;
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetRange("<<fXmin<<","<<fXmax<<");"<<endl;
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetName("<<quote<<GetName()<<quote<<");"<<endl;
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetTitle("<<quote<<GetTitle()<<quote<<");"<<endl;
if (fNpx != 100) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetNpx("<<fNpx<<");"<<endl;
}
Double_t dx = (fXmax-fXmin)/fNpx;
Double_t xv[1];
InitArgs(xv,fParams);
for (i=0;i<=fNpx;i++) {
xv[0] = fXmin + dx*i;
Double_t save = EvalPar(xv,fParams);
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetSavedPoint("<<i<<","<<save<<");"<<endl;
}
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetSavedPoint("<<fNpx+1<<","<<fXmin<<");"<<endl;
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetSavedPoint("<<fNpx+2<<","<<fXmax<<");"<<endl;
}
if (TestBit(kNotDraw)) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetBit(TF1::kNotDraw);"<<endl;
}
if (GetFillColor() != 0) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetFillColor("<<GetFillColor()<<");"<<endl;
}
if (GetFillStyle() != 1001) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetFillStyle("<<GetFillStyle()<<");"<<endl;
}
if (GetMarkerColor() != 1) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetMarkerColor("<<GetMarkerColor()<<");"<<endl;
}
if (GetMarkerStyle() != 1) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetMarkerStyle("<<GetMarkerStyle()<<");"<<endl;
}
if (GetMarkerSize() != 1) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetMarkerSize("<<GetMarkerSize()<<");"<<endl;
}
if (GetLineColor() != 1) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetLineColor("<<GetLineColor()<<");"<<endl;
}
if (GetLineWidth() != 4) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetLineWidth("<<GetLineWidth()<<");"<<endl;
}
if (GetLineStyle() != 1) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetLineStyle("<<GetLineStyle()<<");"<<endl;
}
if (GetChisquare() != 0) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetChisquare("<<GetChisquare()<<");"<<endl;
}
Double_t parmin, parmax;
for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetParameter("<<i<<","<<GetParameter(i)<<");"<<endl;
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetParError("<<i<<","<<GetParError(i)<<");"<<endl;
GetParLimits(i,parmin,parmax);
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetParLimits("<<i<<","<<parmin<<","<<parmax<<");"<<endl;
}
if (!strstr(option,"nodraw")) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->Draw("
<<quote<<option<<quote<<");"<<endl;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SetCurrent(TF1 *f1)
{
// static function setting the current function.
// the current function may be accessed in static C-like functions
// when fitting or painting a function.
fgCurrent = f1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SetNDF(Int_t ndf)
{
// Set the number of degrees of freedom
// ndf should be the number of points used in a fit - the number of free parameters
fNDF = ndf;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SetNpx(Int_t npx)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Set the number of points used to draw the function*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==================================================
if(npx > 4 && npx < 100000) fNpx = npx;
Update();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SetParError(Int_t ipar, Double_t error)
{
// set error for parameter number ipar
if (ipar < 0 || ipar > fNpar-1) return;
fParErrors[ipar] = error;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SetParErrors(const Double_t *errors)
{
// set errors for all active parameters
// when calling this function, the array errors must have at least fNpar values
if (!errors) return;
for (Int_t i=0;i<fNpar;i++) fParErrors[i] = errors[i];
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SetParLimits(Int_t ipar, Double_t parmin, Double_t parmax)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*Set limits for parameter ipar*-*-*-*
//*-* =============================
// The specified limits will be used in a fit operation
// when the option "B" is specified (Bounds).
// To fix a parameter, use TF1::FixParameter
if (ipar < 0 || ipar > fNpar-1) return;
Int_t i;
if (!fParMin) {fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar]; for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) fParMin[i]=0;}
if (!fParMax) {fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar]; for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) fParMax[i]=0;}
fParMin[ipar] = parmin;
fParMax[ipar] = parmax;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SetRange(Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*Initialize the upper and lower bounds to draw the function*-*-*-*
//*-* ==========================================================
// The function range is also used in an histogram fit operation
// when the option "R" is specified.
fXmin = xmin;
fXmax = xmax;
Update();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SetSavedPoint(Int_t point, Double_t value)
{
// Restore value of function saved at point
if (!fSave) {
fNsave = fNpx+3;
fSave = new Double_t[fNsave];
}
if (point < 0 || point >= fNsave) return;
fSave[point] = value;
}
//_______________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Streamer(TBuffer &b)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Stream a class object*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =========================================
if (b.IsReading()) {
UInt_t R__s, R__c;
Version_t v = b.ReadVersion(&R__s, &R__c);
if (v > 4) {
TF1::Class()->ReadBuffer(b, this, v, R__s, R__c);
if (v == 5 && fNsave > 0) {
//correct badly saved fSave in 3.00/06
Int_t np = fNsave - 3;
fSave[np] = fSave[np-1];
fSave[np+1] = fXmin;
fSave[np+2] = fXmax;
}
return;
}
//====process old versions before automatic schema evolution
TFormula::Streamer(b);
TAttLine::Streamer(b);
TAttFill::Streamer(b);
TAttMarker::Streamer(b);
if (v < 4) {
Float_t xmin,xmax;
b >> xmin; fXmin = xmin;
b >> xmax; fXmax = xmax;
} else {
b >> fXmin;
b >> fXmax;
}
b >> fNpx;
b >> fType;
b >> fChisquare;
b.ReadArray(fParErrors);
if (v > 1) {
b.ReadArray(fParMin);
b.ReadArray(fParMax);
} else {
fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar+1];
fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar+1];
}
b >> fNpfits;
if (v == 1) {
b >> fHistogram;
delete fHistogram; fHistogram = 0;
}
if (v > 1) {
if (v < 4) {
Float_t minimum,maximum;
b >> minimum; fMinimum =minimum;
b >> maximum; fMaximum =maximum;
} else {
b >> fMinimum;
b >> fMaximum;
}
}
if (v > 2) {
b >> fNsave;
if (fNsave > 0) {
fSave = new Double_t[fNsave+10];
b.ReadArray(fSave);
//correct fSave limits to match new version
fSave[fNsave] = fSave[fNsave-1];
fSave[fNsave+1] = fSave[fNsave+2];
fSave[fNsave+2] = fSave[fNsave+3];
fNsave += 3;
} else fSave = 0;
}
b.CheckByteCount(R__s, R__c, TF1::IsA());
//====end of old versions
} else {
Int_t saved = 0;
if (fType > 0 && fNsave <= 0) { saved = 1; Save(fXmin,fXmax,0,0,0,0);}
TF1::Class()->WriteBuffer(b,this);
if (saved) {delete [] fSave; fSave = 0; fNsave = 0;}
}
}
//_______________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Update()
{
// called by functions such as SetRange, SetNpx, SetParameters
// to force the deletion of the associated histogram or Integral
delete fHistogram;
fHistogram = 0;
if (fIntegral) {
delete [] fIntegral; fIntegral = 0;
delete [] fAlpha; fAlpha = 0;
delete [] fBeta; fBeta = 0;
delete [] fGamma; fGamma = 0;
}
}
//_______________________________________________________________________
void TF1::RejectPoint(Bool_t reject)
{
// static function to set the global flag to reject points
// the fgRejectPoint global flag is tested by all fit functions
// if TRUE the point is not included in the fit.
// This flag can be set by a user in a fitting function.
// The fgRejectPoint flag is reset by the TH1 and TGraph fitting functions.
fgRejectPoint = reject;
}
//_______________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TF1::RejectedPoint()
{
// see TF1::RejectPoint above
return fgRejectPoint;
}
*/
//
//
// Author(s): A.C. Genz, A.A. Malik
// converted/adapted by R.Brun to C++ from Fortran CERNLIB routine RADMUL (D120)
// The new code features many changes compared to the Fortran version.
// Note that this function is currently called only by TF2::Integral (n=2)
// and TF3::Integral (n=3).
//
// This function computes, to an attempted specified accuracy, the value of
// the integral over an n-dimensional rectangular region.
//
// N Number of dimensions.
// A,B One-dimensional arrays of length >= N . On entry A[i], and B[i],
// contain the lower and upper limits of integration, respectively.
// EPS Specified relative accuracy.
// RELERR Contains, on exit, an estimation of the relative accuray of RESULT.
//
// Method:
//
// An integration rule of degree seven is used together with a certain
// strategy of subdivision.
// For a more detailed description of the method see References.
//
// Notes:
//
// 1.Multi-dimensional integration is time-consuming. For each rectangular
// subregion, the routine requires function evaluations.
// Careful programming of the integrand might result in substantial saving
// of time.
// 2.Numerical integration usually works best for smooth functions.
// Some analysis or suitable transformations of the integral prior to
// numerical work may contribute to numerical efficiency.
//
// References:
//
// 1.A.C. Genz and A.A. Malik, Remarks on algorithm 006:
// An adaptive algorithm for numerical integration over
// an N-dimensional rectangular region, J. Comput. Appl. Math. 6 (1980) 295-302.
// 2.A. van Doren and L. de Ridder, An adaptive algorithm for numerical
// integration over an n-dimensional cube, J.Comput. Appl. Math. 2 (1976) 207-217.
//
//=========================================================================
Double_t ctr[15], wth[15], wthl[15], z[15];
const Double_t xl2 = 0.358568582800318073;
const Double_t xl4 = 0.948683298050513796;
const Double_t xl5 = 0.688247201611685289;
const Double_t w2 = 980./6561;
const Double_t w4 = 200./19683;
const Double_t wp2 = 245./486;
const Double_t wp4 = 25./729;
Double_t wn1[14] = { -0.193872885230909911, -0.555606360818980835,
-0.876695625666819078, -1.15714067977442459, -1.39694152314179743,
-1.59609815576893754, -1.75461057765584494, -1.87247878880251983,
-1.94970278920896201, -1.98628257887517146, -1.98221815780114818,
-1.93750952598689219, -1.85215668343240347, -1.72615963013768225};
Double_t wn3[14] = { 0.0518213686937966768, 0.0314992633236803330,
0.0111771579535639891,-0.00914494741655235473,-0.0294670527866686986,
-0.0497891581567850424,-0.0701112635269013768, -0.0904333688970177241,
-0.110755474267134071, -0.131077579637250419, -0.151399685007366752,
-0.171721790377483099, -0.192043895747599447, -0.212366001117715794};
Double_t wn5[14] = { 0.871183254585174982e-01, 0.435591627292587508e-01,
0.217795813646293754e-01, 0.108897906823146873e-01, 0.544489534115734364e-02,
0.272244767057867193e-02, 0.136122383528933596e-02, 0.680611917644667955e-03,
0.340305958822333977e-03, 0.170152979411166995e-03, 0.850764897055834977e-04,
0.425382448527917472e-04, 0.212691224263958736e-04, 0.106345612131979372e-04};
Double_t wpn1[14] = { -1.33196159122085045, -2.29218106995884763,
-3.11522633744855959, -3.80109739368998611, -4.34979423868312742,
-4.76131687242798352, -5.03566529492455417, -5.17283950617283939,
-5.17283950617283939, -5.03566529492455417, -4.76131687242798352,
-4.34979423868312742, -3.80109739368998611, -3.11522633744855959};
Double_t wpn3[14] = { 0.0445816186556927292, -0.0240054869684499309,
-0.0925925925925925875, -0.161179698216735251, -0.229766803840877915,
-0.298353909465020564, -0.366941015089163228, -0.435528120713305891,
-0.504115226337448555, -0.572702331961591218, -0.641289437585733882,
-0.709876543209876532, -0.778463648834019195, -0.847050754458161859};
Double_t result = 0;
Double_t abserr = 0;
Int_t ifail = 3;
if (n < 2 || n > 15) return 0;
Double_t twondm = TMath::Power(2,n);
Int_t ifncls = 0;
Bool_t ldv = kFALSE;
Int_t irgnst = 2*n+3;
Int_t irlcls = Int_t(twondm) +2*n*(n+1)+1;
Int_t isbrgn = irgnst;
Int_t isbrgs = irgnst;
// The original algorithm expected a parameter MAXPTS
// where MAXPTS = Maximum number of function evaluations to be allowed.
// Here we set MAXPTS to 1000*(the lowest possible value)
Int_t maxpts = 1000*irlcls;
Int_t minpts = 1;
// The original agorithm expected a working space array WK of length IWK
// with IWK Length ( >= (2N + 3) * (1 + MAXPTS/(2**N + 2N(N + 1) + 1))/2).
// Here, this array is allocated dynamically
Int_t iwk = irgnst*(1 +maxpts/irlcls)/2;
Double_t *wk = new Double_t[iwk+10];
Int_t j;
for (j=0;j<n;j++) {
ctr[j] = (b[j] + a[j])*0.5;
wth[j] = (b[j] - a[j])*0.5;
}
Double_t rgnvol, sum1, sum2, sum3, sum4, sum5, difmax, f2, f3, dif, aresult;
Double_t rgncmp=0, rgnval, rgnerr;
Int_t j1, k, l, m, idvaxn=0, idvax0=0, isbtmp, isbtpp;
InitArgs(z,fParams);
L20:
rgnvol = twondm;
for (j=0;j<n;j++) {
rgnvol *= wth[j];
z[j] = ctr[j];
}
sum1 = EvalPar(z,fParams); //evaluate function
difmax = 0;
sum2 = 0;
sum3 = 0;
for (j=0;j<n;j++) {
z[j] = ctr[j] - xl2*wth[j];
f2 = EvalPar(z,fParams);
z[j] = ctr[j] + xl2*wth[j];
f2 += EvalPar(z,fParams);
wthl[j] = xl4*wth[j];
z[j] = ctr[j] - wthl[j];
f3 = EvalPar(z,fParams);
z[j] = ctr[j] + wthl[j];
f3 += EvalPar(z,fParams);
sum2 += f2;
sum3 += f3;
dif = TMath::Abs(7*f2-f3-12*sum1);
if (dif >= difmax) {
difmax=dif;
idvaxn=j+1;
}
z[j] = ctr[j];
}
sum4 = 0;
for (j=1;j<n;j++) {
j1 = j-1;
for (k=j;k<n;k++) {
for (l=0;l<2;l++) {
wthl[j1] = -wthl[j1];
z[j1] = ctr[j1] + wthl[j1];
for (m=0;m<2;m++) {
wthl[k] = -wthl[k];
z[k] = ctr[k] + wthl[k];
sum4 += EvalPar(z,fParams);
}
}
z[k] = ctr[k];
}
z[j1] = ctr[j1];
}
sum5 = 0;
for (j=0;j<n;j++) {
wthl[j] = -xl5*wth[j];
z[j] = ctr[j] + wthl[j];
}
L90:
sum5 += EvalPar(z,fParams);
for (j=0;j<n;j++) {
wthl[j] = -wthl[j];
z[j] = ctr[j] + wthl[j];
if (wthl[j] > 0) goto L90;
}
rgncmp = rgnvol*(wpn1[n-2]*sum1+wp2*sum2+wpn3[n-2]*sum3+wp4*sum4);
rgnval = wn1[n-2]*sum1+w2*sum2+wn3[n-2]*sum3+w4*sum4+wn5[n-2]*sum5;
rgnval *= rgnvol;
rgnerr = TMath::Abs(rgnval-rgncmp);
result += rgnval;
abserr += rgnerr;
ifncls += irlcls;
aresult = TMath::Abs(result);
if (aresult < 1e-100) {
delete [] wk;
return result;
}
if (ldv) {
L110:
isbtmp = 2*isbrgn;
if (isbtmp > isbrgs) goto L160;
if (isbtmp < isbrgs) {
isbtpp = isbtmp + irgnst;
if (wk[isbtmp-1] < wk[isbtpp-1]) isbtmp = isbtpp;
}
if (rgnerr >= wk[isbtmp-1]) goto L160;
for (k=0;k<irgnst;k++) {
wk[isbrgn-k-1] = wk[isbtmp-k-1];
}
isbrgn = isbtmp;
goto L110;
}
L140:
isbtmp = (isbrgn/(2*irgnst))*irgnst;
if (isbtmp >= irgnst && rgnerr > wk[isbtmp-1]) {
for (k=0;k<irgnst;k++) {
wk[isbrgn-k-1] = wk[isbtmp-k-1];
}
isbrgn = isbtmp;
goto L140;
}
L160:
wk[isbrgn-1] = rgnerr;
wk[isbrgn-2] = rgnval;
wk[isbrgn-3] = Double_t(idvaxn);
for (j=0;j<n;j++) {
isbtmp = isbrgn-2*j-4;
wk[isbtmp] = ctr[j];
wk[isbtmp-1] = wth[j];
}
if (ldv) {
ldv = kFALSE;
ctr[idvax0-1] += 2*wth[idvax0-1];
isbrgs += irgnst;
isbrgn = isbrgs;
goto L20;
}
relerr = abserr/aresult;
if (relerr < 1e-1 && aresult < 1e-20) ifail = 0;
if (relerr < 1e-3 && aresult < 1e-10) ifail = 0;
if (relerr < 1e-5 && aresult < 1e-5) ifail = 0;
if (isbrgs+irgnst > iwk) ifail = 2;
if (ifncls+2*irlcls > maxpts) ifail = 1;
if (relerr < eps && ifncls >= minpts) ifail = 0;
if (ifail == 3) {
ldv = kTRUE;
isbrgn = irgnst;
abserr -= wk[isbrgn-1];
result -= wk[isbrgn-2];
idvax0 = Int_t(wk[isbrgn-3]);
for (j=0;j<n;j++) {
isbtmp = isbrgn-2*j-4;
ctr[j] = wk[isbtmp];
wth[j] = wk[isbtmp-1];
}
wth[idvax0-1] = 0.5*wth[idvax0-1];
ctr[idvax0-1] -= wth[idvax0-1];
goto L20;
}
// IFAIL On exit:
// 0 Normal exit. . At most MAXPTS calls to the function F were performed.
// 1 MAXPTS is too small for the specified accuracy EPS. RESULT and RELERR
// contain the values obtainable for the specified value of MAXPTS.
//
delete [] wk;
// Int_t nfnevl = ifncls; //number of function evaluations performed.
return result; //an approximate value of the integral
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TF1::IsInside(const Double_t *x) const
{
// Return kTRUE is the point is inside the function range
if (x[0] < fXmin || x[0] > fXmax) return kFALSE;
return kTRUE;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Paint(Option_t *option)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Paint this function with its current attributes*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ===============================================
Int_t i;
Double_t xv[1];
fgCurrent = this;
TString opt = option;
opt.ToLower();
Double_t xmin=fXmin, xmax=fXmax, pmin=fXmin, pmax=fXmax;
if (gPad) {
pmin = gPad->PadtoX(gPad->GetUxmin());
pmax = gPad->PadtoX(gPad->GetUxmax());
}
if (opt.Contains("same")) {
if (xmax < pmin) return; // Otto: completely outside
if (xmin > pmax) return;
if (xmin < pmin) xmin = pmin;
if (xmax > pmax) xmax = pmax;
}
// Create a temporary histogram and fill each channel with the function value
// Preserve axis titles
TString xtitle = "";
TString ytitle = "";
if (fHistogram) {
xtitle = fHistogram->GetXaxis()->GetTitle();
ytitle = fHistogram->GetYaxis()->GetTitle();
if (!gPad->GetLogx() && fHistogram->TestBit(TH1::kLogX)) { delete fHistogram; fHistogram = 0;}
if ( gPad->GetLogx() && !fHistogram->TestBit(TH1::kLogX)) { delete fHistogram; fHistogram = 0;}
}
if (fHistogram) {
// if (xmin != fXmin || xmax != fXmax) fHistogram->GetXaxis()->SetLimits(xmin,xmax);
fHistogram->GetXaxis()->SetLimits(xmin,xmax);
} else {
// if logx, we must bin in logx and not in x !!!
// otherwise if several decades, one gets crazy results
if (xmin > 0 && gPad && gPad->GetLogx()) {
Axis_t *xbins = new Axis_t[fNpx+1];
Double_t xlogmin = TMath::Log10(xmin);
Double_t xlogmax = TMath::Log10(xmax);
Double_t dlogx = (xlogmax-xlogmin)/((Double_t)fNpx);
for (i=0;i<=fNpx;i++) {
xbins[i] = gPad->PadtoX(xlogmin+ i*dlogx);
}
fHistogram = new TH1D("Func",GetTitle(),fNpx,xbins);
fHistogram->SetBit(TH1::kLogX);
delete [] xbins;
} else {
fHistogram = new TH1D("Func",GetTitle(),fNpx,xmin,xmax);
}
if (!fHistogram) return;
fHistogram->SetDirectory(0);
}
//restore axis titles
fHistogram->GetXaxis()->SetTitle(xtitle.Data());
fHistogram->GetYaxis()->SetTitle(ytitle.Data());
InitArgs(xv,fParams);
for (i=1;i<=fNpx;i++) {
xv[0] = fHistogram->GetBinCenter(i);
fHistogram->SetBinContent(i,EvalPar(xv,fParams));
}
//*-*- Copy Function attributes to histogram attributes
Double_t minimum = fHistogram->GetMinimumStored();
Double_t maximum = fHistogram->GetMaximumStored();
if (minimum == -1111) { //this can happen after unzooming
if (fHistogram->TestBit(TH1::kIsZoomed)) {
minimum = fHistogram->GetYaxis()->GetXmin();
} else {
minimum = fMinimum;
}
fHistogram->SetMinimum(minimum);
}
if (maximum == -1111) {
if (fHistogram->TestBit(TH1::kIsZoomed)) {
maximum = fHistogram->GetYaxis()->GetXmax();
} else {
maximum = fMaximum;
}
fHistogram->SetMaximum(maximum);
}
fHistogram->SetBit(TH1::kNoStats);
fHistogram->SetLineColor(GetLineColor());
fHistogram->SetLineStyle(GetLineStyle());
fHistogram->SetLineWidth(GetLineWidth());
fHistogram->SetFillColor(GetFillColor());
fHistogram->SetFillStyle(GetFillStyle());
fHistogram->SetMarkerColor(GetMarkerColor());
fHistogram->SetMarkerStyle(GetMarkerStyle());
fHistogram->SetMarkerSize(GetMarkerSize());
//*-*- Draw the histogram
if (!gPad) return;
if (opt.Length() == 0) fHistogram->Paint("lf");
else if (opt == "same") fHistogram->Paint("lfsame");
else fHistogram->Paint(option);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Print(Option_t *option) const
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Dump this function with its attributes*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==================================
TFormula::Print(option);
if (fHistogram) fHistogram->Print(option);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::ReleaseParameter(Int_t ipar)
{
// Release parameter number ipar If used in a fit, the parameter
// can vary freely. The parameter limits are reset to 0,0.
if (ipar < 0 || ipar > fNpar-1) return;
SetParLimits(ipar,0,0);
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Save(Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax, Double_t, Double_t, Double_t, Double_t)
{
// Save values of function in array fSave
if (fSave != 0) {delete [] fSave; fSave = 0;}
fNsave = fNpx+3;
if (fNsave <= 3) {fNsave=0; return;}
fSave = new Double_t[fNsave];
Int_t i;
Double_t dx = (xmax-xmin)/fNpx;
if (dx <= 0) {
dx = (fXmax-fXmin)/fNpx;
fNsave--;
xmin = fXmin +0.5*dx;
xmax = fXmax -0.5*dx;
}
Double_t xv[1];
InitArgs(xv,fParams);
for (i=0;i<=fNpx;i++) {
xv[0] = xmin + dx*i;
fSave[i] = EvalPar(xv,fParams);
}
fSave[fNpx+1] = xmin;
fSave[fNpx+2] = xmax;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SavePrimitive(ofstream &out, Option_t *option)
{
// Save primitive as a C++ statement(s) on output stream out
Int_t i;
char quote = '"';
out<<" "<<endl;
if (!fMethodCall) {
out<<" TF1 *"<<GetName()<<" = new TF1("<<quote<<GetName()<<quote<<","<<quote<<GetTitle()<<quote<<","<<fXmin<<","<<fXmax<<");"<<endl;
if (fNpx != 100) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetNpx("<<fNpx<<");"<<endl;
}
} else {
out<<" TF1 *"<<GetName()<<" = new TF1("<<quote<<"*"<<GetName()<<quote<<","<<fXmin<<","<<fXmax<<","<<GetNpar()<<");"<<endl;
out<<" //The original function : "<<GetTitle()<<" had originally been created by:" <<endl;
out<<" //TF1 *"<<GetName()<<" = new TF1("<<quote<<GetName()<<quote<<","<<GetTitle()<<","<<fXmin<<","<<fXmax<<","<<GetNpar()<<");"<<endl;
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetRange("<<fXmin<<","<<fXmax<<");"<<endl;
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetName("<<quote<<GetName()<<quote<<");"<<endl;
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetTitle("<<quote<<GetTitle()<<quote<<");"<<endl;
if (fNpx != 100) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetNpx("<<fNpx<<");"<<endl;
}
Double_t dx = (fXmax-fXmin)/fNpx;
Double_t xv[1];
InitArgs(xv,fParams);
for (i=0;i<=fNpx;i++) {
xv[0] = fXmin + dx*i;
Double_t save = EvalPar(xv,fParams);
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetSavedPoint("<<i<<","<<save<<");"<<endl;
}
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetSavedPoint("<<fNpx+1<<","<<fXmin<<");"<<endl;
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetSavedPoint("<<fNpx+2<<","<<fXmax<<");"<<endl;
}
if (TestBit(kNotDraw)) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetBit(TF1::kNotDraw);"<<endl;
}
if (GetFillColor() != 0) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetFillColor("<<GetFillColor()<<");"<<endl;
}
if (GetFillStyle() != 1001) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetFillStyle("<<GetFillStyle()<<");"<<endl;
}
if (GetMarkerColor() != 1) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetMarkerColor("<<GetMarkerColor()<<");"<<endl;
}
if (GetMarkerStyle() != 1) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetMarkerStyle("<<GetMarkerStyle()<<");"<<endl;
}
if (GetMarkerSize() != 1) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetMarkerSize("<<GetMarkerSize()<<");"<<endl;
}
if (GetLineColor() != 1) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetLineColor("<<GetLineColor()<<");"<<endl;
}
if (GetLineWidth() != 4) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetLineWidth("<<GetLineWidth()<<");"<<endl;
}
if (GetLineStyle() != 1) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetLineStyle("<<GetLineStyle()<<");"<<endl;
}
if (GetChisquare() != 0) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetChisquare("<<GetChisquare()<<");"<<endl;
}
Double_t parmin, parmax;
for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetParameter("<<i<<","<<GetParameter(i)<<");"<<endl;
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetParError("<<i<<","<<GetParError(i)<<");"<<endl;
GetParLimits(i,parmin,parmax);
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->SetParLimits("<<i<<","<<parmin<<","<<parmax<<");"<<endl;
}
if (!strstr(option,"nodraw")) {
out<<" "<<GetName()<<"->Draw("
<<quote<<option<<quote<<");"<<endl;
}
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SetCurrent(TF1 *f1)
{
// static function setting the current function.
// the current function may be accessed in static C-like functions
// when fitting or painting a function.
fgCurrent = f1;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SetNDF(Int_t ndf)
{
// Set the number of degrees of freedom
// ndf should be the number of points used in a fit - the number of free parameters
fNDF = ndf;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SetNpx(Int_t npx)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Set the number of points used to draw the function*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* ==================================================
if(npx > 4 && npx < 100000) fNpx = npx;
Update();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SetParError(Int_t ipar, Double_t error)
{
// set error for parameter number ipar
if (ipar < 0 || ipar > fNpar-1) return;
fParErrors[ipar] = error;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SetParErrors(const Double_t *errors)
{
// set errors for all active parameters
// when calling this function, the array errors must have at least fNpar values
if (!errors) return;
for (Int_t i=0;i<fNpar;i++) fParErrors[i] = errors[i];
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SetParLimits(Int_t ipar, Double_t parmin, Double_t parmax)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*Set limits for parameter ipar*-*-*-*
//*-* =============================
// The specified limits will be used in a fit operation
// when the option "B" is specified (Bounds).
// To fix a parameter, use TF1::FixParameter
if (ipar < 0 || ipar > fNpar-1) return;
Int_t i;
if (!fParMin) {fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar]; for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) fParMin[i]=0;}
if (!fParMax) {fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar]; for (i=0;i<fNpar;i++) fParMax[i]=0;}
fParMin[ipar] = parmin;
fParMax[ipar] = parmax;
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SetRange(Double_t xmin, Double_t xmax)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*Initialize the upper and lower bounds to draw the function*-*-*-*
//*-* ==========================================================
// The function range is also used in an histogram fit operation
// when the option "R" is specified.
fXmin = xmin;
fXmax = xmax;
Update();
}
//______________________________________________________________________________
void TF1::SetSavedPoint(Int_t point, Double_t value)
{
// Restore value of function saved at point
if (!fSave) {
fNsave = fNpx+3;
fSave = new Double_t[fNsave];
}
if (point < 0 || point >= fNsave) return;
fSave[point] = value;
}
//_______________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Streamer(TBuffer &b)
{
//*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*Stream a class object*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*
//*-* =========================================
if (b.IsReading()) {
UInt_t R__s, R__c;
Version_t v = b.ReadVersion(&R__s, &R__c);
if (v > 4) {
TF1::Class()->ReadBuffer(b, this, v, R__s, R__c);
if (v == 5 && fNsave > 0) {
//correct badly saved fSave in 3.00/06
Int_t np = fNsave - 3;
fSave[np] = fSave[np-1];
fSave[np+1] = fXmin;
fSave[np+2] = fXmax;
}
return;
}
//====process old versions before automatic schema evolution
TFormula::Streamer(b);
TAttLine::Streamer(b);
TAttFill::Streamer(b);
TAttMarker::Streamer(b);
if (v < 4) {
Float_t xmin,xmax;
b >> xmin; fXmin = xmin;
b >> xmax; fXmax = xmax;
} else {
b >> fXmin;
b >> fXmax;
}
b >> fNpx;
b >> fType;
b >> fChisquare;
b.ReadArray(fParErrors);
if (v > 1) {
b.ReadArray(fParMin);
b.ReadArray(fParMax);
} else {
fParMin = new Double_t[fNpar+1];
fParMax = new Double_t[fNpar+1];
}
b >> fNpfits;
if (v == 1) {
b >> fHistogram;
delete fHistogram; fHistogram = 0;
}
if (v > 1) {
if (v < 4) {
Float_t minimum,maximum;
b >> minimum; fMinimum =minimum;
b >> maximum; fMaximum =maximum;
} else {
b >> fMinimum;
b >> fMaximum;
}
}
if (v > 2) {
b >> fNsave;
if (fNsave > 0) {
fSave = new Double_t[fNsave+10];
b.ReadArray(fSave);
//correct fSave limits to match new version
fSave[fNsave] = fSave[fNsave-1];
fSave[fNsave+1] = fSave[fNsave+2];
fSave[fNsave+2] = fSave[fNsave+3];
fNsave += 3;
} else fSave = 0;
}
b.CheckByteCount(R__s, R__c, TF1::IsA());
//====end of old versions
} else {
Int_t saved = 0;
if (fType > 0 && fNsave <= 0) { saved = 1; Save(fXmin,fXmax,0,0,0,0);}
TF1::Class()->WriteBuffer(b,this);
if (saved) {delete [] fSave; fSave = 0; fNsave = 0;}
}
}
//_______________________________________________________________________
void TF1::Update()
{
// called by functions such as SetRange, SetNpx, SetParameters
// to force the deletion of the associated histogram or Integral
delete fHistogram;
fHistogram = 0;
if (fIntegral) {
delete [] fIntegral; fIntegral = 0;
delete [] fAlpha; fAlpha = 0;
delete [] fBeta; fBeta = 0;
delete [] fGamma; fGamma = 0;
}
}
//_______________________________________________________________________
void TF1::RejectPoint(Bool_t reject)
{
// static function to set the global flag to reject points
// the fgRejectPoint global flag is tested by all fit functions
// if TRUE the point is not included in the fit.
// This flag can be set by a user in a fitting function.
// The fgRejectPoint flag is reset by the TH1 and TGraph fitting functions.
fgRejectPoint = reject;
}
//_______________________________________________________________________
Bool_t TF1::RejectedPoint()
{
// see TF1::RejectPoint above
return fgRejectPoint;
}